Charger Tomo V6-2



This charger is a cheap two slot charger that can charge both LiIon and NiMH.




The cardboard retail box list the specifications on the back.

The box contained the charger and a usb cable.

The charger has a micro usb connector for power input.

The only indication on the charger is a led for each channel, it will flash red when charging and show green when finished with charging.
With no batteries in the charger the leds will be off.


The battery slot can handle cells from 30mm to 67.6mm, this means very few protected 18650 cells will fit in the charger.
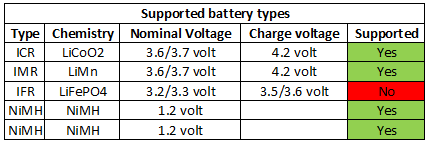
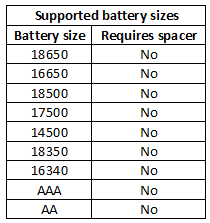







Measurements
- Below 0.5 volt the led will be off and charger will charge with about 40mA
- Above 0.5 volt the charger will start regular charging.
- Above 1.7 volt the charger assumes LiIon.
- The charger will restart if battery voltage drops below 4.10 volt.
- Charge will restart charging after power loss, or battery insertion.
- When not connected to power the batteries are drained with 0.5mA
- The charger uses trickle charger for both LiIon (very bad) and NiMH cells.
Charging LiIon
%20%231.png)
The charge curve is not a CC/CV curve. The charger stops at a high current and low voltage, this means the batteries are not filled. This might be a good idea, because the charge do not turn current fully off, but continues to charge with a low current (Very bad).
%20%232.png)
Second channel looks the same.
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
Not any difference with other cell capacities.
%20%231.png)
The older cell looks about the same, except the voltage jumps more up and down due to a higher internal resistance.
%20%231.png)
With a smaller cell it looks like the charge voltage is up to 4.2 volt due to the pulsing current, but when charge is finished the voltage drops again.
%20%231.png)
This cell probably has lower internal resistance and the pulsing is not as obvious.
.png)
When including the input current it hides everything due to the pulsing.
a.png)
Removing the input current makes the curve look like all the other charge curves.
.png)
Adding a series resistance to the usb power to simulate a long cable or weak charger did not prevent charging, but it is slower.
a.png)
Same as above, but with input current removed.
%20%231.png)
I wanted to see what happens if you do not remove the batteries when they are full. The test is done with a 4.35 volt cell and my equipment is programmed to turn the power to the charger off at 4.4 volt.
After about 2 days 4.4 volt was reached and the charger turned off, this is very bad. For smaller batteries the over charge will go much faster.
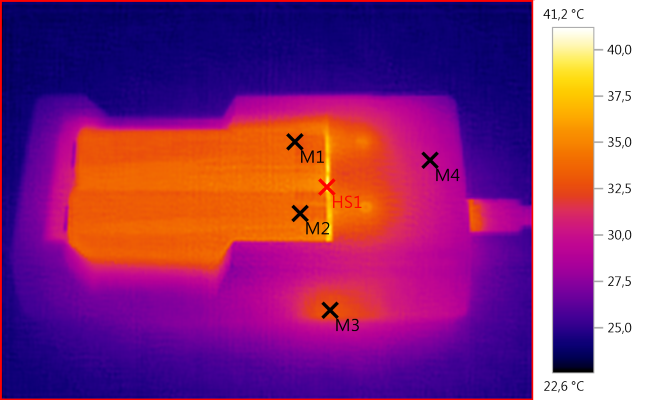
M1: 33,5°C, M2: 33,4°C, M3: 32,9°C, M4: 29,9°C, HS1: 41,2°C
When charging LiIon the charger is fairly cool.
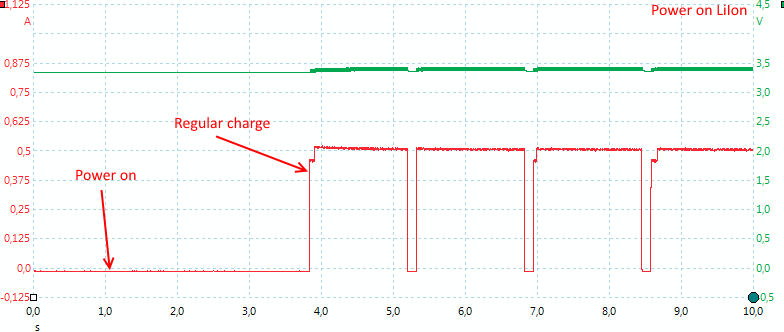
The charger need about 2.5 second to start up and uses pulsing on LiIon.
Charging NiMH
%20%231.png)
My NiMH cell is only charged with about half its capacity, this is not very good.
It do have some trickle charge and will eventually fill the cell in a day or two.
%20%232.png)
It is the same on the other channel.
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
The Pro and XX is even worse, only 700mAh and 800mAh is filled into them.
%20%231.png)
The powerex gets some more energy, but far from enough.
%20%231.png)
250mAh for an AAA cell, again way to little.
%20%231.png)
At least it can detect a full battery fairly fast.
.png)
Charging two cells is just as bad as one cell.
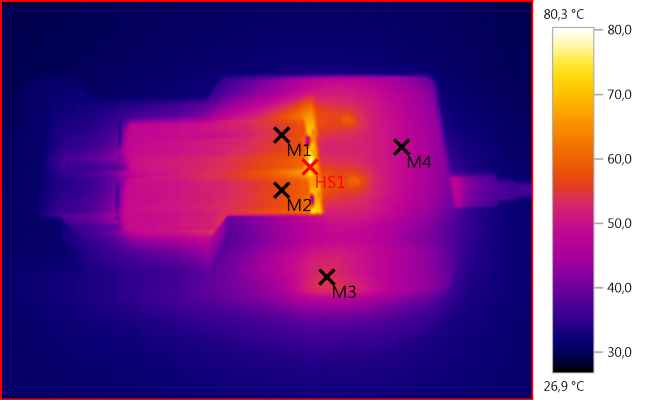
M1: 55,2°C, M2: 56,9°C, M3: 53,7°C, M4: 48,8°C, HS1: 80,3°C
With NiMH the charger is do generate a lot of heat.
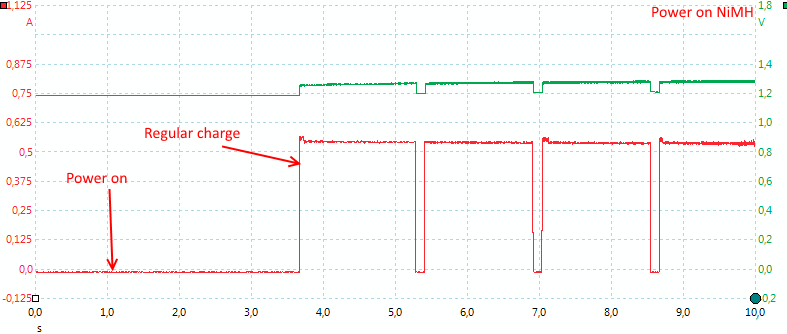
The charger need about 2.5 second to start up and uses pulsing.
Conclusion
The charger can be used for LiIon, but it is very important to remove the cells within a few hours, when the charging is finished.
For NiMH it is not really useful because it only partial charges the cells.
I will not recommend this charger for any type of battery.
Notes
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger





















%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
.png)
a.png)
.png)
a.png)
%20%231.png)


%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
.png)

