Charger Yi Fang EIZFAN WF1



Yi Fang Technology is a company selling chargers and batteries branded EFAN and EIZFAN.

The charger arrived in a cardboard box with the model number on it and not any other information.

The box contained the charger, a power supply, a car adapter and a instruction manual in English and probably Chinese.

The charger has a single 12V input for use with the power supply and car adapter.

The user interface is a small display and a single button.
The button can be used to select current, turn background light off/on and activate usb output.

The display shows voltage with two decimal places and animated battery symbols when charging.

Background light can be turned off or on with a long press on the button. Default is on when power is connected.
Like many other chargers it is missing a dedicated battery full indicator, you have to look at the animation. It will stop with all blocks in the battery shown, when the battery is full.

The charger has a usb output connector, that can be used with one or both batteries.

When usb output is on the display will show battery voltage. Background light will be off.


The slots uses the typical design with a slider. They are with metal rails, but the slider is not moving very smooth.
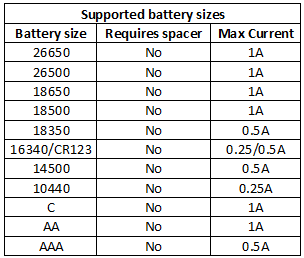
The slots can accept batteries from 31 to 71.4 mm.

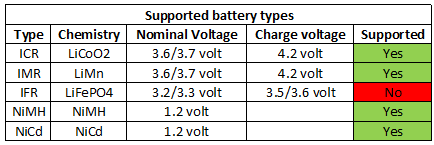
The charger is marked with some of the supported battery sizes, but is missing NiMH batteries. The label on the backside do include them.










The charger can easily handle 70 mm long batteries including flat top cells.
Measurements
- When not connected to power it will drain about 17mA from batteries.
- Voltmeter is within 0.06V.
- The voltmeter can show voltage down to about 0.4V, but meter is not very precise below 1 volt.
- The voltmeter will freze when voltage is above 4.2 volt and will be turned off if voltage is above about 4.3 volt.
- The charger will charge with 1.3mA from 0 volt and not report any battery.
- At 0.4 volt regular charge current will be applied and show a blinking battery symbol.
- Above 1 volt the battery symbol will be steady and show the charge animation.
- Above 2 volt the charger assumes LiIon and shows the blinking battery symbol
- Above 2.5 volt the battery symbol will be steady and show the charge animation.
- Charger always starts with the 0.25A setting.
- When charge is finished the charger will charge with 0.1mA.
- Charger will restart if voltage drops to 3.9 volt
- Charger will restart charging after power loss, or battery insertion.
Charging LiIon
%20%231.png)
At 0.25A the charger does a nice CC/CV charging with about 20mA termination current. This low termination current is good for smaller cells.
%20%231.png)
At 0.5A the charger has the same nice CC/CV curve and 20mA termination.
%20%231.png)
And also at 1A. Here the 20mA termination is on the low side and makes the charging take longer than necessary.
%20%232.png)
The second channel is also charging fine.
%20%231.png)
With the 2600mAh battery the charger voltage is around the maximum allowed voltage for a short time during the charge. I do not believe it has any significant effect on the battery, but I would have prefered the voltage had been slighty lower.
%20%231.png)
Again there is a little bit of overshoot, but within allowable tolerances.
%20%231.png)
The charger does also handle this old cell nicely.
%20%231.png)
A more realistic charge current for this old cell.
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
Two more normal small cells are charged fine.
.png)
Using both channels is no problem, there is full current for both cells.
.png)
The charger uses about 1A at 12 volt.
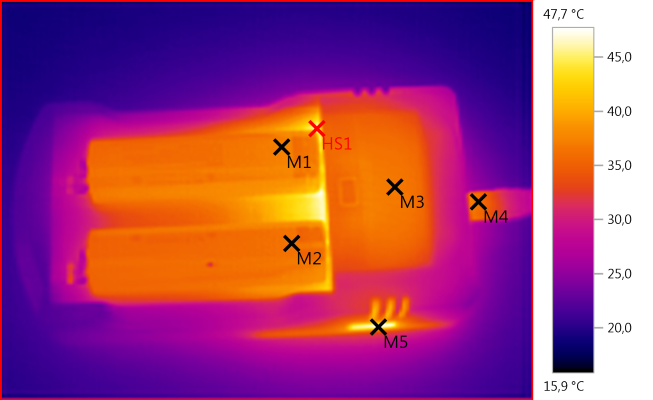
M1: 37,1°C, M2: 36,4°C, M3: 36,8°C, M4: 36,3°C, M5: 46,3°C, HS1: 47,7°C
Battery temperature looks as expected and as usual there is som hot parts inside the charger.
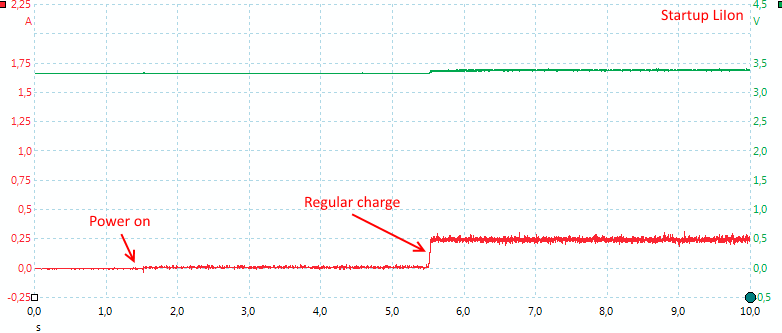
The charger needs 4 seconds to initialize.
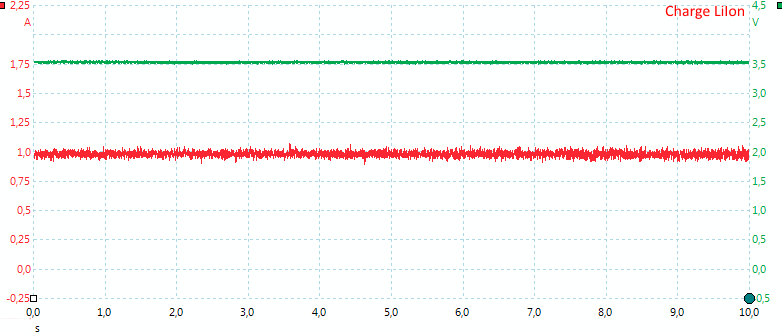
With LiIon the charging is a stable current.
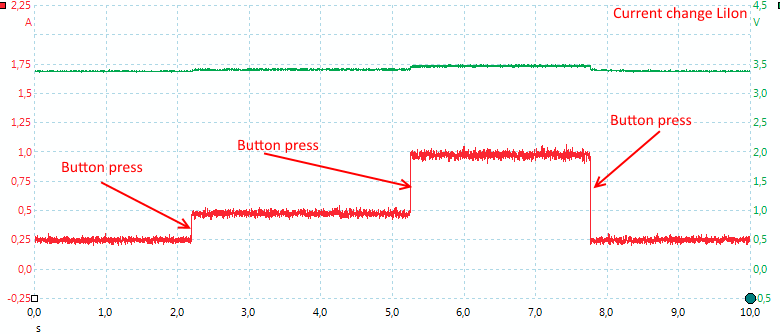
Current can be changed at any time during charge.
Charging NiMH
%20%231.png)
With 0.25A current the cell is charged fine and it terminates.
%20%231.png)
With 0.5A current the termination looks like maximum voltage termination.
%20%231.png)
At 1A it is also a maximum voltage termination.
The charger has about 50mA trickle charge here (It is changed with charge current) and it does not turn off.
%20%232.png)
Second channel look similar.
%20%231.png)
With the XX cell the temperature raise is present, i.e. the cell is filled.
%20%231.png)
Same with the Powerex and here it looks like a -dv/dt termination.
%20%231.png)
The AAA is also a little bit short of full.
%20%231.png)
The charger is fairly fast at detecting a full cell.
.png)
Two eneloops is no problem, here the termination is on voltage.
.png)
With an external power supply I can see the charger uses about 0.5A at 12V when charging.
It does not uses 300mA when trickle charging, that is more like the maximum current.
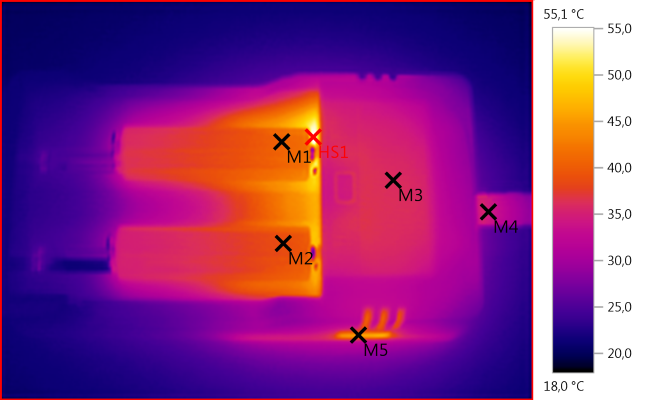
M1: 40,6°C, M2: 38,8°C, M3: 36,0°C, M4: 34,7°C, M5: 45,1°C, HS1: 55,1°C
NiMH do get slightly hotter than LiIon, but not much.
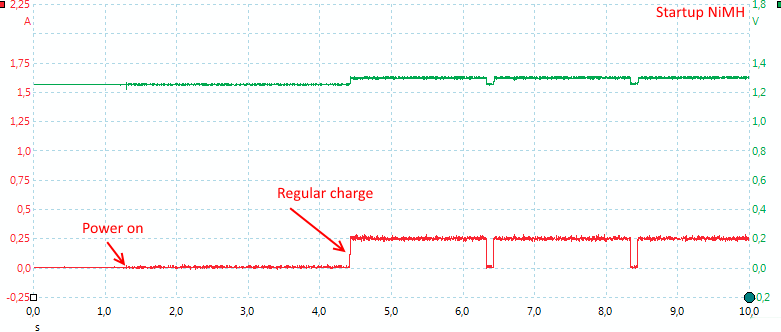
The charger only need 3 seconds to start a NiMH charger.
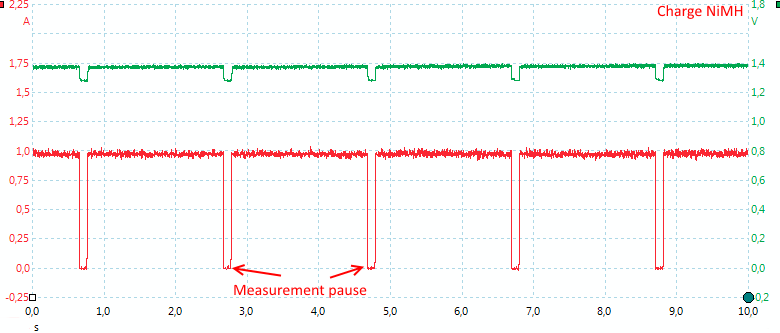
The charger stops charging to measure NiMH voltage during charge. These pulses are also the reason for the pulsing input current.
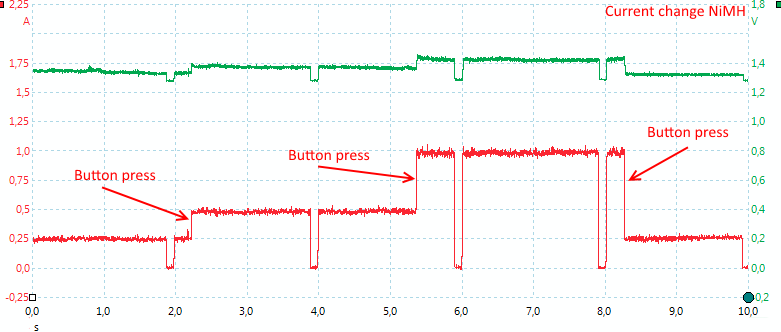
Again the current change can be used at any time.
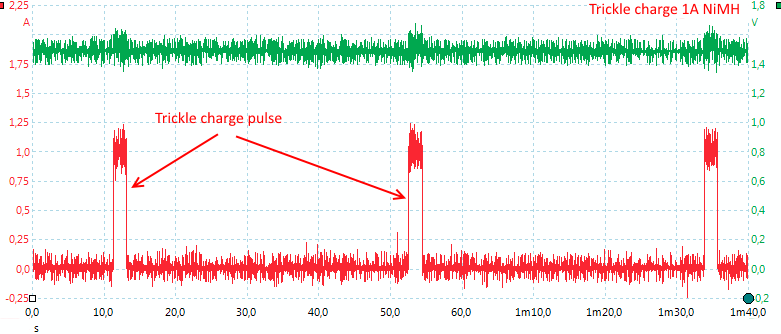
The trickle charger is done with pulses at selected charge current. There is about 40 seconds between the pulses.
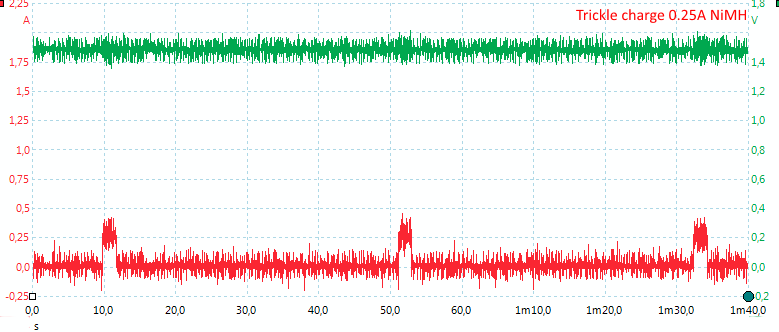
Here is a trickle charge pulse with selected current at 0.25A, the pulse is adjusted depending on selected charge current.
LiIon & NiMH mixed charge
There is no problem charging one LiIon and one NiMH battery at the same time.
.png)
.png)
USB output
- Usb output works from both slots and batteries in both slots will increase maximum current.
- Press the button to turn on or off usb output when no power is connected to the charger.
- When usb output is on and unloaded it will drain about 30mA from the battery (17mA when off).
- USB output is coded as Apple 1A
- Charger show voltage when usb out is active.
- Voltmeter is within 0.07 volt for usb output
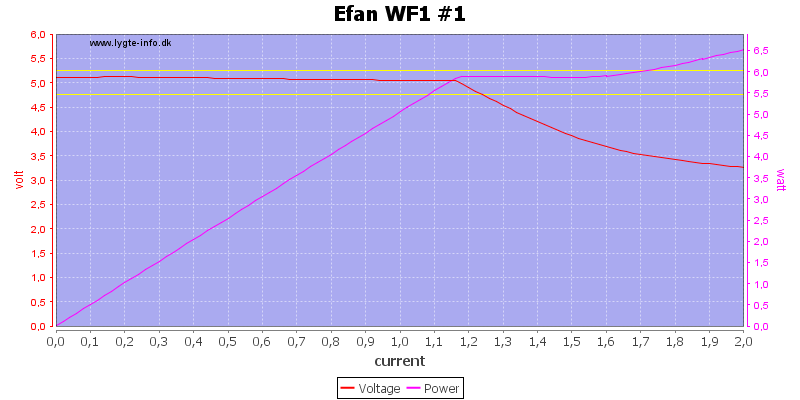
The USB output can deliver 1.1A from battery #1, but it does not shut down the output when overloaded.
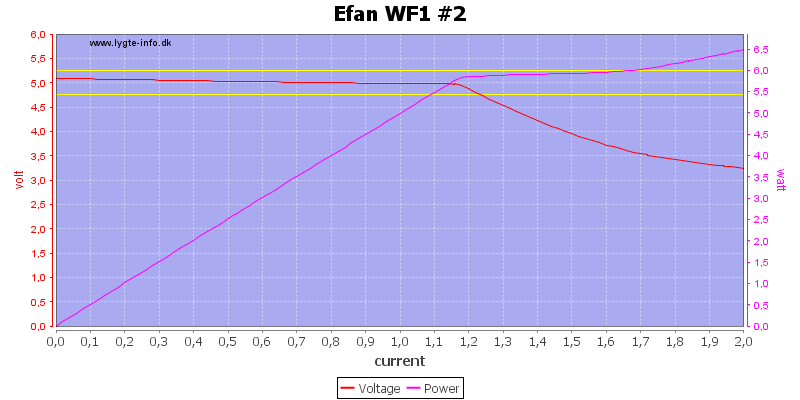
Battery #2 works the same way.
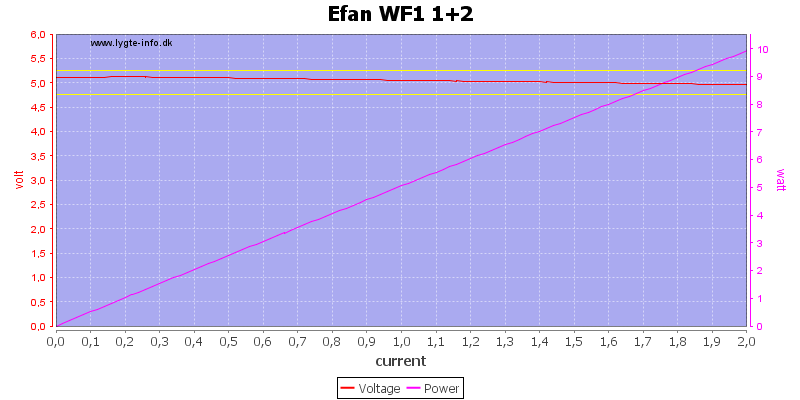
When using both batteries at the same time, the output can easily deliver 2A, at least with newly charged batteries.
%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
A single battery in either slot can easily deliver 0.5A for more than 3 hours. The output is disabled at about 2.7 volt on the battery.
.png)
With both slots containing batteries the runtime is doubled. The batteries are not discharged at the same rate.
Notice: The efficiency calculations are invalid, I do only measure current on one battery.
%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
Increasing the current to 1A does not look as good with a single battery. The 5 volt output can only be maintained for about 1 hour.
.png)
Using two batteries works much better, but when the first battery is empty, the output voltage will slowly drop.
Notice: The efficiency calculations are invalid, I do only measure current on one battery.
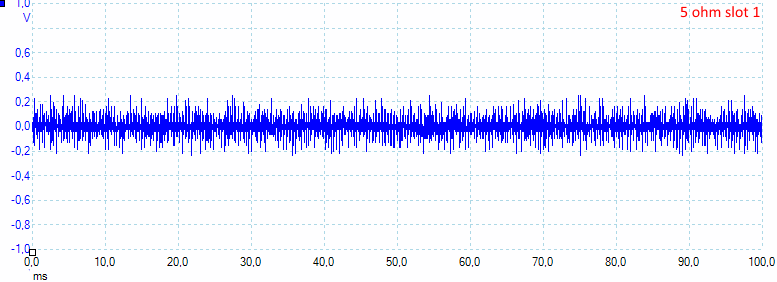
At 1A load the usb output has 60mV rms and 580mVpp noise in the output, measured with a full battery.
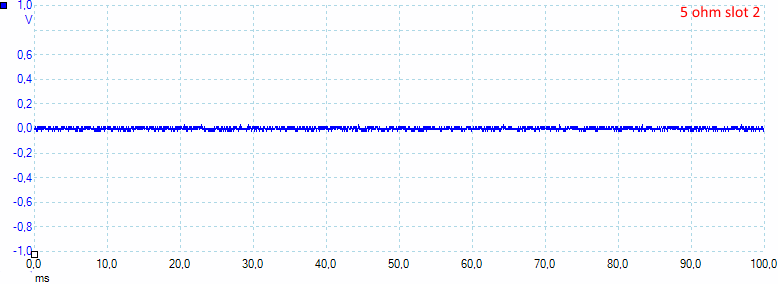
But using slot 2 looks much better: 9mV rms and 80mVpp noise.
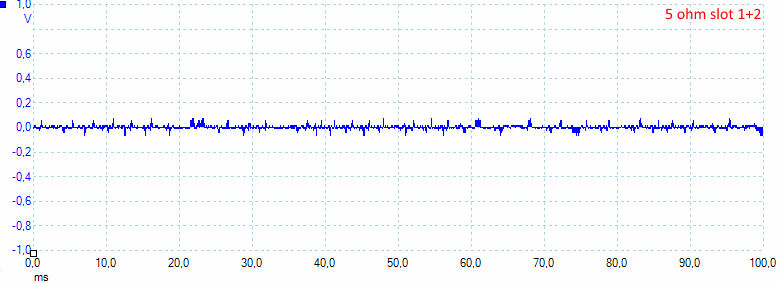
Combining both slots gived 12mV rms and 130mVpp
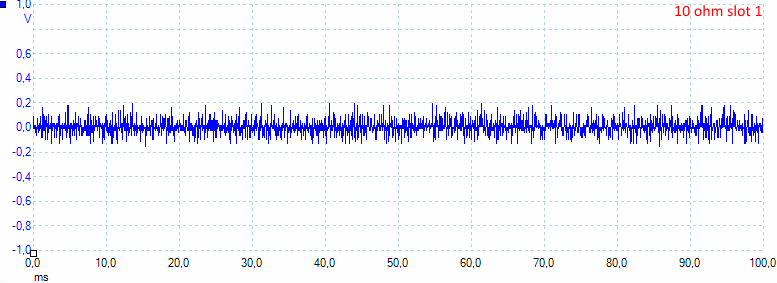
At 0.5A load the usb output has 40mV rms and 400mV pp noise in the output, slot 2 is again considerable better with 5mV rms and 70mVpp.
The charger passed a isolation test with 2500 volt, but failed a 5000 volt test, this makes the charger acceptable for 110VAC usage, but doubtful for 230VAC usage (Not good when the supplied adapter is for EU). Usage with 12 volt (in a car) is, of course, always possible and safe.
Conclusion
With the low termination current and low current ranges this charger is good for charging 10440, 14500, 16340 cells, it can also be used for 18650 or 26650.
With NiMH it uses maximum voltage termination or -dv/dt depending on battery, i.e. battery may not be fully charged.
The usb output does 0.5A fine but need two batteries to do 1A fine and I could have wished for less noise.
I like the charger, it can be used for many charging purposes, but it need a better power adapter.
Notes
The charger was supplied by Yi Fang for review.
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger
Read more about how I test USB power supplies and chargers


























%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
.png)
.png)




%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
.png)
.png)






.png)
.png)



%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
.png)



