BlitzWolf 30W PD charger BW-S11

Official specifications:
- Brand: BlitzWolf®
- Model: BW-S11
- Plug: EU
- USB Port: TYPE-C PD Port + USB Type-A Port
- Total Power: 30W (Max)
- Input: AC 100-240V 50/60Hz 0.85A Max
- Output: Spower: 5V/2.4A (Max)
- PD/QC: 5V/3A 9V/2A 12V/1.5A (Max)
- Size: 54.5x54x28.5 mm / 2.2 x2.1x1.1 inch
- Color: White
- Weight: 100g±10g
I got it from Banggood.




I got it in a white cardboard box with some specifications on it.

The box contained the charger and a instruction sheet.






Measurements
- USB output is coded as Apple 2.4A, Samsung and DCP
- USB-C is PD with 5V 3A, 9V 2A and 12V 1.5A
- USB-C output also has QC3
- There is a blue led inside the charger next to the USB output.
- Power consumption when idle is 0.12 Watt
- Weight: 105g
- Size: 92 x 54.2 x 28.4mm
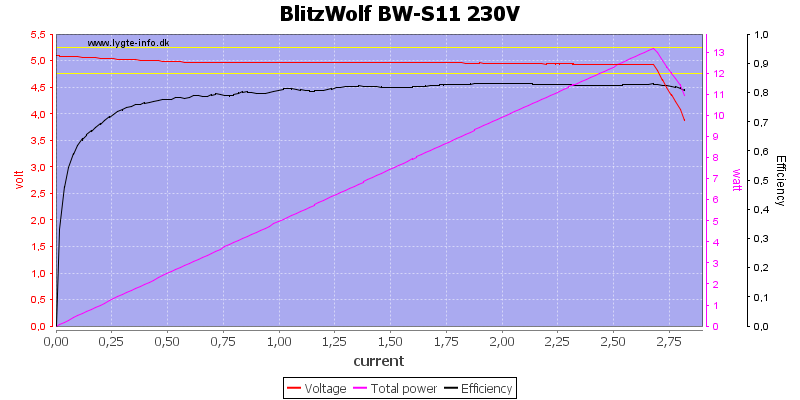
The regular USB output is rated for 2.4A and can deliver about 2.7A, this is fine.
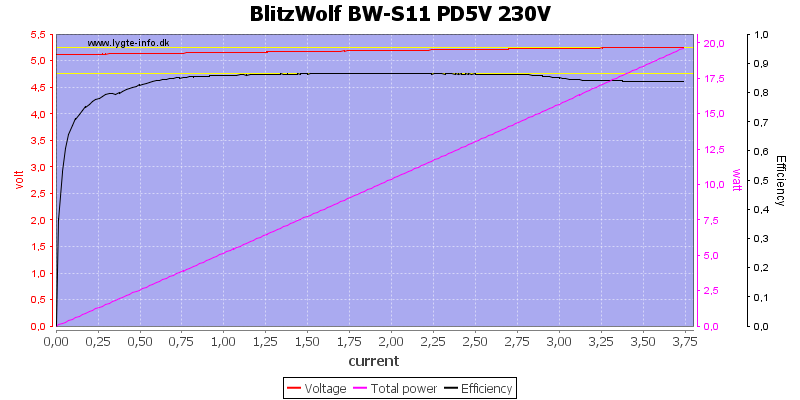
The PD output is rated for 3A on 5V and can deliver 3.7A, it have some cable compensation.
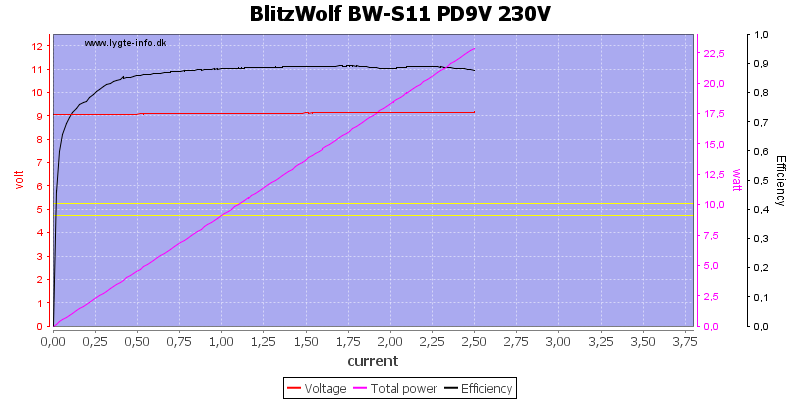
At 9V the maximum current is down to 2.5A with a rating of 2A
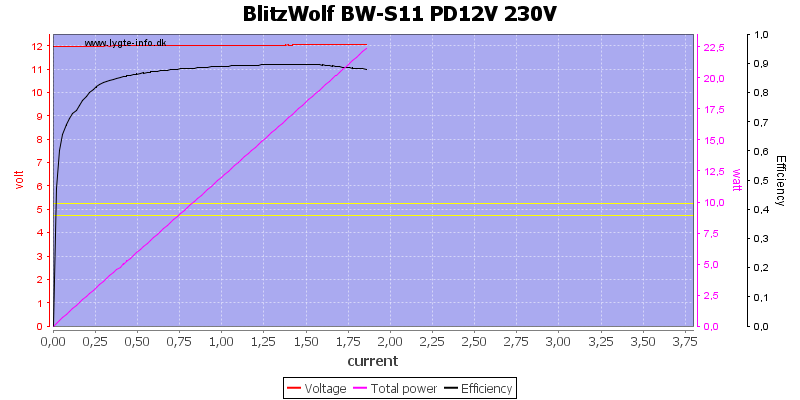
And at 12V the current is limited to 1.8A with a rating of 1.5A, again fine.
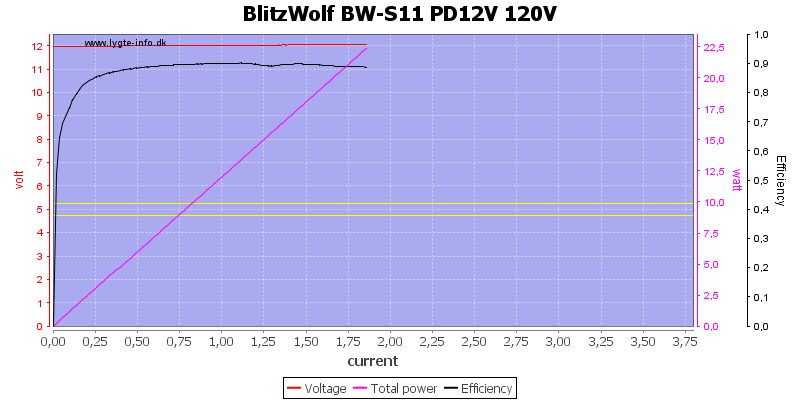
Using 120VAC did not change anything.
For a load test I used 2.4A on USB output and 9V 2A on PD output for one hour, it worked fine.
The temperature photos below are taken between 30 minutes and 60 minutes into the one hour test.
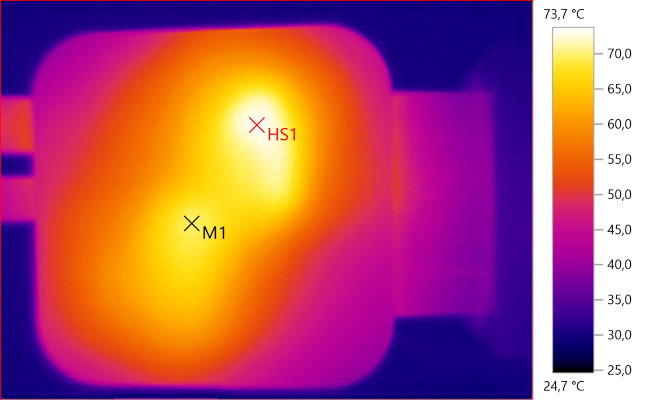
M1: 69.4°C, HS1: 73.7°C
HS1 is the USB transformer and M1 is the PD transformer.
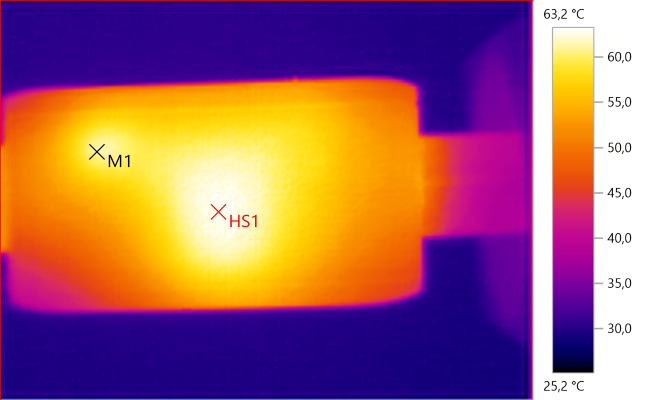
M1: 60.9°C, HS1: 63.2°C
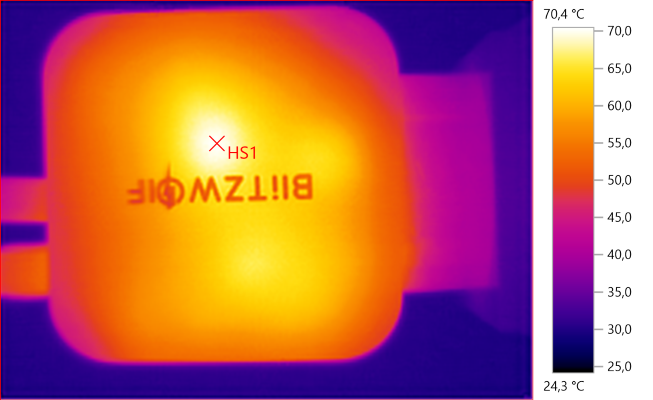
HS1: 70.4°C
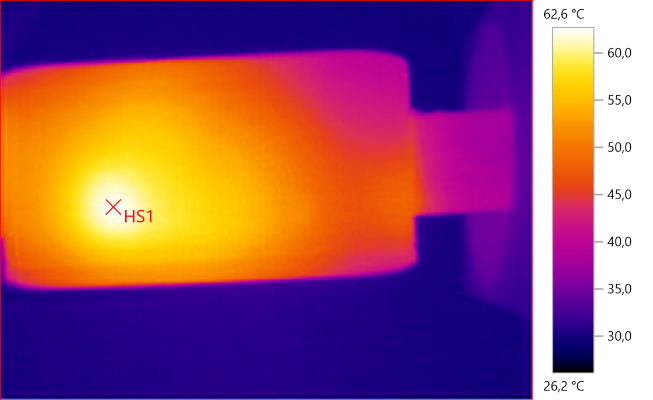
HS1: 62.6°C
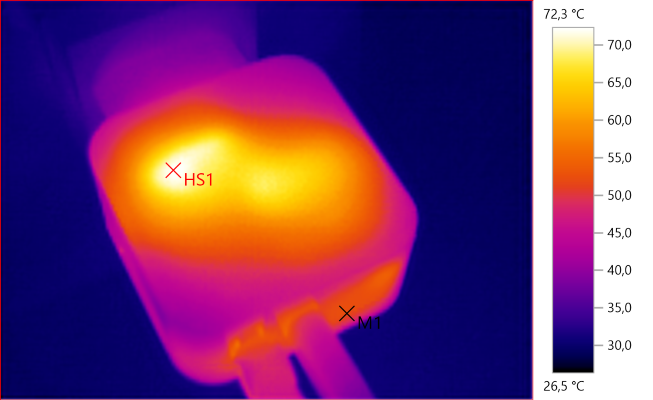
M1: 52.3°C, HS1: 72.3°C
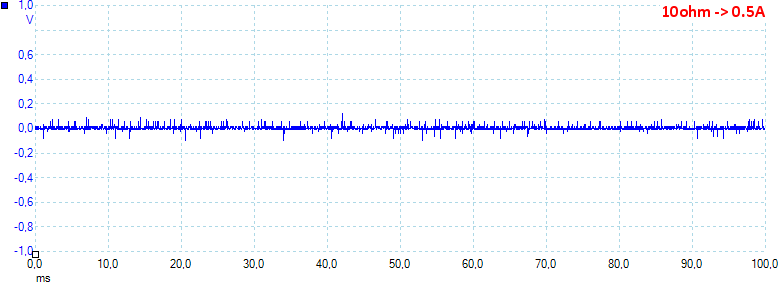
At 0.5A the noise is 12mV rms and 273mVpp.
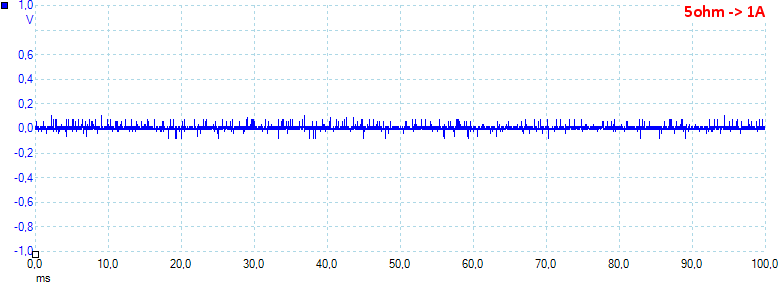
At 1A the noise is 15mV rms and 241mVpp.
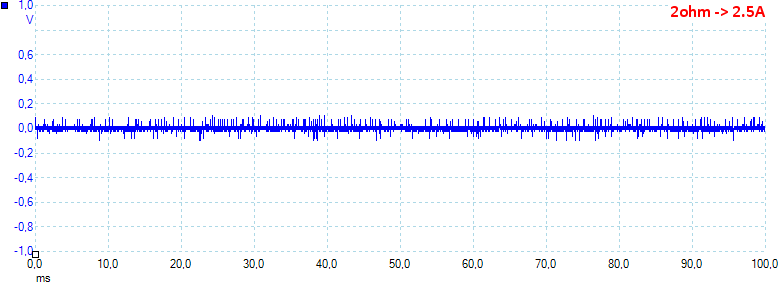
At 2.5A the noise is 96mV rms and 965mVpp.
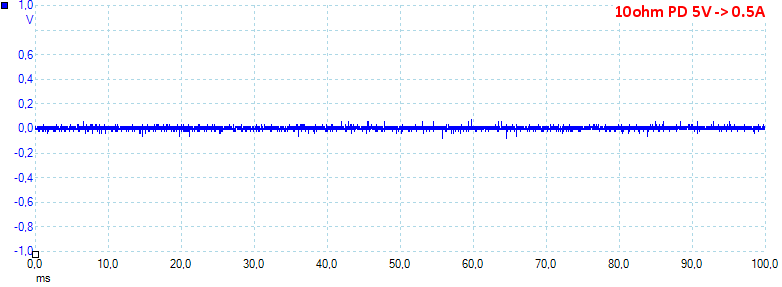
At 5V 0.5A on PD output the noise is 149mV rms and 613mVpp.
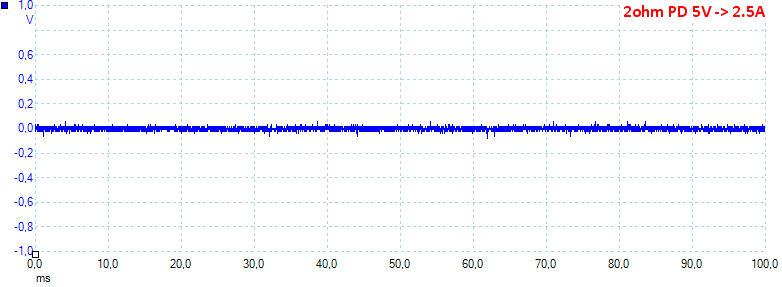
At 5V 2.5A on PD output the noise is 14mV rms and 203mVpp.
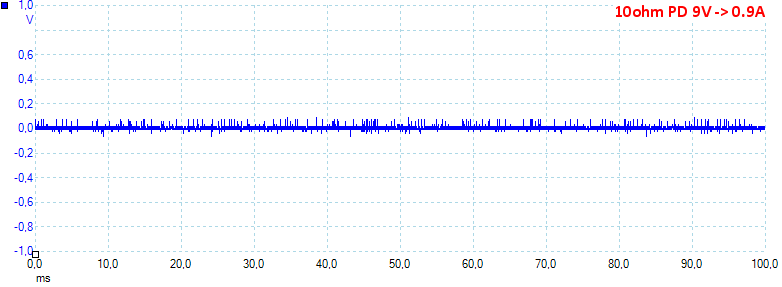
At 9V 0.9A on PD output the noise is 29mV rms and 278mVpp.
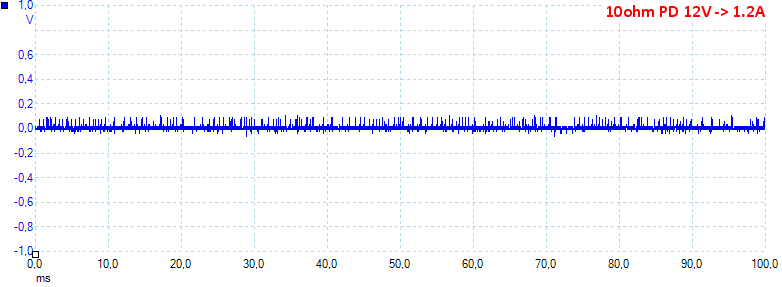
At 12V 1.2A on PD output the noise is 45mV rms and 331mVpp, the noise level is fairly low.
Tear down

Pressing with my vice I could break one lid of the charger.

This USB supply has two mostly separate supplies (the input and rectification circuit is shared). AT the mains input is a fuse and a common mode coil. There is two mains smoothing capacitors with a inductor between. The mains switcher transistor for USB output is next to the transformer. Between the two transformers are the safe capacitors. The PD output has its own small circuit board with some parts on it.




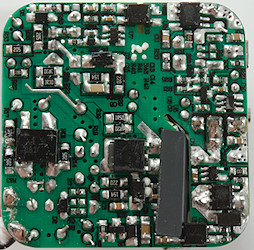
On this side is the mains bridge rectifier (BD1). It has the mains switcher transistor for the QC output. The switcher controller for the QC output is a small 6 pin chip hidden below the black paper. The switcher controller (U7) for the normal USB output is visible. Both switchers has opto feedback, one of them with a slot in the circuit board, the other without.
The USB output uses a synchronous rectifier chip (U9: LN5S19A), it has a auto coding IC (U5) and a reference (431).
The PD output has a rectifier transistor with a synchronous rectifier controller chip next to it, there is nothing to handle PD on this circuit board.
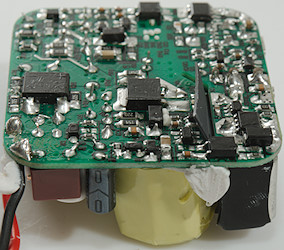


Handling of PD is done on the small circuit board with the USB-C connector. Here is a chip (U1: WT6155) to handle the PD protocol and a transistor (WSP4407) to turn the output on/off.
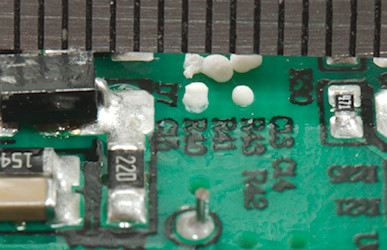
The distance on the circuit board between mains and low volt side is fine.
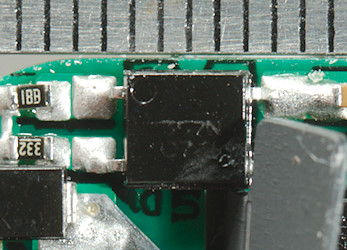
But there is an issue with one of the opto couplers, it is around 5.5mm and that is below requirements. The other opto coupler has a slot underneath it and is fine.
Testing with 2830 volt and 4242 volt between mains and low volt side, did not show any safety problems.
Conclusion
This charger is fine for phones and tablets, but the USB-C PD output cannot be used for laptop computers with only PD support up to 12V. The outputs has a couple of codings and there is individual overload protection on the two outputs.
The slightly low creepage distance is not a serious safety issue.
Notes
Index of all tested USB power supplies/chargers
Read more about how I test USB power supplies/charger
How does a usb charger work?









































