Yojock USC-C PD 60W charger S-TR-140

Official specifications:
- Original Yojock USB-C Charger
- 60W Max Smart Output
- 5V=3A/9V=3A/12V=3A/15V=3A/20V=2.25A
- Type-C Port
- USB PD 2.0 Quick Charge
- Dimension: 62(L) x 62(W) x 32(H) mm
I got it from aliexpress dealer: YOJOCK Official Store


I got the charger in a cardboard box with a model specification.

The charger included the charger, one mains plug and a instruction sheet.


The mains plug is a separate item, without this the charger has a foldable US plug.












Measurements
- Power consumption when idle is 0.09 watt
- PD output supports: 5V 3A, 9V 3A, 12V 3A, 15V 3A, 20V 3A
- PD output supports DCP, QC3 and Apple 2.1A
- Default output is off.
- Weight: 152g
- Size: 105 x 62 x 31.8 mm
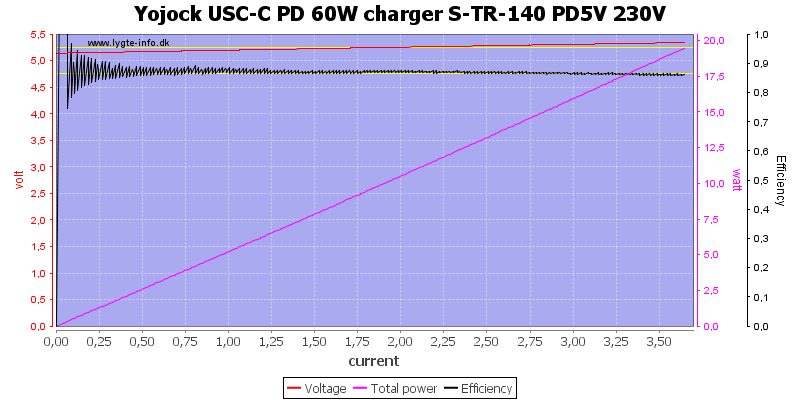
The charger can deliver about 3.6A on 5V with good efficiency.
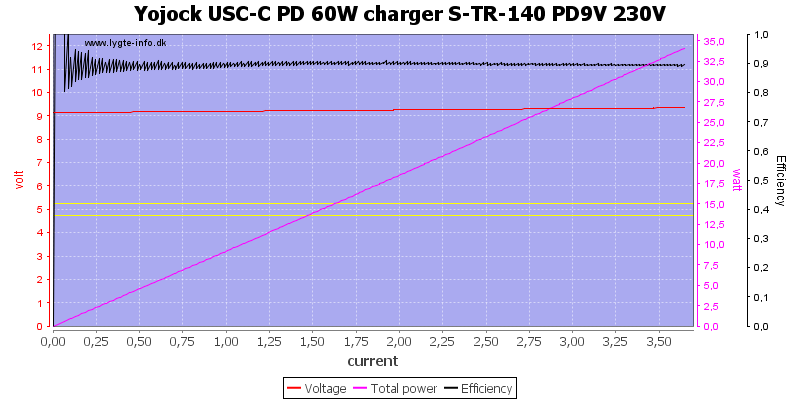
At 9V it is the same
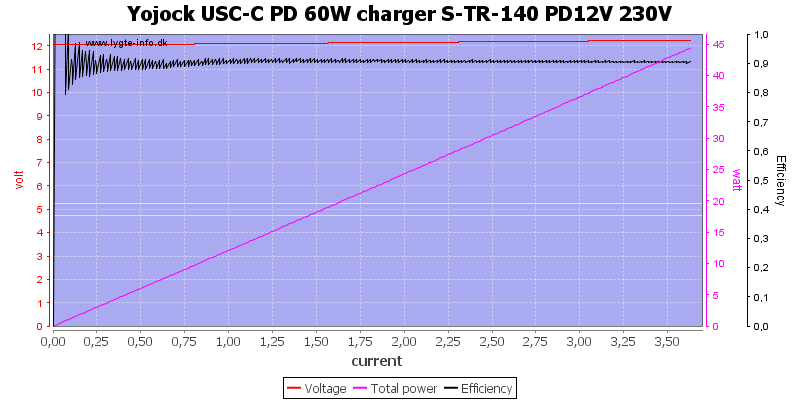
And at 12V
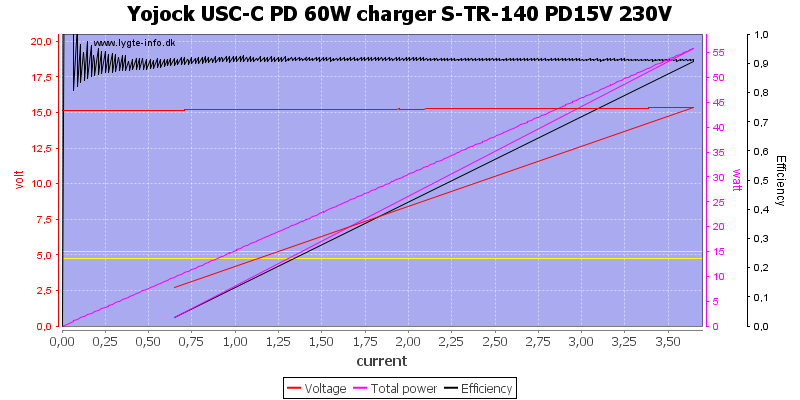
At 15V it still maintains around 3.7A
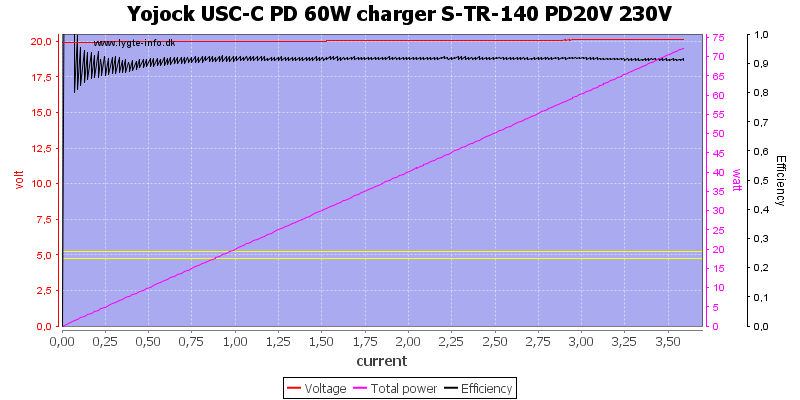
Even at 20V
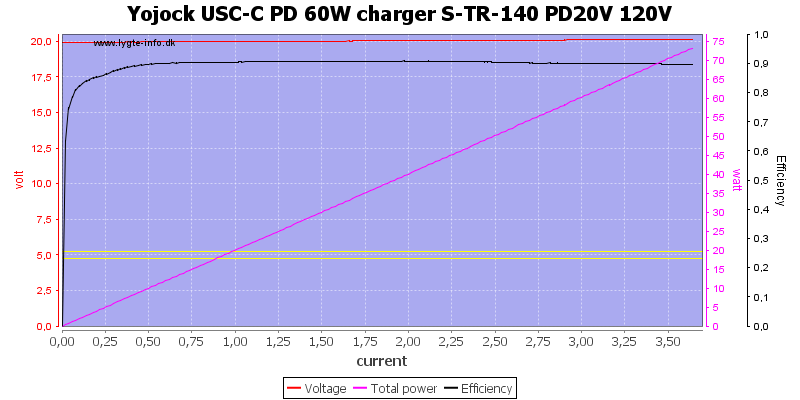
Dropping the mains voltage to 120VAC do not affect output current.
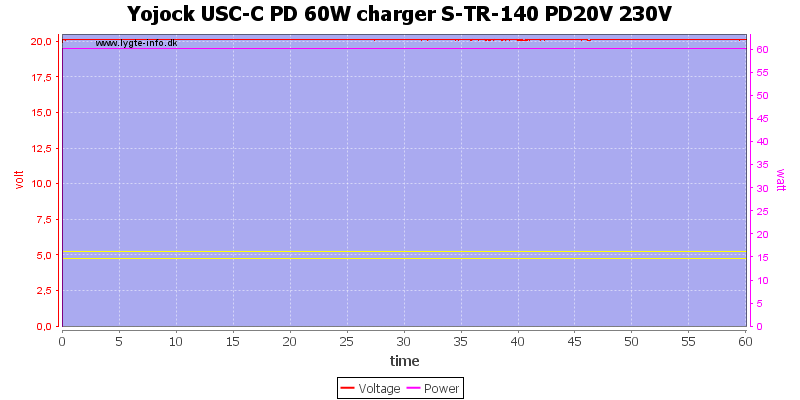
Here I did a one hour run at 20V 3A, this worked fine.
The temperature photos below are taken between 30 minutes and 60 minutes into the one hour test.
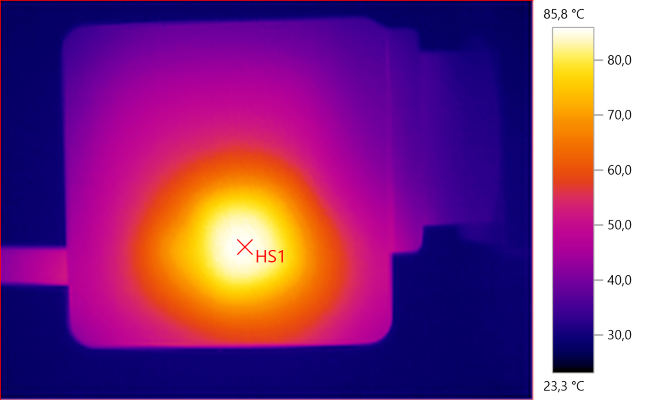
HS1: 85.8°C
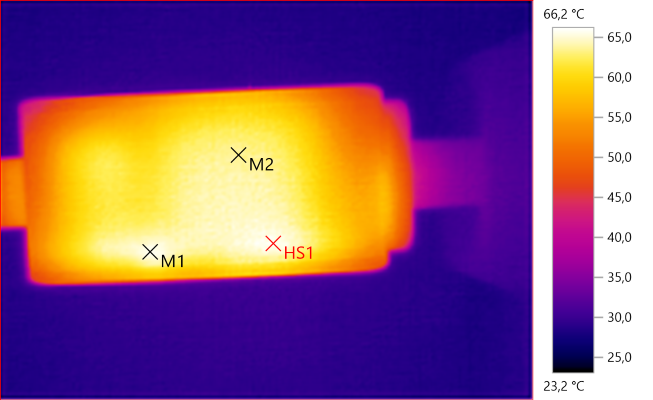
M1: 65.7°C, M2: 63.6°C, HS1: 66.2°C
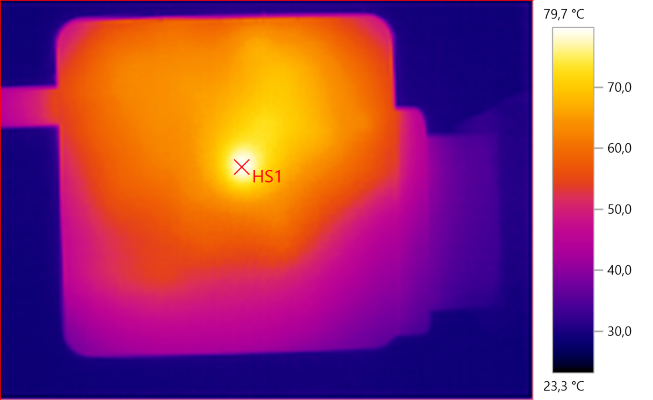
HS1: 79.7°C
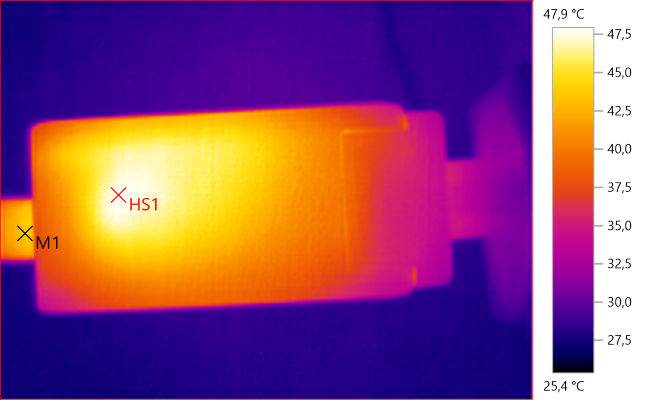
M1: 43.6°C, HS1: 47.9°C
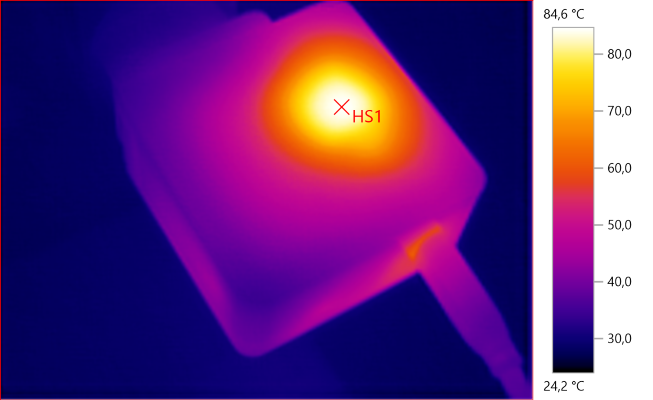
HS1: 84.6°C
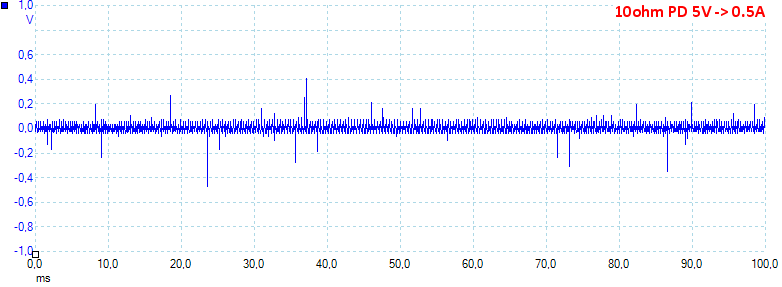
At 5V 0.5A the noise is 33mV rms and 1412mVpp.
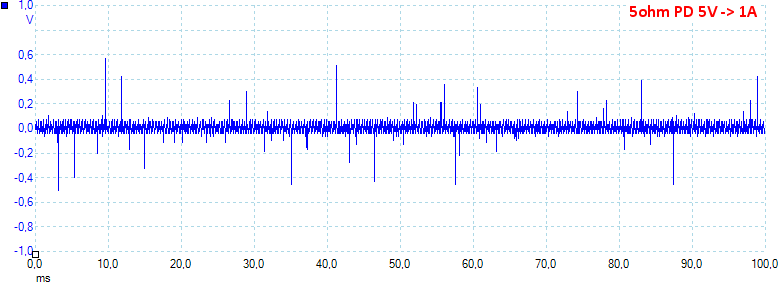
At 5V 1A the noise is 89mV rms and 1368mVpp.
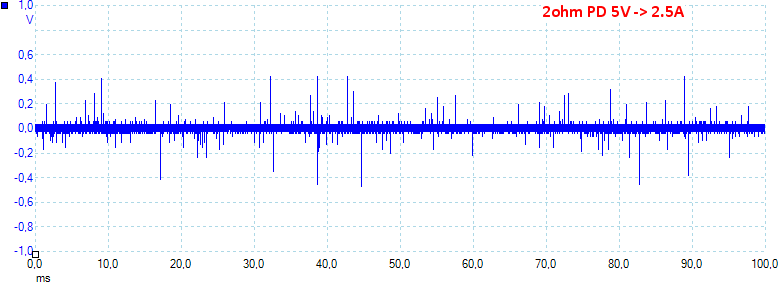
At 5V 2.5A the noise is 45mV rms and 1341mVpp.
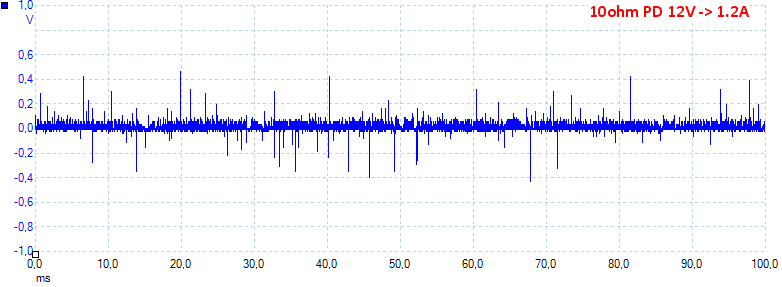
At 12V 1.2A the noise is 42mV rms and 1447mVpp.
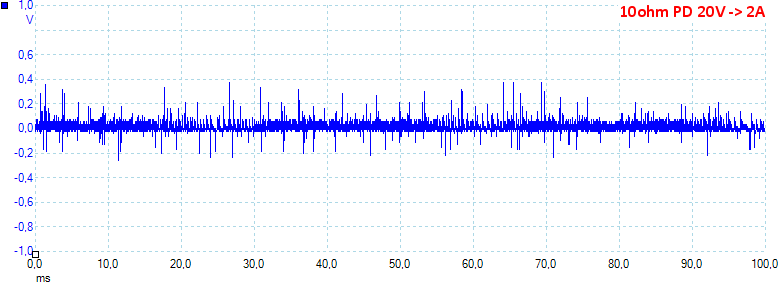
At 20V 2A the noise is 49mV rms and 1174mVpp.
Tear down

It could not squeeze, break or whack this charger open, I had to cut it.

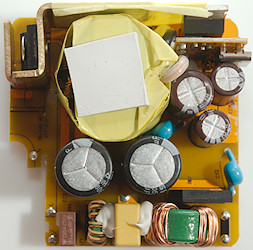
It looks fairly filled this side of the circuit board. At the input is a fuse (FR1) and two common mode coils (LF1 & LF2), followed by the bridge rectifier (BD1) with a safety capacitor next to it (CY2), there is also a safety capacitor (CY1) next to the transformer. The mains switcher transistor (Q1) is mounted on the heatsink. On the low volt side is a rectifier transistor for synchronous rectification, it do not need a heatsink.





A side view of the usb connector board, it has the PD chip (U6: Marked WT661SF) on it.
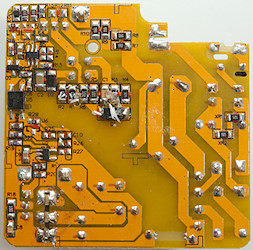
On this side is the mains switcher (U1) and a synchronous rectification controller (U2). There is also opto feedback (U5)
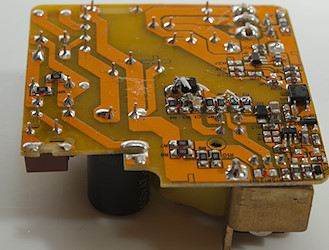
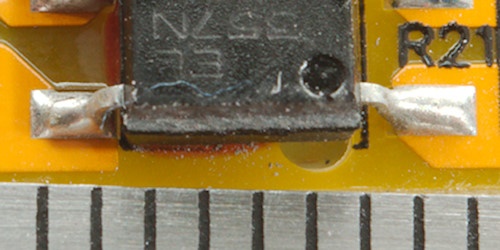
Because the slot below the opto coupler is too short, the distance between mains and low volt side is slightly low.
The charger passed the 2830 volt and 4242 volt test, this means it is it is fairly safe.
Conclusion
This charger delivers the rated 60W to the USB-C connector, but only at 20V. The output supports both PD and the most common older protocols. Generally the design longs fine, but there is a lot of noise.
Notes
Index of all tested USB power supplies/chargers
Read more about how I test USB power supplies/charger
How does a usb charger work?













































