Charger Xiamen Nanfu HG-1412W



This charger is a fairly cheap multi chemistry charger that supports a wide variety of battery sizes.




The charger is delivered in a retail box with both Chinese and English text on it.

The charger has a fixed mains cord and is universal voltage (100-240AC).

The charger has one led for each slot and a common led that shows when power is connected.

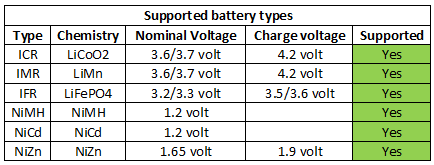
Selection of chemistry is done with a slide switch it is marked:
1.2V for NiMH
1.5V for NiZn
3.6V for LiFePO4
4.2V for Normal LiIon
The text beside the slider is rather difficult to read.


The charger uses the usual slider constrution and support from 28mm to 69mm, this means it will not support long protected 18650 cells.
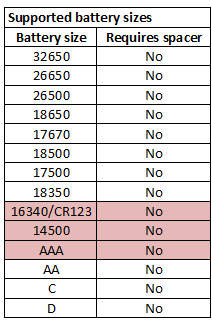











The charge current is a bit high for small cells. The charger can only handle up to 69mm long cells, with both flat and button tops cells.
Measurements
- Power consumption when idle is 0.1 watt
- When starting a charge the current can be up to 1.7A for some seconds.
- The charger never terminates the charge, current just drops when voltage raises.
- The charger will always restart when voltage drops below termination voltage, because it never really turned off.
Charging 4.2V LiIon
%20%231.png)
The charge current is around 0.6 to 0.7A, there is no termination, the current will just drop while the voltage raises.
The charger voltage is a bit on the high side.
%20%232.png)
%20%233.png)
%20%234.png)
The 3 other slots are the same.
%20%231.png)
Another LiIon cell looks the same.
.png)
With all slots in use the actual charge current is lower, but the charge methode is the same.
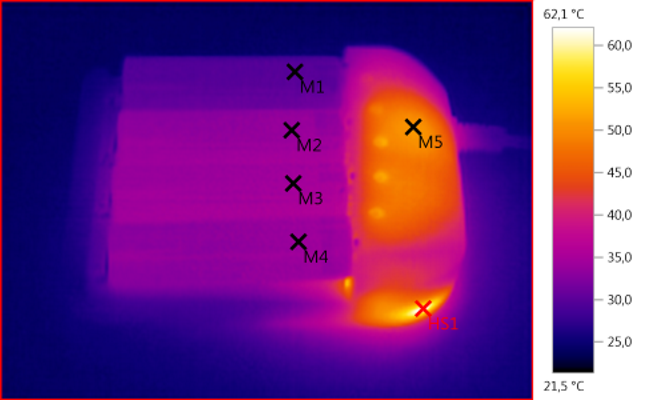
M1: 29,8°C, M2: 33,9°C, M3: 34,5°C, M4: 34,0°C, M5: 51,2°C, HS1: 62,1°C
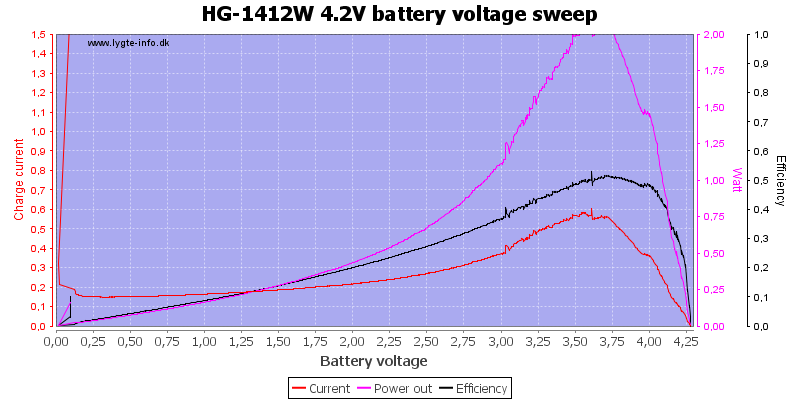
Here is a profile of the charge current with varying battery voltages, the red charge led turns off at 4.25 volt.
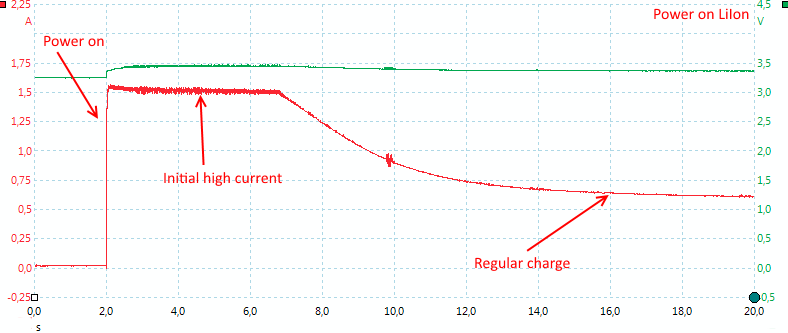
The charger starts immediately with a rather high current, in a couple of seconds this will drop to the regular charge current.
Charging 3.6V LiFePO4
%20%231.png)
Same with LiFePO4, it never terminates the charging.
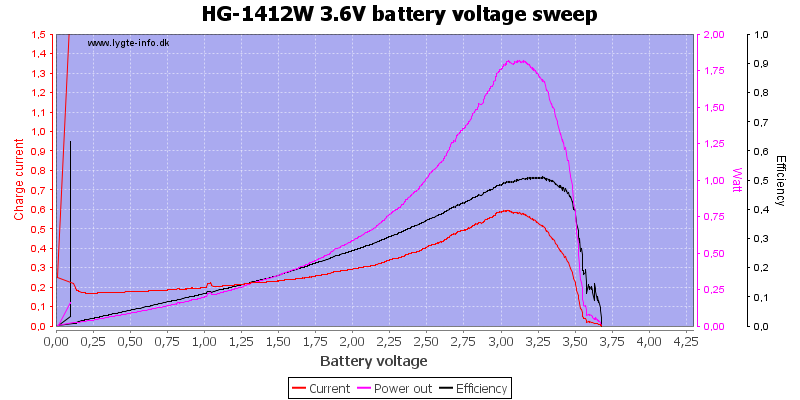
Here is a profile of the charge current with varying battery voltages, the red charge led turns off at 3.63 volt.
Charging 1.5V NiZn
I did not try charging any NiZn batteries, but only did a charge profile:
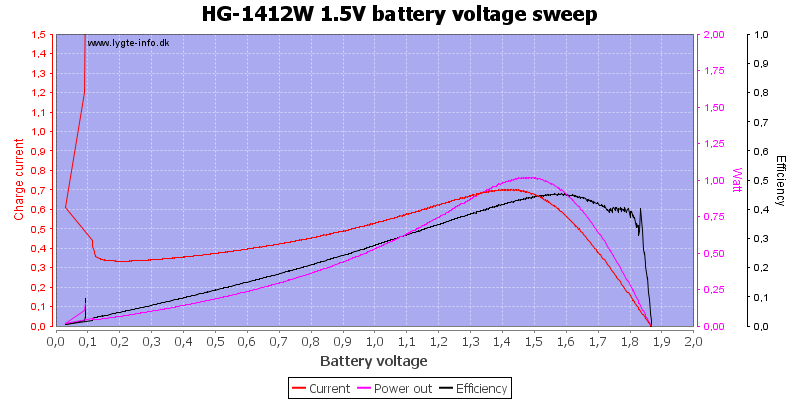
Here is a profile of the charge current with varying battery voltages, the red charge led turns off at 1.8 volt.
Charging 1.2V NiMH
%20%231.png)
Like the above charging curves there is no termination, only a slowly falling charge current.
%20%232.png)
%20%233.png)
%20%234.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
It is the same for all NiMH cells.
.png)
And with more cells the current will e reduced.
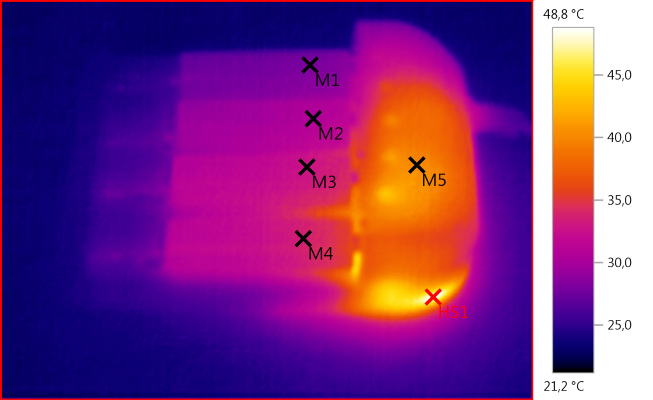
M1: 28,3°C, M2: 30,5°C, M3: 32,7°C, M4: 33,7°C, M5: 40,3°C, HS1: 48,8°C
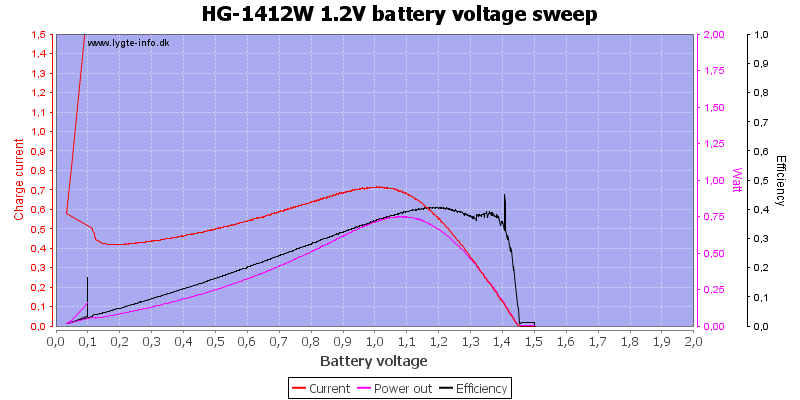
Here is a profile of the charge current with varying battery voltages, the red charge led turns off at 1.4 volt.
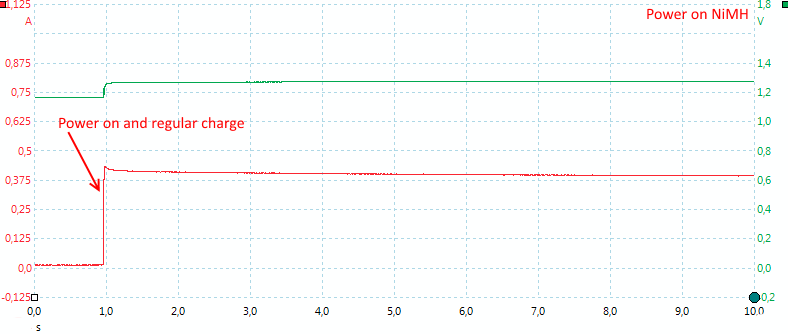
The charger starts immediately and do not pulse the current.
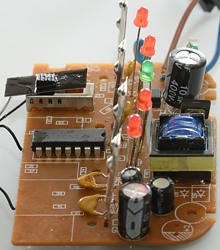
Tear down
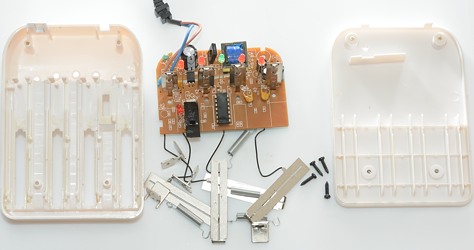
I had to remove four screws to open the charger.
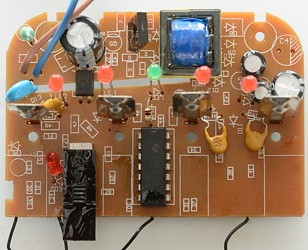
The charger is very simple. On the input side is uses a resistor for a fuse. A opto feedback chip is placed over the gab in the circuit board. The LM339 is a quad comparator and is used to control the leds. I suspect the led besides the switch is used as a reference to control the charge voltages.
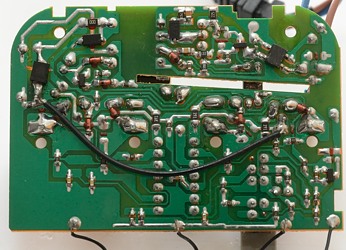
The charger has a bridge rectifier on the mains input and uses two transistors to make the switching circuit.
It looks like there is a diode for each battery, to avoid problems with full/empty batteries.




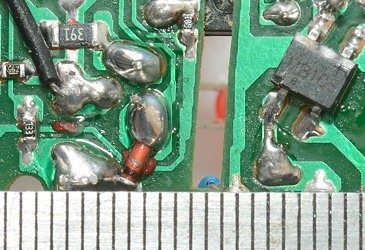
Distance between mains and low volt side must be at least 4 mm (for 230VAC) when some of the distance is through air. This is not the case here.
There is also a problem with the mains lead flapping around inside the charger.
Testing the mains transformer with 2500 volt and 5000 volt between mains and low volt side, did not show any safety problems (But see above).
Conclusion
The charger will charge lots of chemistries, but it do not use the correct algorithm for any of them.
The charger is useable, but not the correct charger if you care about your batteries or want a safe charger.
Notes
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger

























%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
%20%233.png)
%20%234.png)
%20%231.png)
.png)



%20%231.png)


%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
%20%233.png)
%20%234.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
.png)











