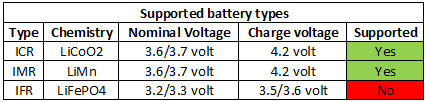
Charger Xtar MC1Plus



Xtar has updated their smallest 18650 charger, now it supports two charge currents. This has made it faster to charge 18650/26650 cells and maintained the support for smaller cells.




I got the charger in a small cardboard box with the specifications printed on it.

The box contains the charger, a bag to keep the charger in, a usb cable, a instruction manual and a warranty card.

The charger must be supplied from a usb power supply with 1A current. The connector is a micro usb, making it compatible with smart phone chargers.

There is not much user interface on the charger, only a red/green led. It is red while charging and green at all other times.


The charger can handle both button top and flat top batteries.
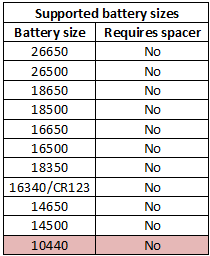
The slider moves smoothly and can hand cells from 30mm to 71 mm long.
The charger will select 0.5A and 1A charge current depending on battery length, the change point is marked on the charger.
xx500 batteries will usual be charged with 0.5A, but the change point is close when charging a protected xx500 cell.






The charger can easily handle 70 mm long batteries, including flat top cells. (See my small LiIon comparison for length of different brands).
The current is to high for 10440 batteries.
Measurements
- When not powered it will discharge a battery with 0.05mA.
- Below 2.9 volt the charger wil charge with 150 to 180mA (Higher current at lower voltage) for long batteries.
- Below 2.9 volt the charger wil charge with 75 to 90mA (Higher current at lower voltage) for short batteries.
- Above 2.9 volt is use regular charge current.
- When battery is full it will charge with less than 0.01mA.
- If battery drops below 4.10 volt the charger will resume charging.
- Will not restart charging if a cell is reinserted or power cycled.
- Changed between 0.5A and 1A at about 54mm
.png)
The charger uses a CC/CV curve, but current is limited by input voltage and starts dropping at 125 minutes. The charge terminates when the current has dropped to about 65mA. This is a good charge curve.
.png)
A 2600mAh cell is slightly faster to charge, but because the voltage is higher (i.e. current starts to drop earlier) the speed advantage is not that much faster.
.png)
My older 2600mAh is slower to charge due to the higher internal resistance.
.png)
And, of course, a 3400mAh is slower to charge.
.png)
This cell was supposed to be charged at 0.5A, but the 1.5mm thick sensor I stuck between the battery and the charger changed the charging to 1A.
The charging is fine, but current was a bit to high for this cell, due to the sensor. I do not believe this will give problems with protected batteries, except if the trigger point moves a little bit . Protected 14500 is not that long and if a protected 18650 is long enough to trigger 1A, it is acceptable.
.png)
With a 18350 cell there is space for my sensor and I got a 0.5A trace, the termination current is down to 35mA (Good).
.png)
Simulating a weak usb charger did not give the MC1 any problems, charging took longer but was done fine enough.
.png)
A bit more test with dropping voltage. The charger will try to charge with 1A when possible, if the voltage drops to much the current will be reduced and when the voltage is to low to charge it will stop. There is no intelligence to reduce the current if a weak usb charger is used.
.png)
Using a slightly higher voltage made it possible for the charger to maintan full current a bit longer, this improved the charge speed with about 15 minutes.
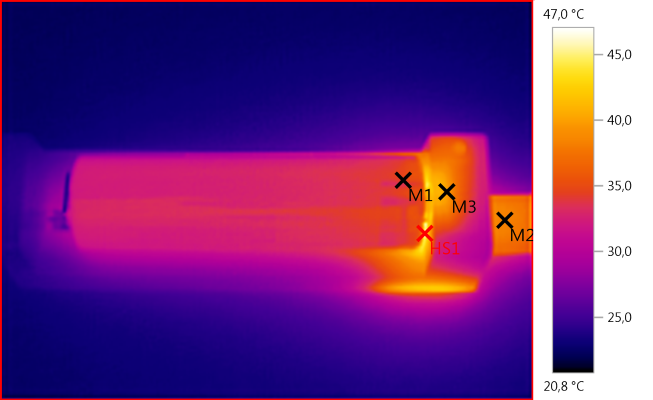
M1: 34,2°C, M2: 38,4°C, M3: 40,0°C, HS1: 47,0°C
Electronic generate heads when handling power, here the heat is generated at the front of the battery, but the battery is keept within limits.
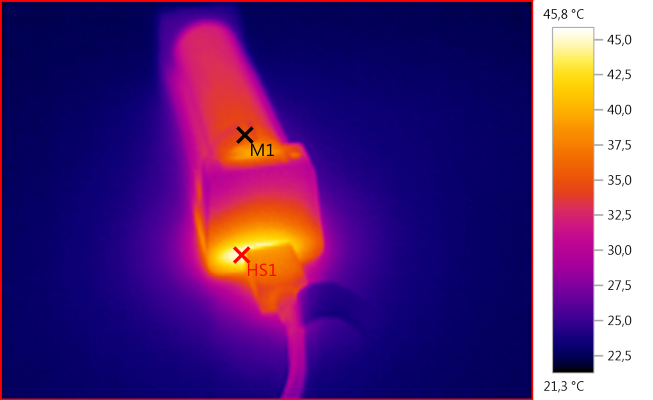
M1: 35,4°C, HS1: 45,8°C
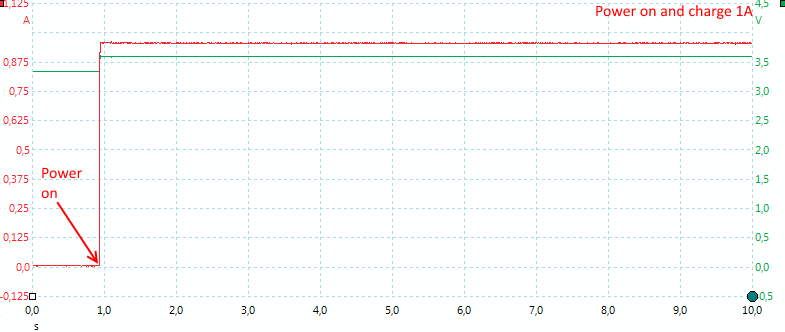
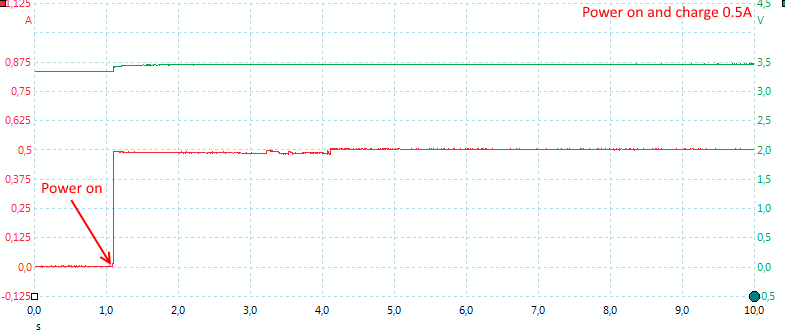
The charger is a simple charger and does not need any time to initialize when power is turned on, it simply starts charging with the selected current. There is no pwm in the charge current.
Conclusion
For a simple and light weight charger, this is a good charger, but it must be used with a usb power supply that can supply 1A.
Notes
The charger was supplied by XTAR for a review.
I have replaced most of my test batteries, this means lower internal resistance and higher capacity.
For information about usb power supplies see my list
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger




















.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)



