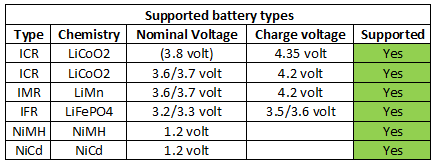
Armytek Uni C2



This charger from Armytek is fairly universal with 4 charge voltages and 3 currents, including a very low one.




The charger was in a cardboard box with specifications on the outside.

The box contains the charger, a mains cable, a 12V car cable and a instruction sheet.


The charger is powered directly from mains or from 12V with the supplied car adapter.

On the bottom is a very short instruction (Good idea) and some specifications.

The user interface is two buttons and 10 dual color leds. The dual color is red and green and using both at the same time is kind of yellowish, but the two colors do not mix very well.

The top led shows the charge current and the bottom four leds the charge state or charge voltage.
When a battery is put in the top led will start blinking shortly after, fast presses on the button at the same side will change current from default 0.5A to 1A to 0.1A and back to 0.5A.
Holding down the button will start one led off the bottom four to blink, click to select charge voltage (This only works for LiIon chemistries).
A press on the button during charging will show the selected charge voltage.
The charger will remember the selected LiIon chemistry and default to that the next time.


The charger uses the classical slider construction and can handle batteries from 30mm to 71.4mm.
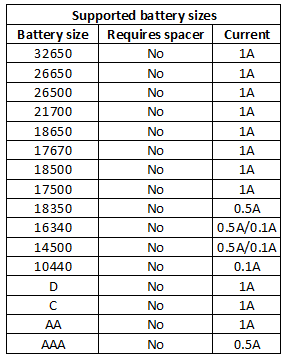












The charger can handle 71mm long batteries, inclusive flat top cells.
Measurements
- Below 0.3 volt the charge will report fault and charge with about 20mA
- Below 1.7 volt the charger will assume NiMH, above LiIon
- Below 3 volt LiIon will be charged with about 140mA.
- When not powered the charger will discharge LiIon with about 0.4mA and NiMH with 0.05mA
- When idle the charger uses 0.37 Watt
- Charger will restart if battery voltage drops below 4.1V on LiIon 4.2V setting.
- Charger will restart if battery voltage drops below 4.2V on LiIon 4.35V setting.
- Charger will restart if battery voltage drops below 3.2V on LiIon 3.7V setting.
- Charge will restart charging after power loss or battery insertion.
4.2V LiIon charging
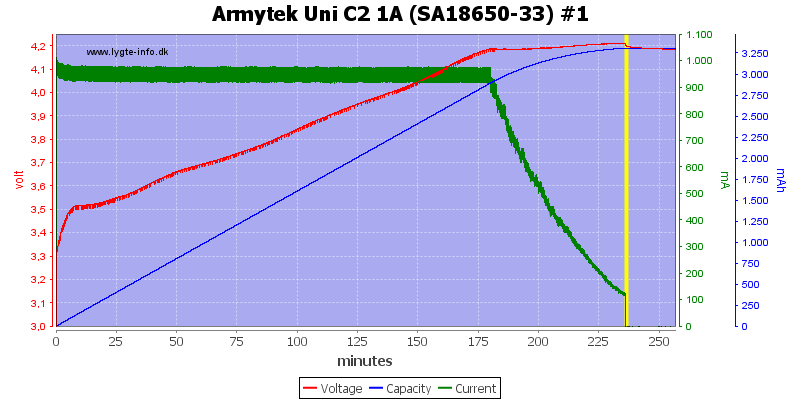
This is a nice CC/CV voltage charge curve, because the charger first goes into CV mode when the voltage is very close to 4.2V, it will charge fairly fast. Termination current is around 120mA
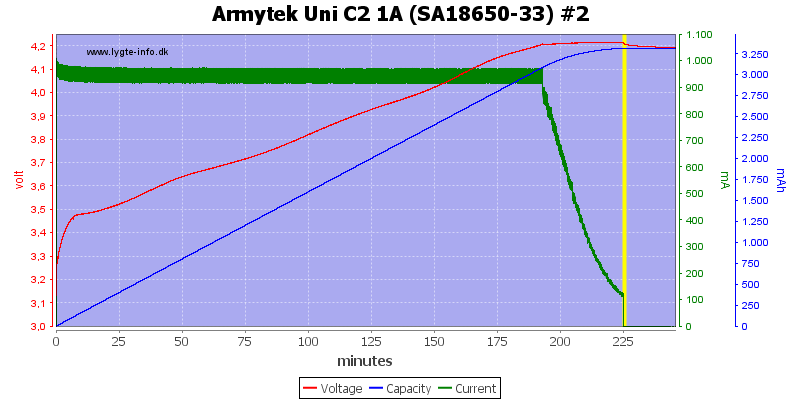
The second channel look the same.
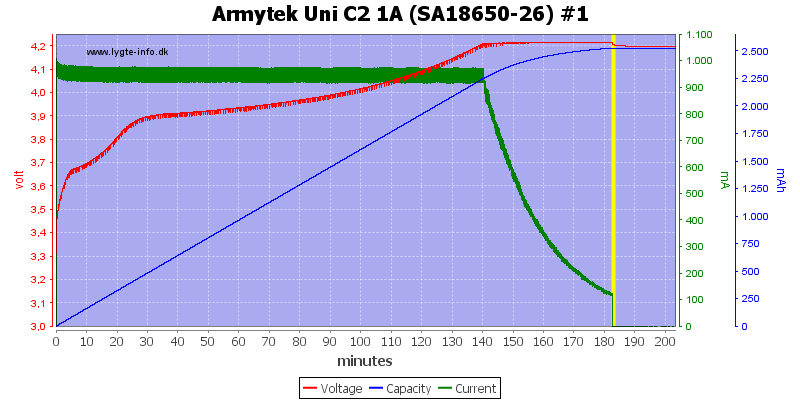
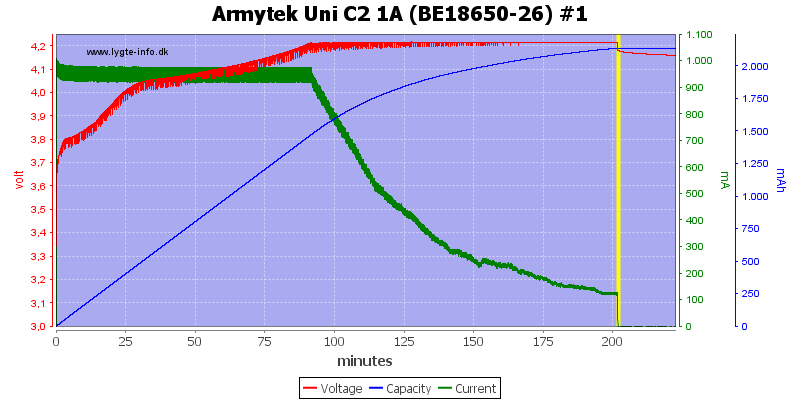
Both these cells are done nicely.
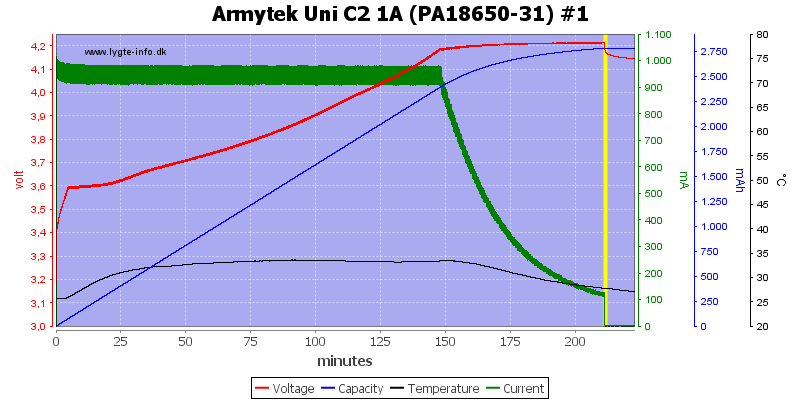
This fairly old cell is also charged nicely.
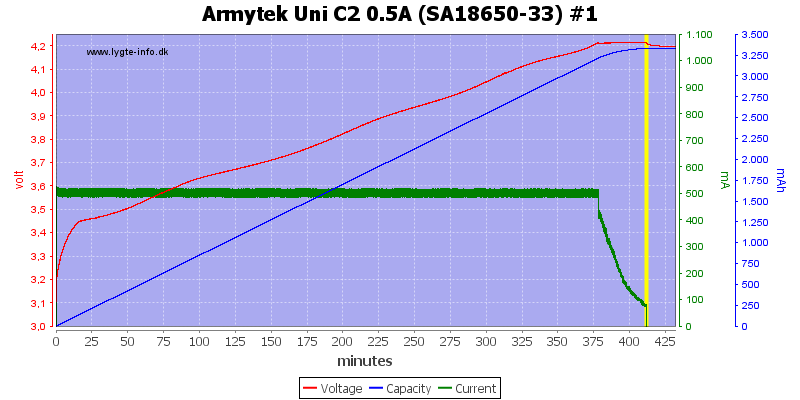
At 0.5A the termination current is a bit lower (nice).
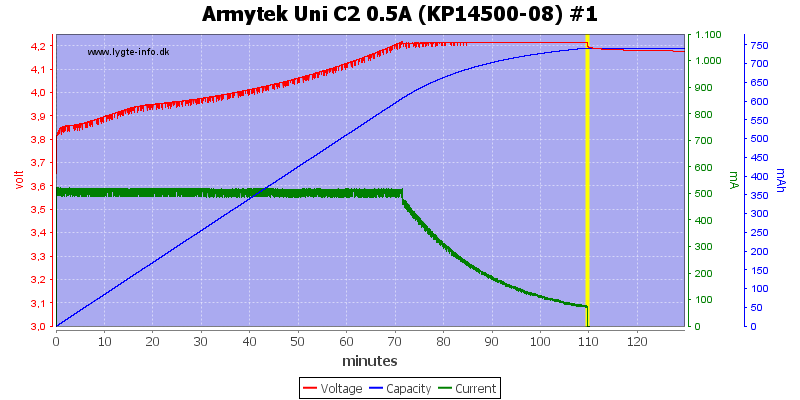
And it chargers a small cell fine.
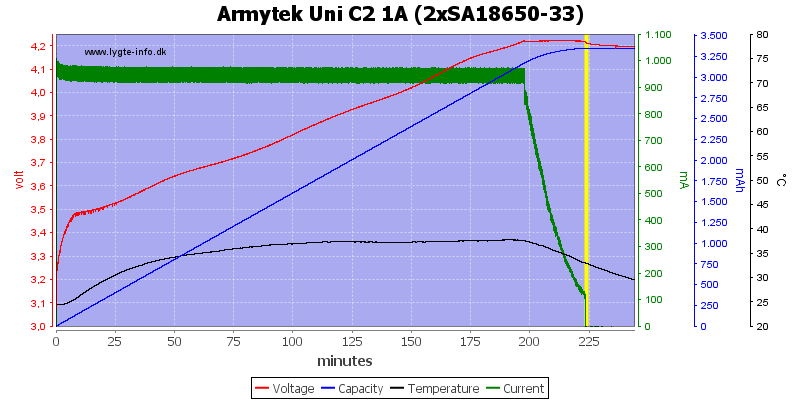
There is no problem charging two cells at a time.
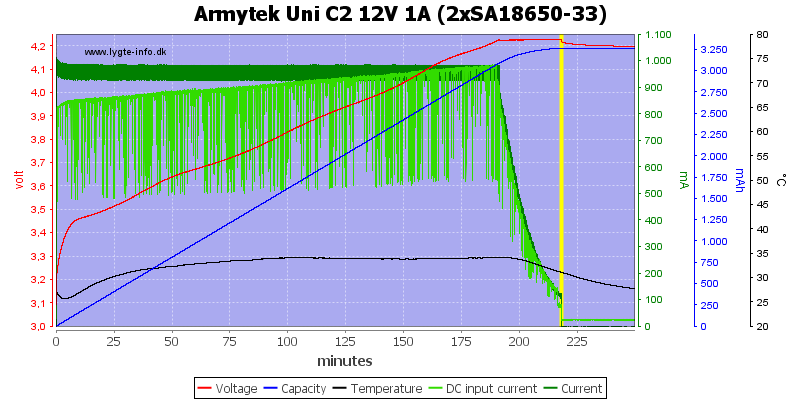
It requires about 1A from a 12V supply.
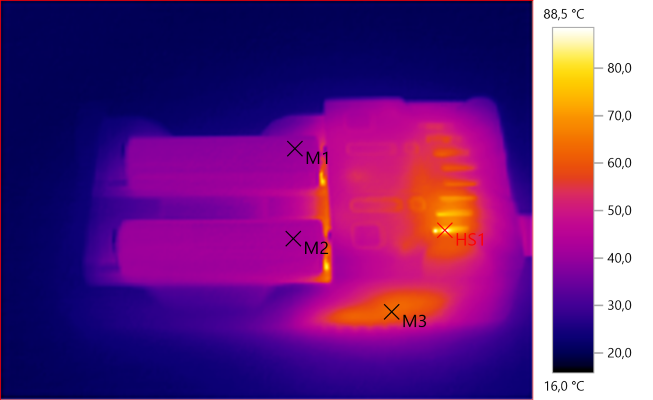
M1: 39,9°C, M2: 41,9°C, M3: 62,5°C, HS1: 88,5°C
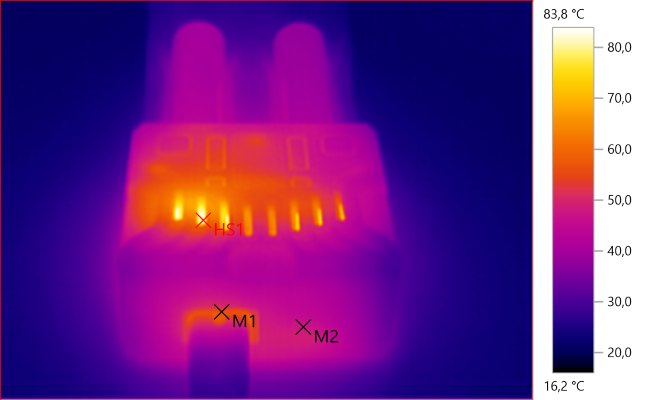
M1: 55,8°C, M2: 47,4°C, HS1: 83,8°C
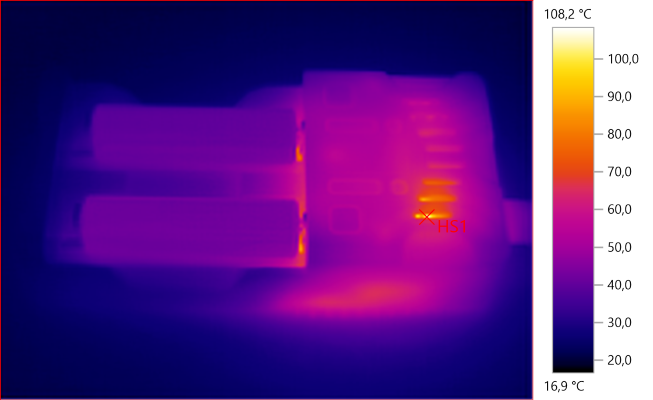
HS1: 108,2°C
There is a part inside the charger that gets rather toasty during charge.
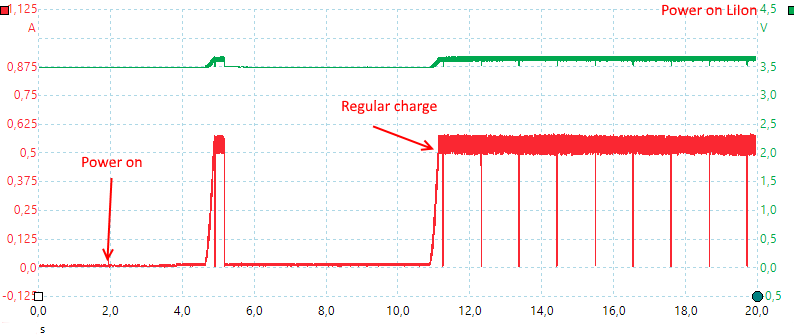
The charger needs about 10 seconds to start, most of the time is used to wait for user current and voltage selection.
It also does a check with a 0.5A current pulse.
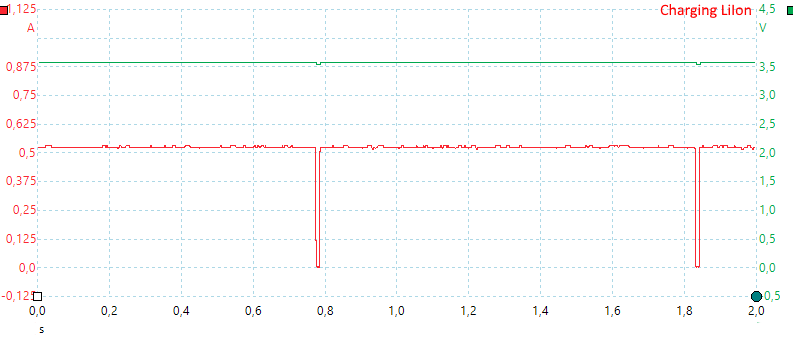
While charging it will turn current of to do a voltage check each second.
4.35V LiIon charging
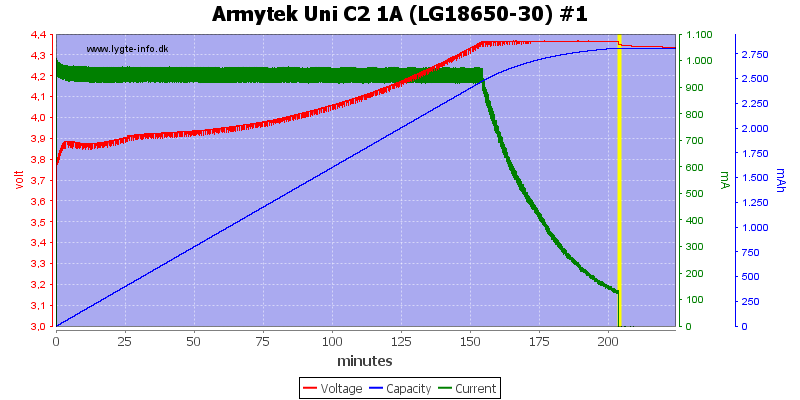
These batteries needs a higher charge voltage and they get it. The result looks fine.
3.7V (LiFePO4) LiIon charging
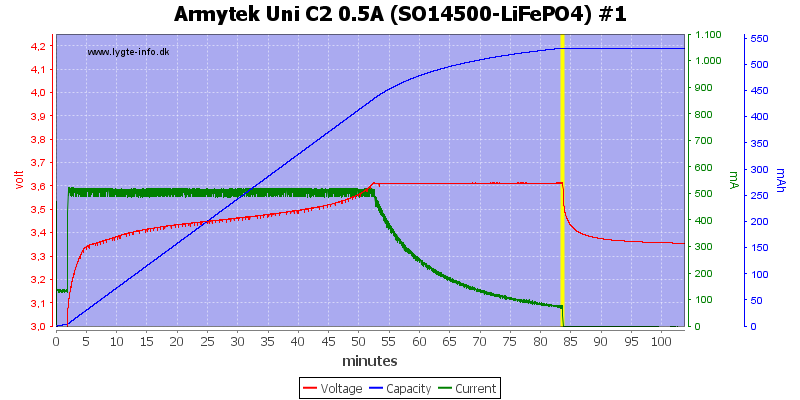
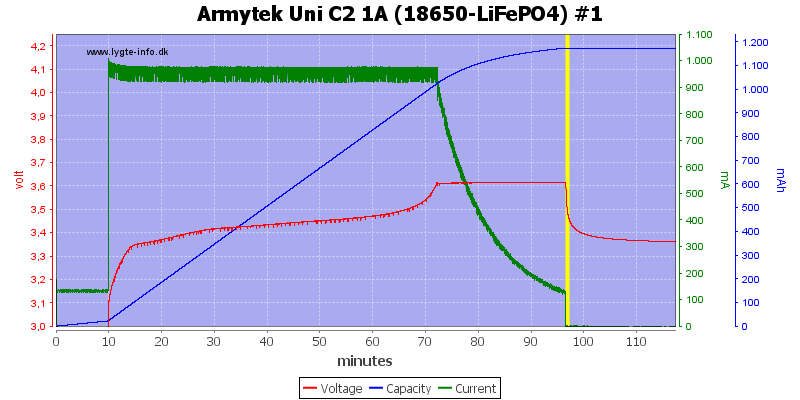
These batteries must be charger to 3.6 to 3.7 volt and will drop significantly in voltage when current is turned off, the charger handles this fine.
It can also be seen that the charger uses a low charge current, until the voltage reached 3 volt.
NiMH charging
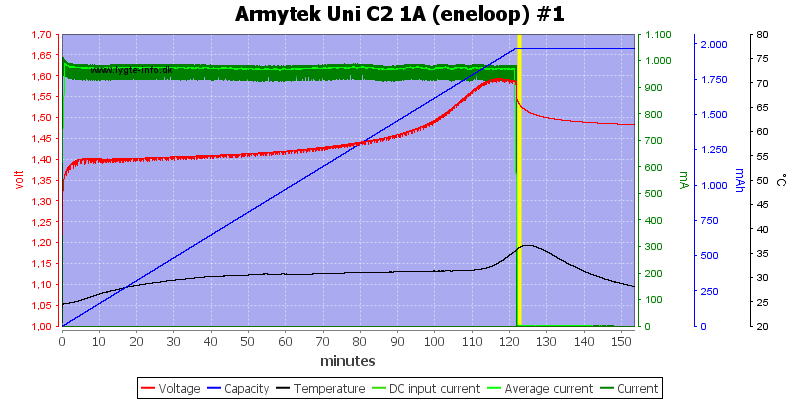
A nice -dv/dt charging.
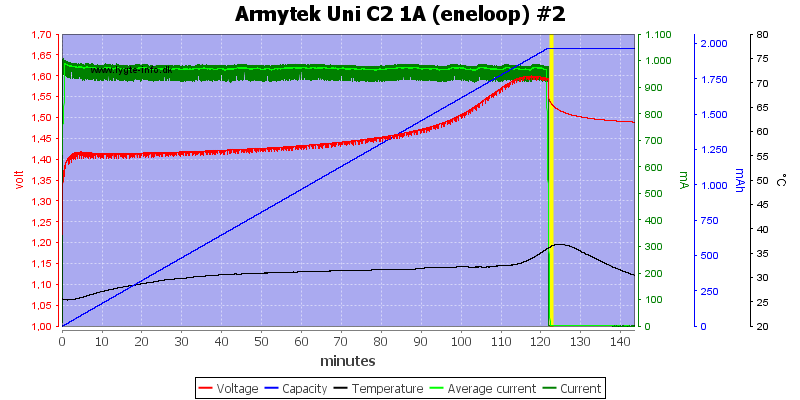
And the same on this channel.
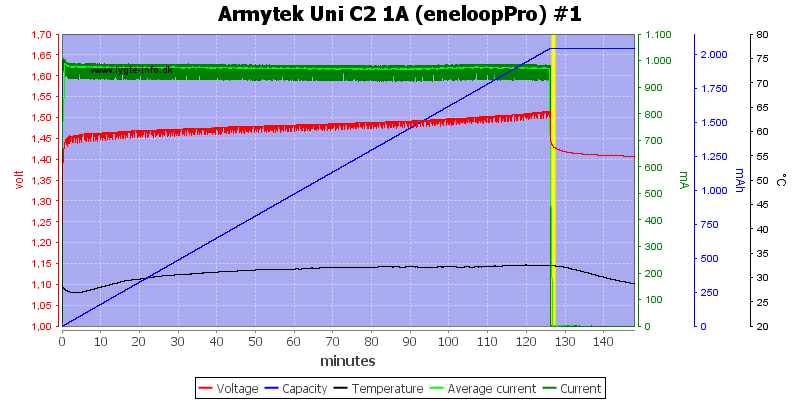
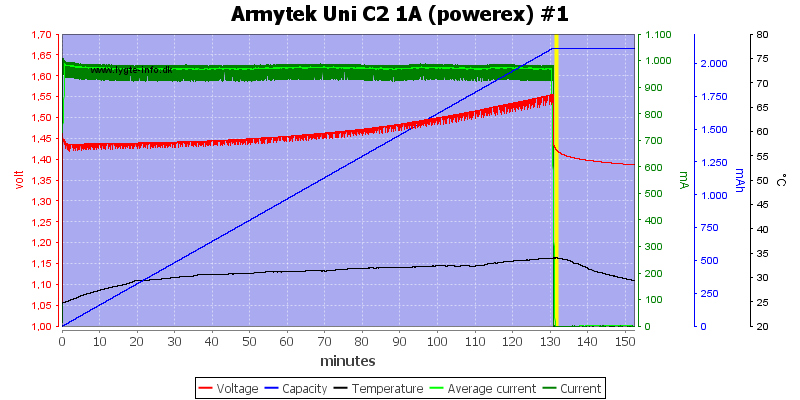
But these two high capacity cells do not look good, they are only partially charged.
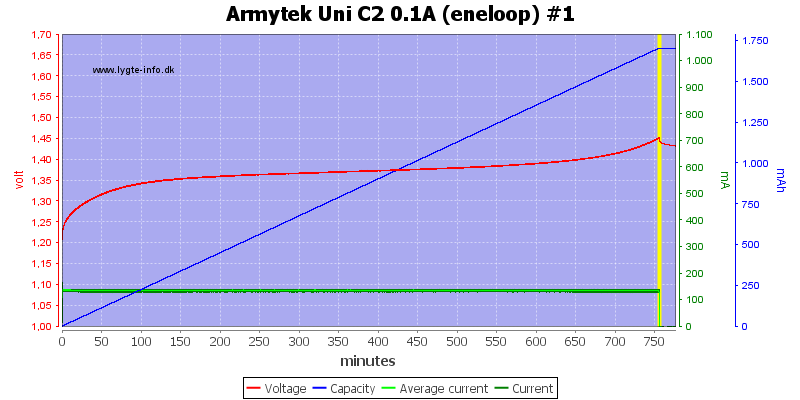
Using 0.1A charge current will prevent a -dv/dt detection from working, this charger do terminate, but a bit early.
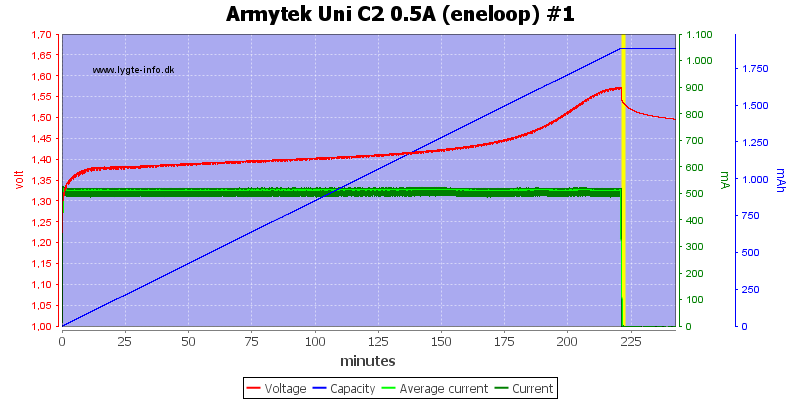
Increasing the current to 0.5A works much better.
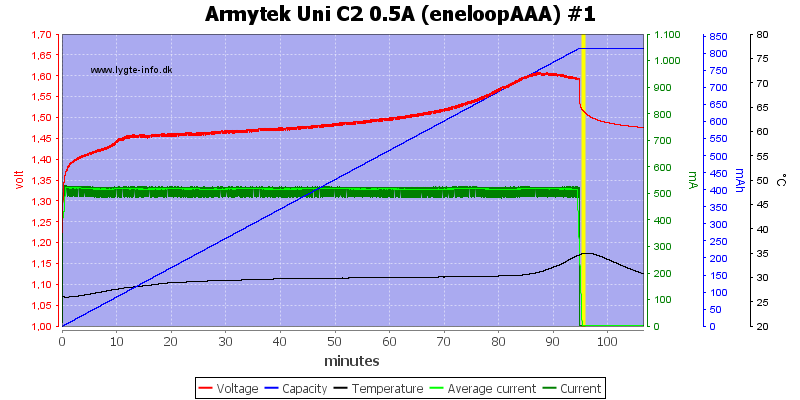
On this AAA cell it was a bit slow to terminate.
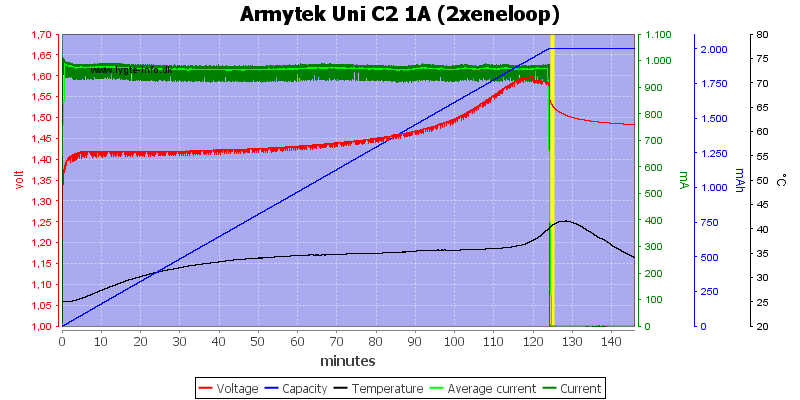
No problem with two cells.
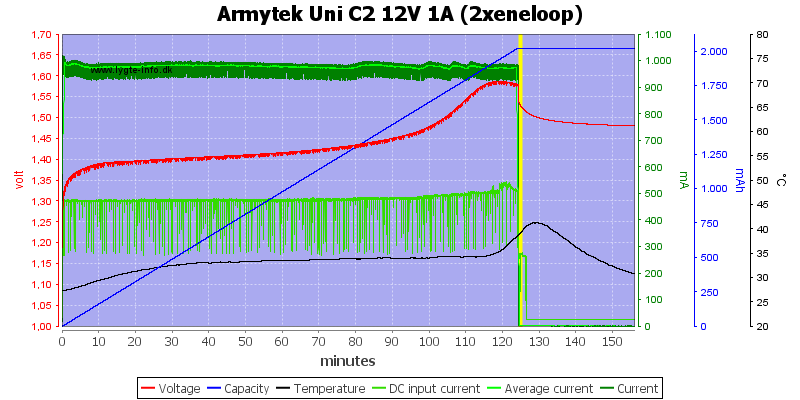
And it requires about 0.5A at 12V to charge two cells.
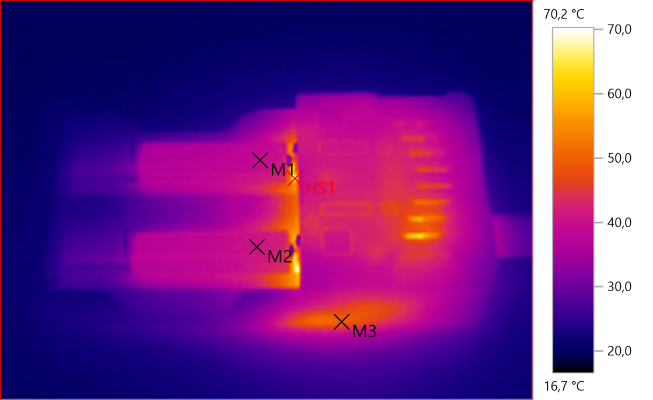
M1: 39,3°C, M2: 41,2°C, M3: 49,4°C, HS1: 70,2°C
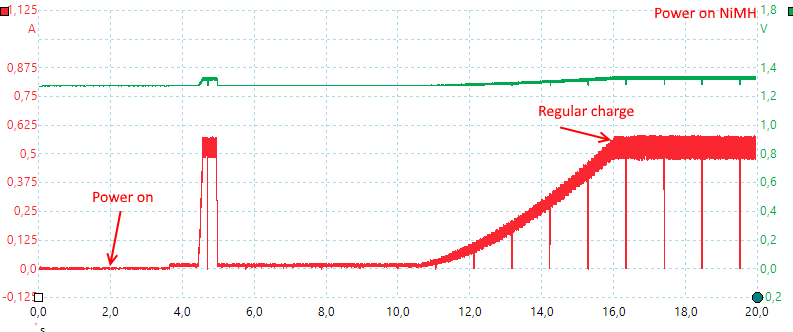
With NiMH batteries it will slowly increase the charge current to the selected level, but it do also make a fast 0.5A pulse before that.
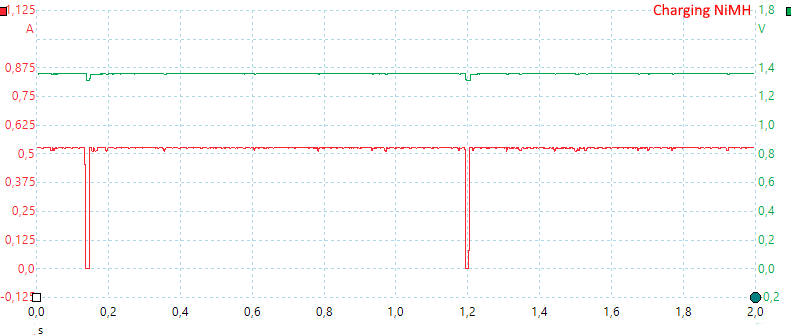
While charging it will turn current of to do a voltage check each second.
Testing with 2500 volt and 5000 volt between mains and low volt side, did not show any safety problems with the charger.
Conclusion
The charger is very good at charging LiIon, but that initial 0.5A pulse is problematic with very old cells or small cells (The charger will not charge this type of cell after the pulse check) and means I will not get full use of the 0.1A range, for this reason I will only rate it good.
The NiMH works perfectly for 2000mAh eneloop cells, but I am not impressed with the two high capacity cells.
Notes
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger
Read more about how I test USB power supplies and chargers

























































