Charger E-SYB E4



E-SYB is new in the charger market, here with a 4 slot charger that can handle LiIon and NiMH and has multiple currents making it possible to charge a wide range battery sizes.




The charger comes in a cardboard box with some specifications on it.

In the box is the charger, a power supply, a manual, a warranty card and a E-SYB sticker.

The charger is powered from 9 volt, i.e. no support for car adapters. There is also usb output and the charger can works as a power bank.

The charger has a display with data for all slots and one button for each slot.
A press on the button will show the detail slot view for a short time and at the start of a charge it is also possible to change charge current for LiIon.
It support a bluetooth link to a phone, but the application cannot be fetched from Googles store.

Here is the normal lcd image.
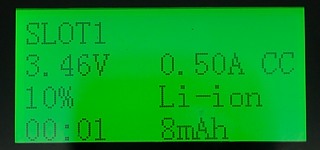
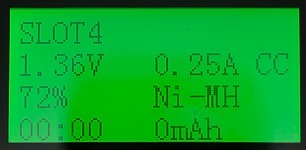
Pressing on the slot button more details about that battery will be shown for a short time.


The slots are the usual slider construction and works very good.
The can handle batteries from 29mm to 71mm, this will handle just about any cell.
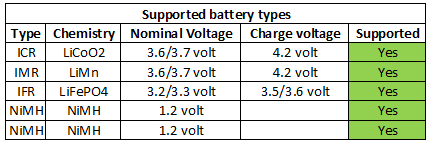
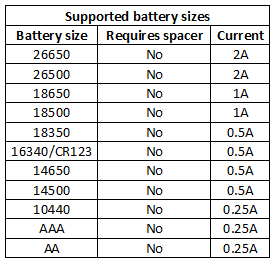









The charger can handle 71 mm long batteries including flat top cells.
Current is a bit to high for 10440 cells.
Measurements
- Power consumption when idle is 0.36 watt
- Current draw from LiIon battery is 10mA when power is off
- Current draw from NiMH battery is 1.6mA when power is off
- Current draw from LiIon battery is 4.4mA when power is on
- When voltage is below 0.6V charge will charge with 0.4mA and not detect a battery.
- Between 0.6V and 1.6V NiMH is assumed.
- Charger assumes LiIon at about 1.6V
- Voltmeter shows about 0.05V to high when charging.
- Charge will not restart if LiIon voltage drops.
- Power cycling and insertion of a battery will restart charger.
- Total charge current is limited to 4A, i.e. only two slots can charge at 2A
- LiIon current is default 0.5A, but can be selected from 0.25A, 0.5A, 1A, 2A
- NiMH current is fixed at 0.25A
4.2V charging (LiIon)
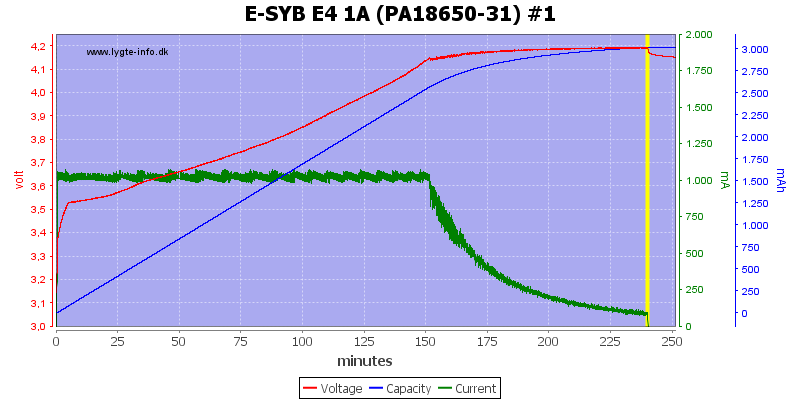
This looks like a nice CC/CV charge curve, termination current is around 80mA.
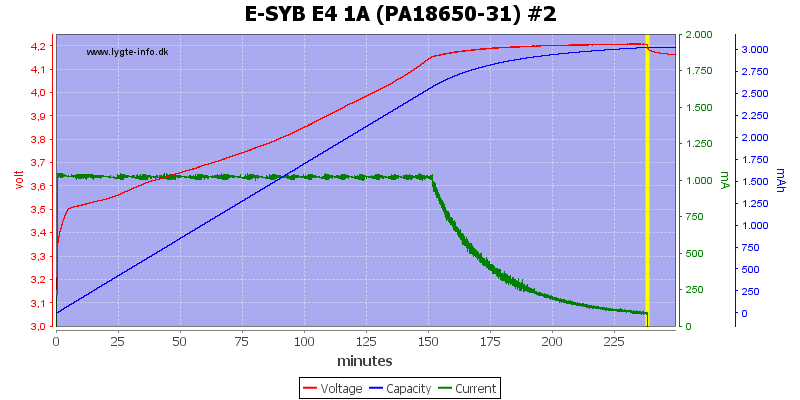
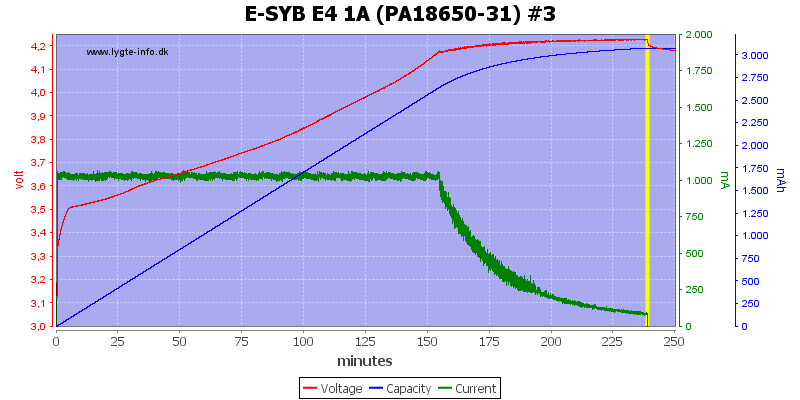
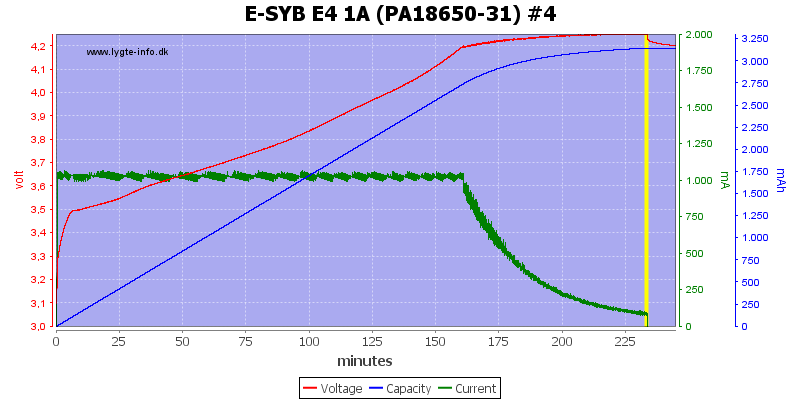
There is some voltage difference between the channels and #4 is a bit high.
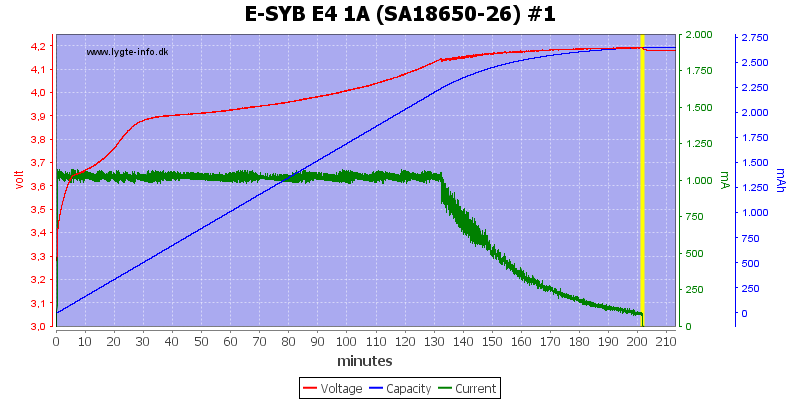

Other capacities means other charge times.
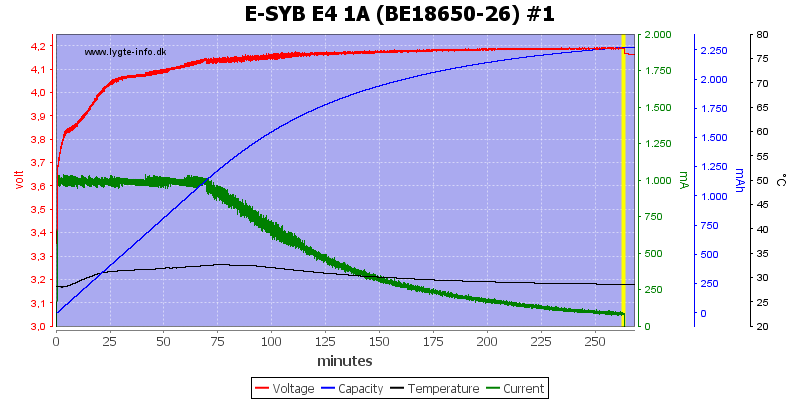
With 1A charge current the CV phase takes a long time (Charge time would not have been faster with lower current).
Note: This is related to the cell, all chargers will do this.
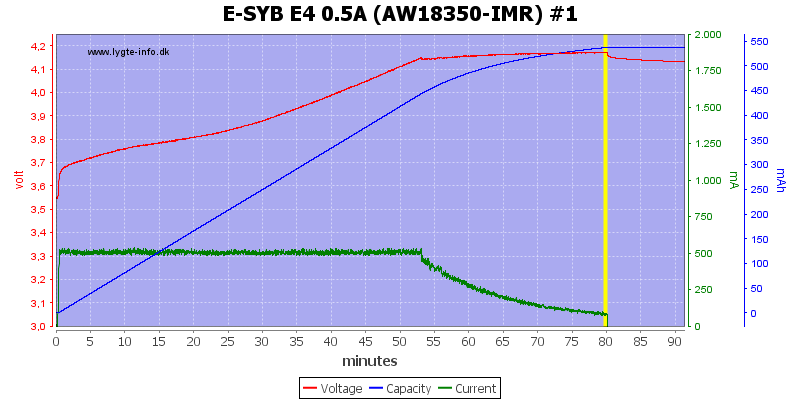
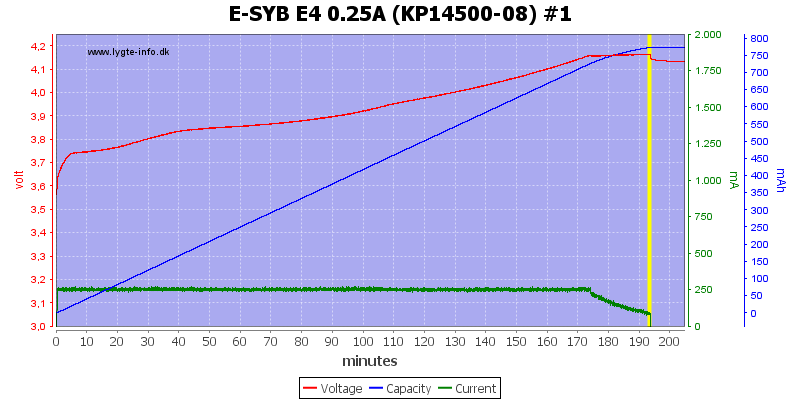
The small cells are also handled acceptable, but the charge voltage is lower. I used the lowest current setting for the 14500 as can be seen the termination current is not reduced.
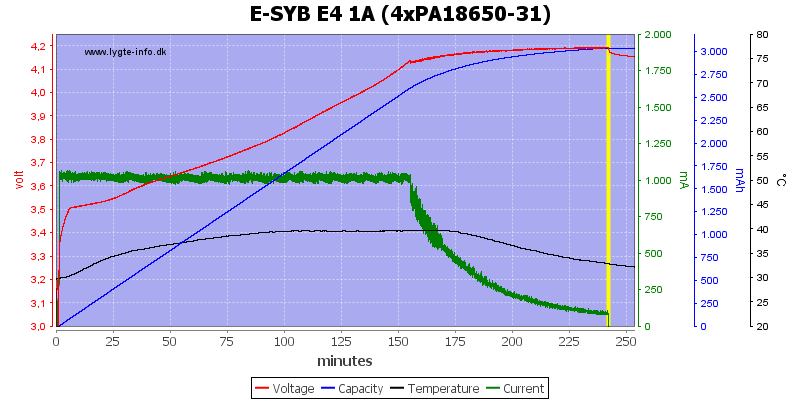
Four batteries can be charged with 1A.
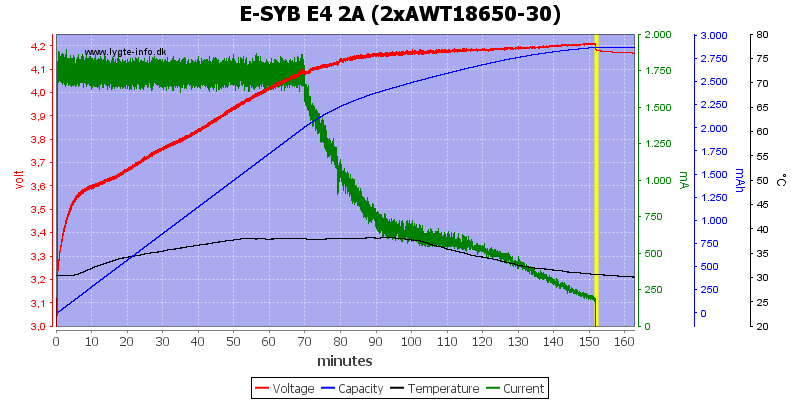
With two batteries the current can be increased to 2A.
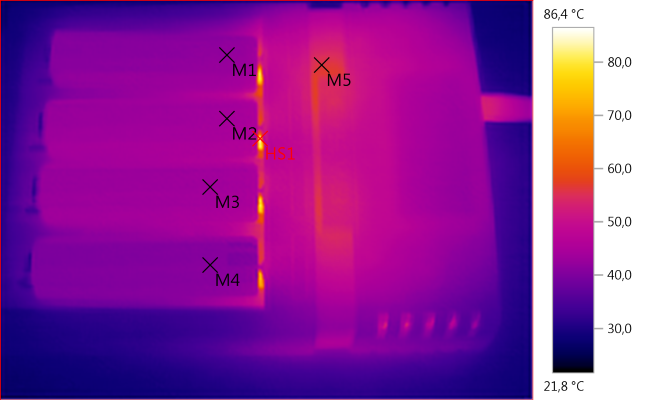
M1: 42,0°C, M2: 43,9°C, M3: 43,5°C, M4: 41,2°C, M5: 56,2°C, HS1: 86,4°C
Four batteries with 1A charging.
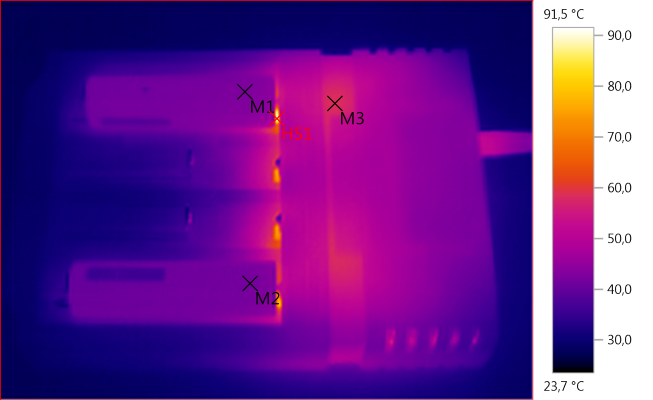
M1: 42,8°C, M2: 42,2°C, M3: 58,7°C, HS1: 91,5°C
Two batteries with 2A charging.
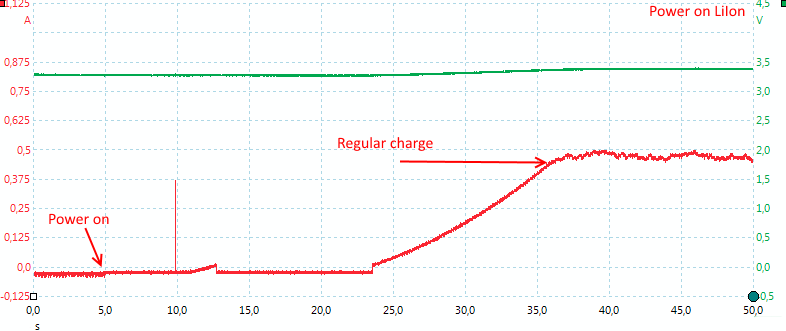
The charger is fairly slow to start, probably because it is waiting for user request to change current.
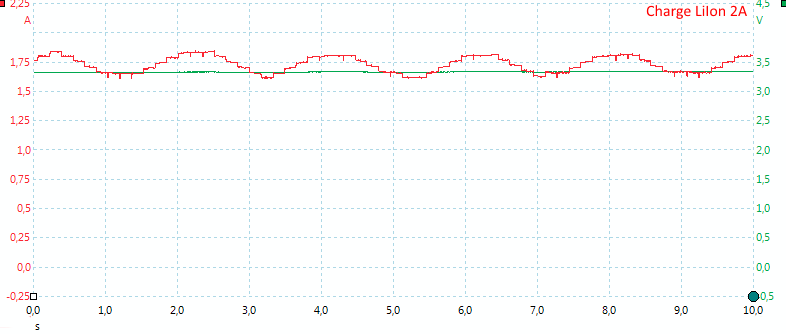
The manual said something about using pulse DC at 2A, the current varies a bit but is not pulsed. I tried with both one and two batteries.
3.6V charging (LiFePO4)
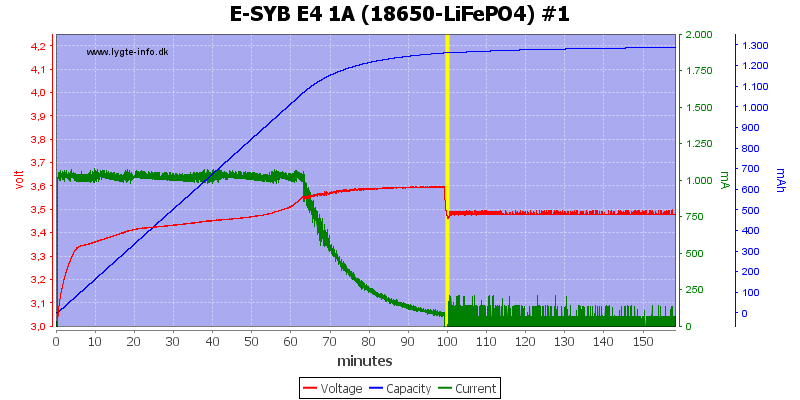
The charger charges to about 3.6V with a 80mA termination current, but it do not really turn the current fully off.
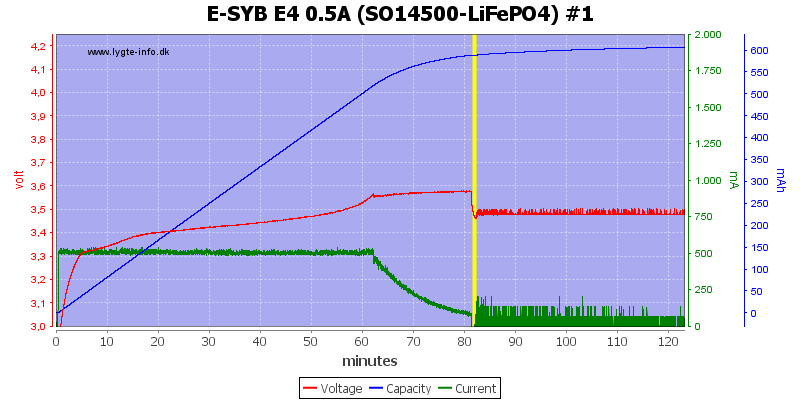
Charging NiMH
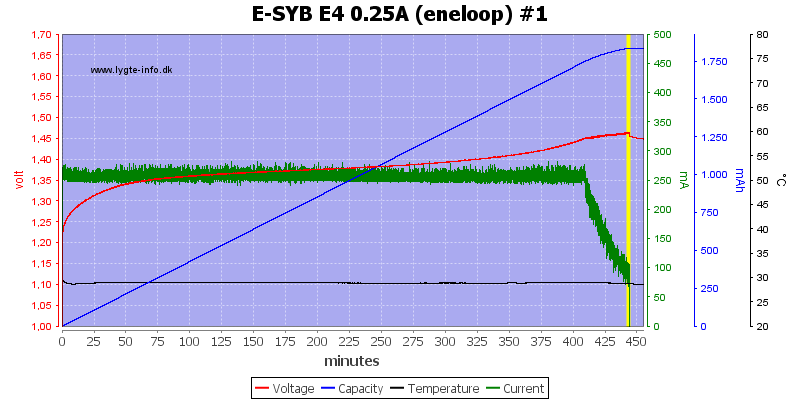
The charge current is very low, this prevents -dv/dt termination and the charger uses a voltage termination, but without a top-off charge.
This means the batteries are slightly under chargered, but looking at the capacity scale it cannot be much.
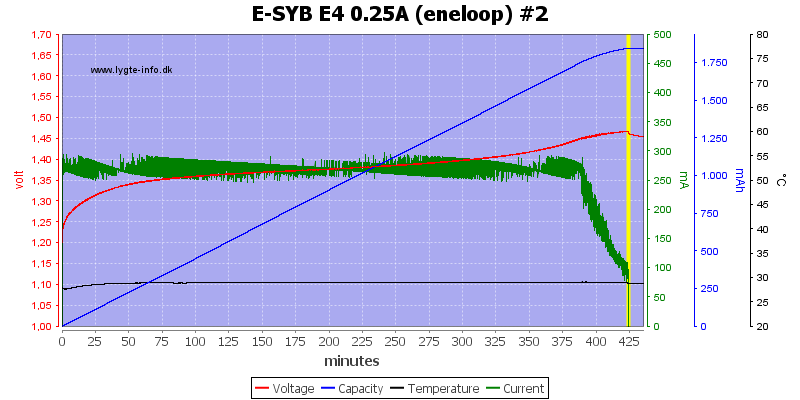
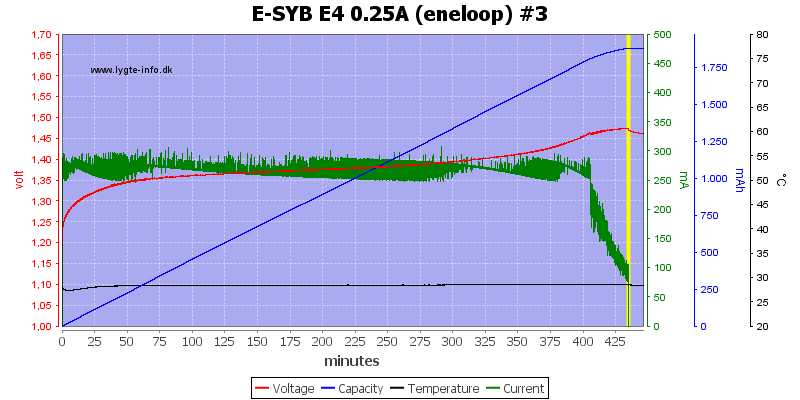
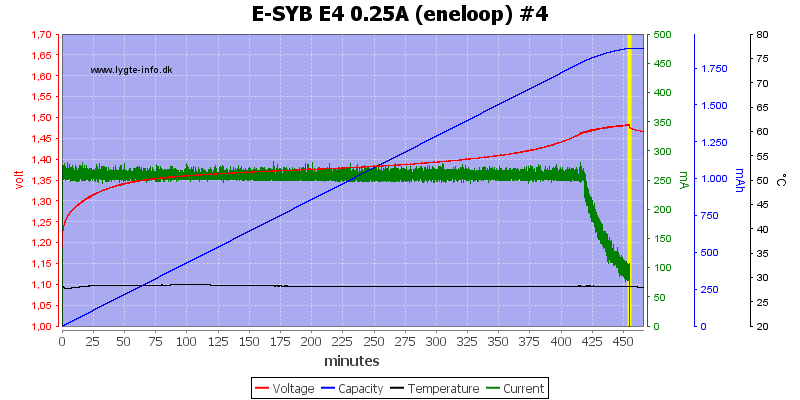
Again #4 has the highest voltage
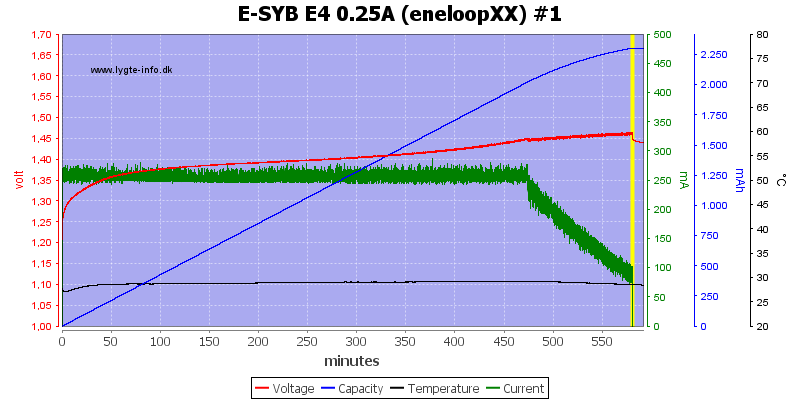
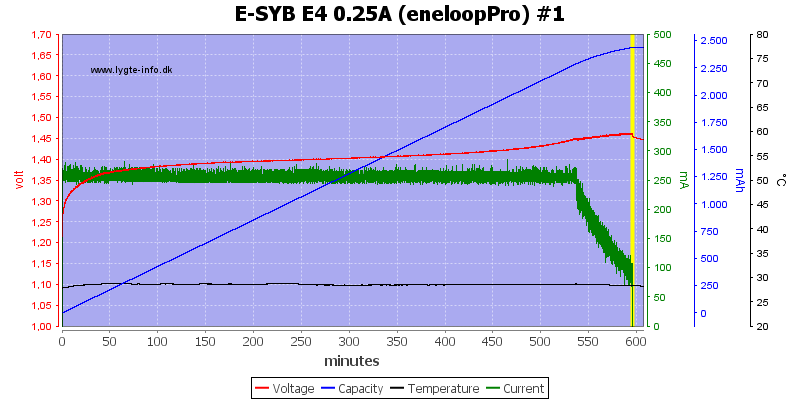
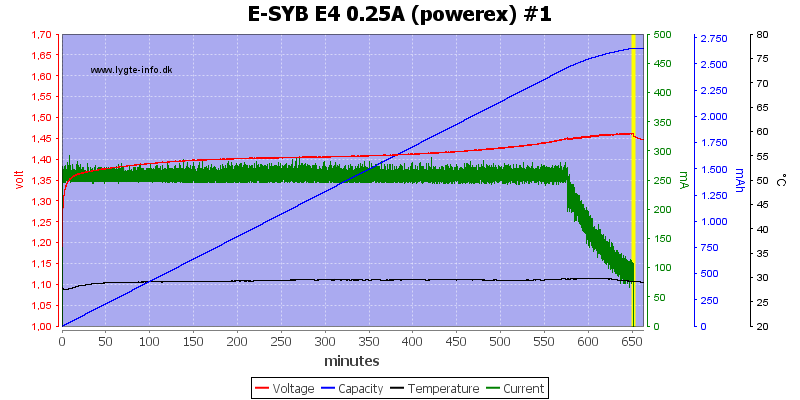
With the large capacity batteries it is the same, no temperature increase when finished.
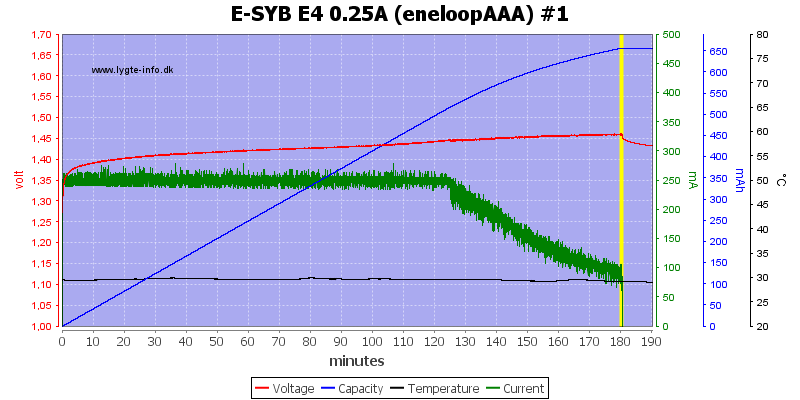
AAA is the same.
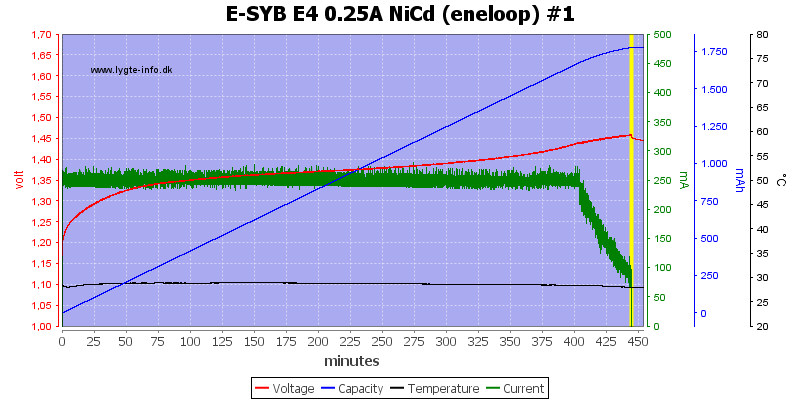
There is a NiCd setting on the charger, I wondered why because they can usual be charged on the NiMH setting without problems. Recording the curve above did not explain it, it looks like the NiMH charging.
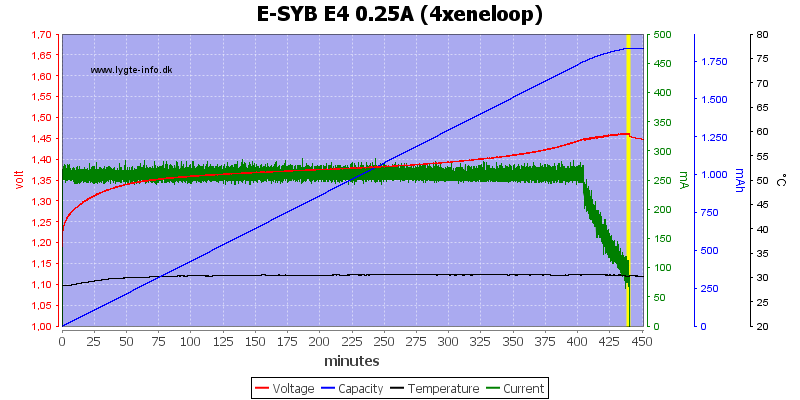
There is no problem charging four NiMH with the low charge rate.
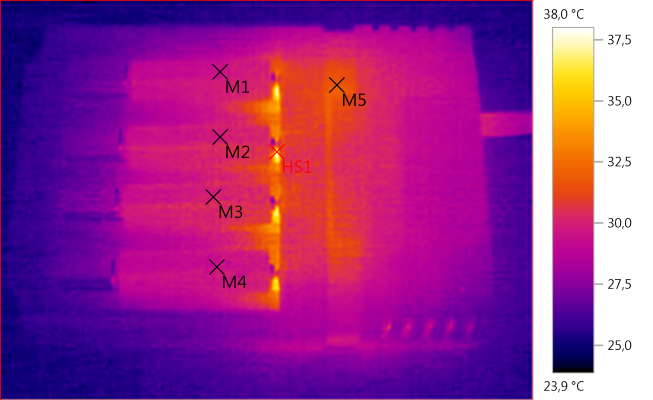
M1: 29,2°C, M2: 29,9°C, M3: 29,9°C, M4: 29,6°C, M5: 31,8°C, HS1: 38,0°C
The batteries stay very cool, this is not really surprising with the charge rate.
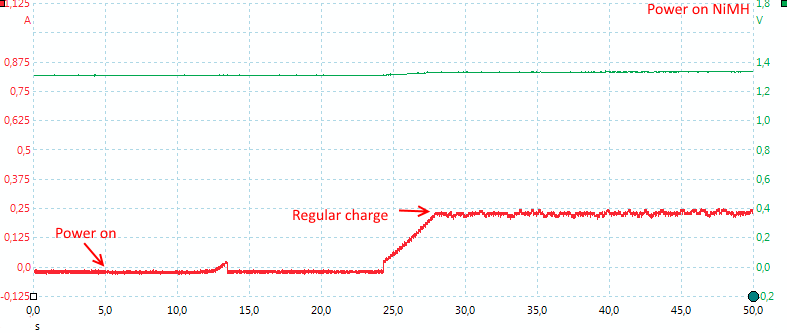
The charger is also slow to start with NiMH batteries. There is a possiblity to select NiCd batteries.
USB output
- Usb output is coded as Apple 2.1A (It is rated for 1A)
- Usb output requires at least two batteries to work.
- Current draw from LiIon battery is 10mA when idle
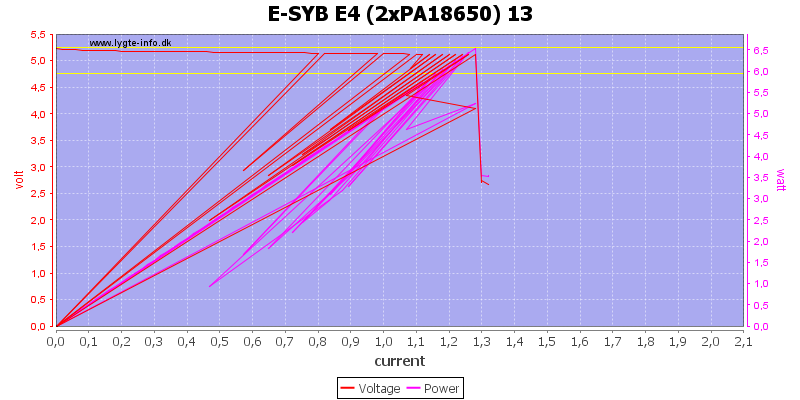
With two batteries the usb output current is fairly limited at about 0.7A
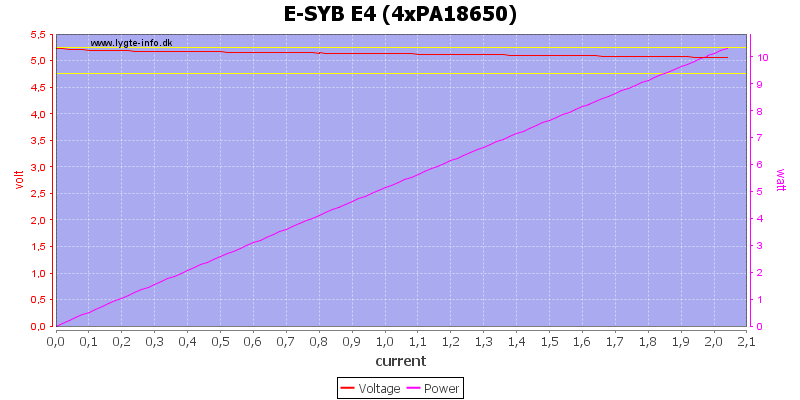
With four batteries I could draw above 2A, this nearly matches the 2.1A coding.
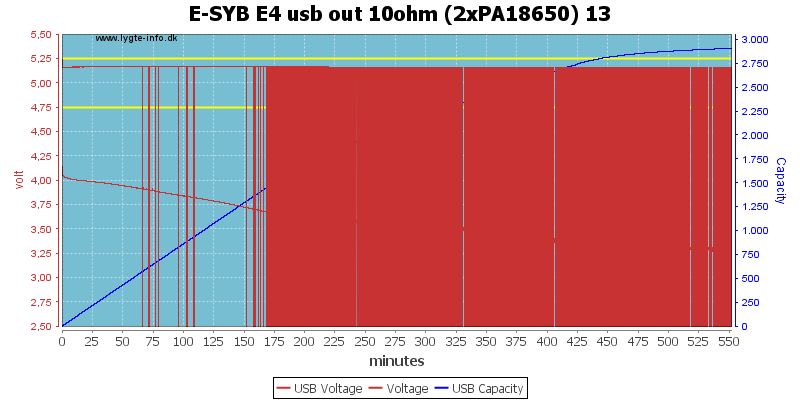
Drawing 0.5A on two batteries only worked for 1 hour.
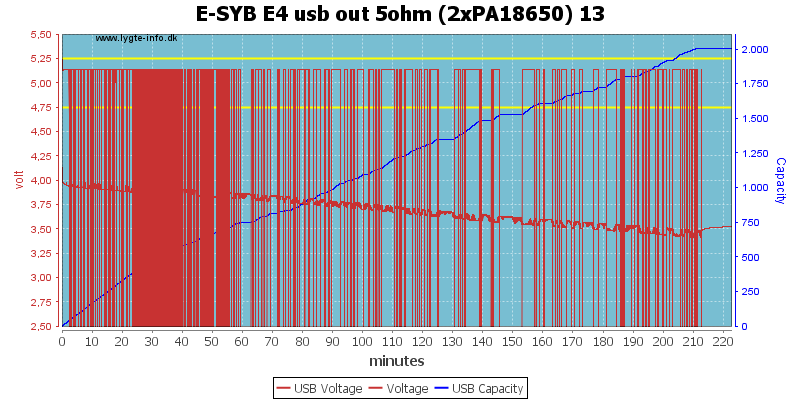
Drawing 1A did not work at all.
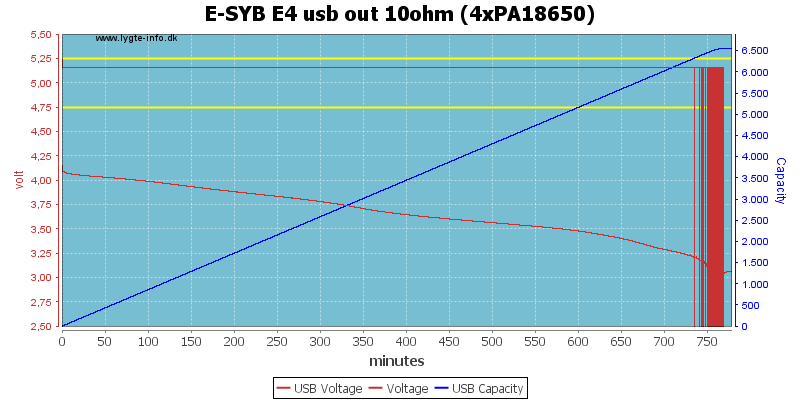
With four batteries it works much better and can run for 12 hours at 0.5A
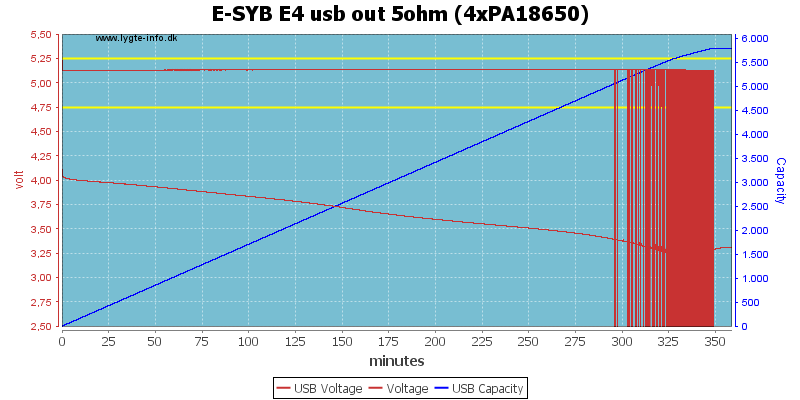
Increasing the load to 1A worked for less than 5 hours.
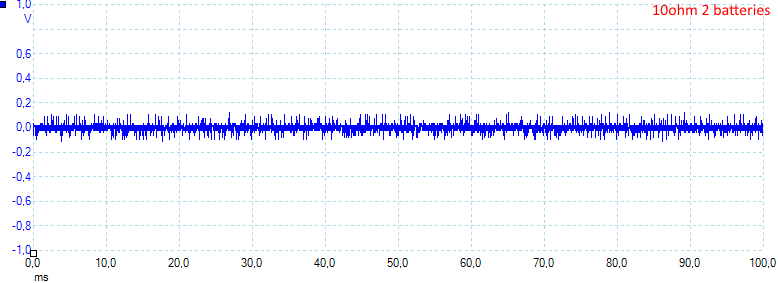
The noise is 26mV rms and 259mVpp
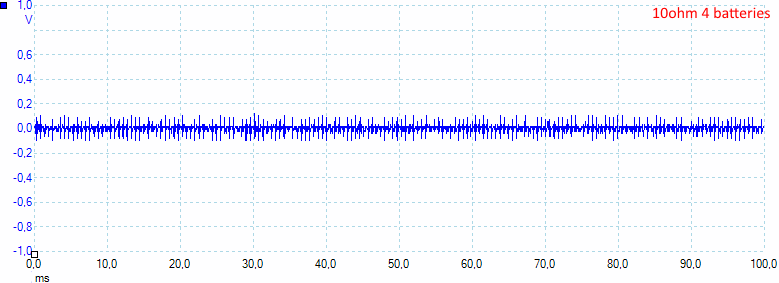
The noise is 25mV rms and 246mVpp
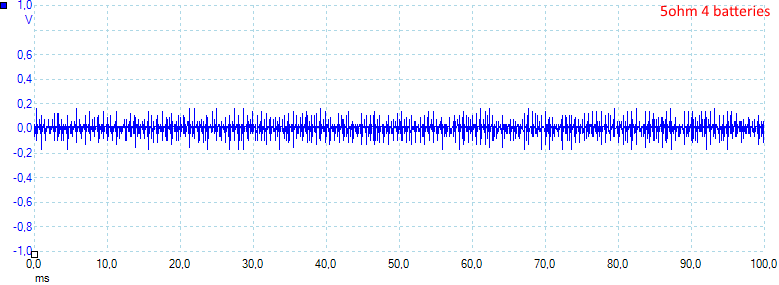
The noise is 43mV rms and 440mVpp.
Testing with 2830 volt and 4242 volt between mains and low volt side, did not show any safety problems.
Conclusion
LiIon charging looks fairly good, but I wonder about the voltage difference between channels and with changing charging current.
NiMH charging is also fairly good, but slow. It may stop a bit early, but not much and it stopped on all batteries. A top-off charge would have been nice.
Usb output is not very impressive, it cannot handle much load.
I did not test with the app. due to a couple of reasons: It was not available from Googles server and the app wants access to phone id, taking pictures, video, read and write data, network access. For an app. to control a charger that is a bit much.
Notes
The charger was supplied by Banggood for review.
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger
Read more about how I test USB power supplies and chargers































































