Charger Enova All-20



Enova has a long line of chargers with 2, 4 and 8 channels. This review is about one of the 2 channel chargers. This charger can handle 32650 batteries.

I got the charger without any box.

The charger has mains and 12 volt input. The mains input is universal voltage (100-240V 50/60Hz).

The front of the charger has a display and a label with specifications.

The display has a nice blue background light and shows both the voltage and the selected charge current. The bars at the top shows the charge state and will be animated when charging.



The battery slots are the usual construction and works acceptable, except for short batteries. At the minus end of the slot is a spring, when the slider touches this spring the charger will charge with 1A current, when not, the charge current is 0.5A. The activation point is at 65mm
It can handle batteries from 31mm to 71.5mm, but the first few mm is a bit doubtfull due to the low tension on the slider spring.
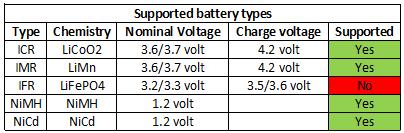
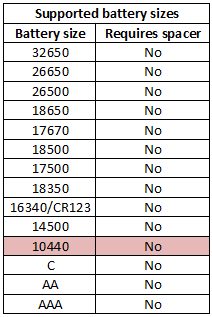










The charger can handle 71.5 mm long batteries including flat top cells.
The current is too high for small cells.
Measurements
- Below 0.3 volt the charger will not charge.
- Above 0.3 volt the charge will charge with full current.
- Above 2 volt charger assumes LiIon battery.
- Charger will not restart if voltage drops.
- Voltmeter freezes when charge is finished.
- Charge will restart charging after power loss, or battery insertion.
- Display readout is within 0.1 volt.
- Current is selected with the spring in the back
- When not connected to power it will drain about 0.2mA from a LiIon battery and 0.05mA from a NiMH battery.
- When charging is finished the charger will draw 0.2mA from the battery.
LiIon charge
I uses a 4.4 volt scale in these charts
%20%231.png)
The charger uses constant current and stops when the voltage, measured with current off, is above 4.2 volt. This means that the charge voltage is way above the allowed 4.25 volt.
%20%232.png)
The other channel works the same way.
%20%231.png)
With the 2600 mAh protected battery the over voltage protection is triggered.
%20%231.png)
With other capacities the charge time is different.
%20%231.png)
It looks like the charger voltage is 4.3 volt in this case. The cell gets charged, but I am not happy about the voltage.
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
Same with the two other cells.
.png)
The charger speed is not changed with two batteries and the over voltage is still present.
.png)
The charger needs about 900mA when powered from 12V
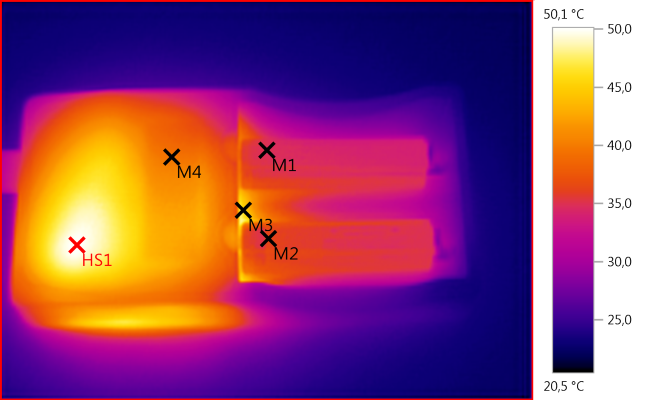
M1: 35,0°C, M2: 36,3°C, M3: 45,7°C, M4: 39,6°C, HS1: 50,1°C
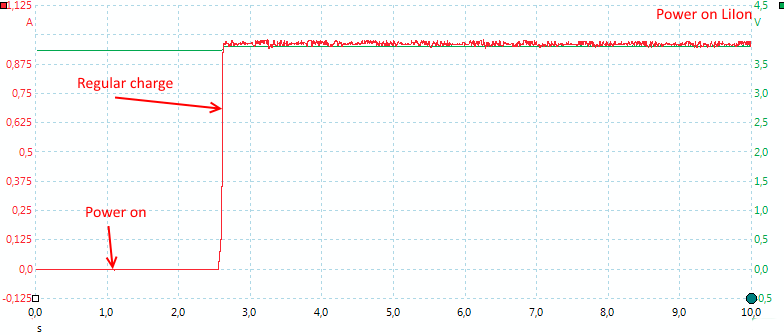
The charger starts in about 1.5 second.
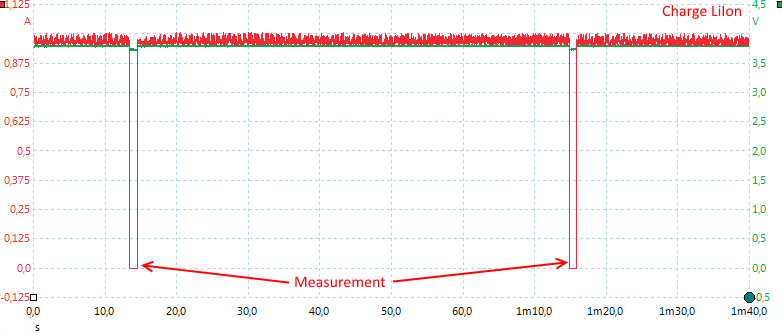
The charger turns the current off when it does a measurement to update the voltage reading.
This happens about once every minute.
NiMH charge
%20%231.png)
I believe it is a -dv/dt charging and as can be seen on the temperature track the cell is filled.
%20%232.png)
The other channel works the same way and here I did not get the inteference pattern, this makes it easier to see the -dv/dt.
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
Both EneloopXX and powerex is charged with a -dv/dt termination
%20%231.png)
Same with the AAA cell.
%20%231.png)
Using -dv/dt usual makes the charger slow to detect a full cell, here the charger needs 26 minutes.
.png)
No problem with two batteries.
.png)
For charging NiMH it needs about 300mA from a 12V power supply.
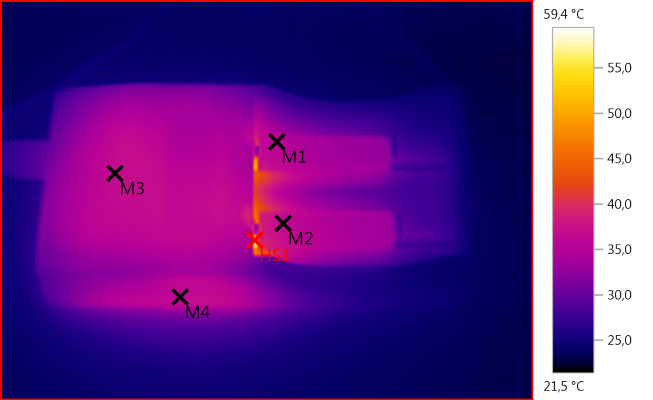
M1: 35,5°C, M2: 36,6°C, M3: 36,9°C, M4: 36,5°C, HS1: 59,4°C
With the lower charge current NiMH charging is cooler than LiIon charging.
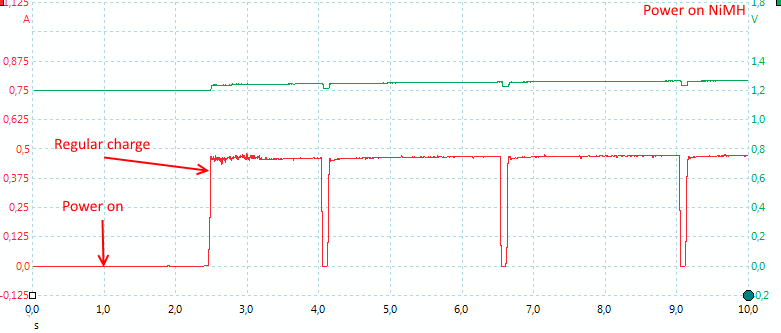
NiMH also starts in 1.5 seconds.
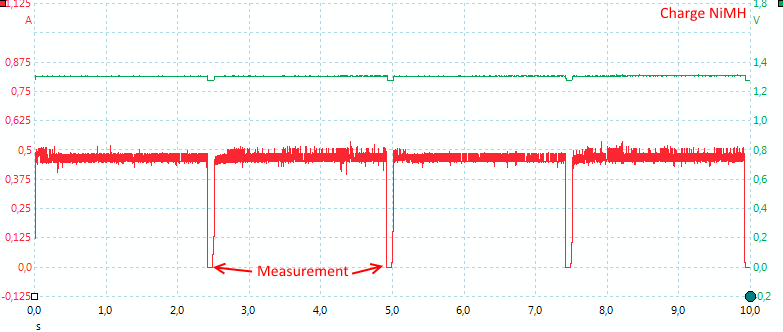
NiMH uses measuring pauses, but much more often than LiIon, but the voltage readout does not update faster.
LiIon & NiMH mixed charge
The charger supports charging a mix of NiMH and LiIon batteries at the same time.
.png)
The NiMH takes the same time to charge as above.
.png)
The LiIon finish a bit before the NiMH, due to the higher charge current.
Testing the supplied power supply with 2500 volt and 5000 volt between mains and low volt side, did not show any safety problems.
Conclusion
The charger has some good details. I like the status display with the voltage and selected charge current.
But the charger fails on LiIon charging with a peak voltage above 4.3 volt. The NiMH charging is good.
I cannot recommend this charger for LiIon.
Notes
The charger was supplied by Enova for a review.
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger






















%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
.png)
.png)



%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
.png)
.png)



.png)
.png)