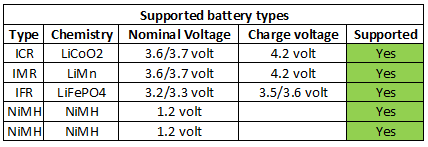
Charger Hexinyu HXY-H1



A single cell universal charger with voltage display and two currents that is powered from usb.




I got it in a cardboard box with specifications on it.

The pack contained the charger, a usb cable and a instruction sheet.

The micro usb power input connector.

The user interface is a display and a single button, the button is used to select chemistry and charge current.
Pressing the button wil show charge current, pressing again will change current. Holding the button down for 10 seconds will change chemistry.


On the first picture I have captured the power up display that shows all segments, the next is the voltage display.


During charging it will change between voltage, current and time.


The charger uses the classical slider construction, it will handle from 35mm to 70.5mm long batteries.
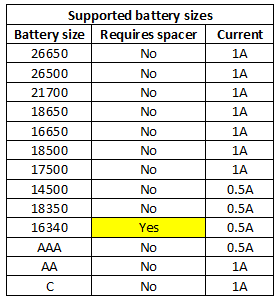









The slider is too loose for 16340 batteries.
Measurements on charger
- LiIon batteries will be discharged with up to 0.3mA when power is either on or off.
- NiMH batteries will be discharged with up to 0.1mA when power is off.
- Below 0.3 volt the charger will charge pulse current trying to start battery and report "Err"
- Below 2.2 volt the charger assumes NiMH batteries.
- At 2.2 volt and above the charger assumes LiIon and charge with 250mA.
- Above 3.2 volt the charger will use full charge current on LiIon
- Meter is within 0.02V measured with current off.
- Meter has a smoothing function, making voltage changes very slow with NiMH.
- Meter will not reduce reading, except if the battery is removed.
- Meter stops updating when battery is full.
- Idle current with display on is about 20mA and 7mA with display off.
- Charger will not restart if battery voltage drops.
- Charger will restart on battery insertion and power cycling.
Charging LiIon
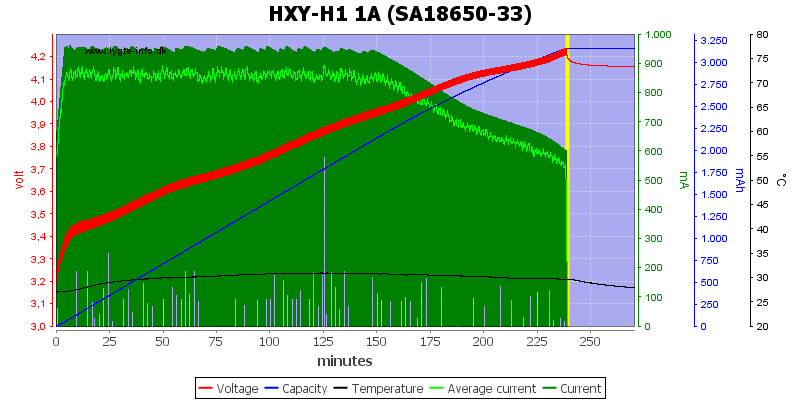
The charger uses some sort of simulate CC/CV voltage curve, but with way to high termination current. This can be seen on the voltage drop when the charger terminates, on newer batteries it is not that bad.
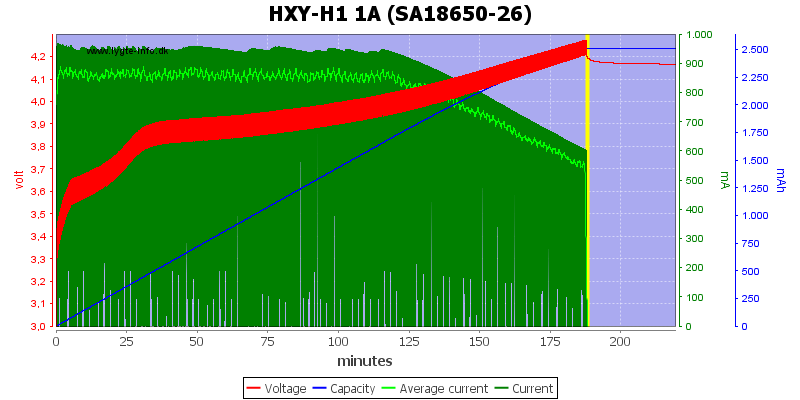
The battery is charged nearly full.
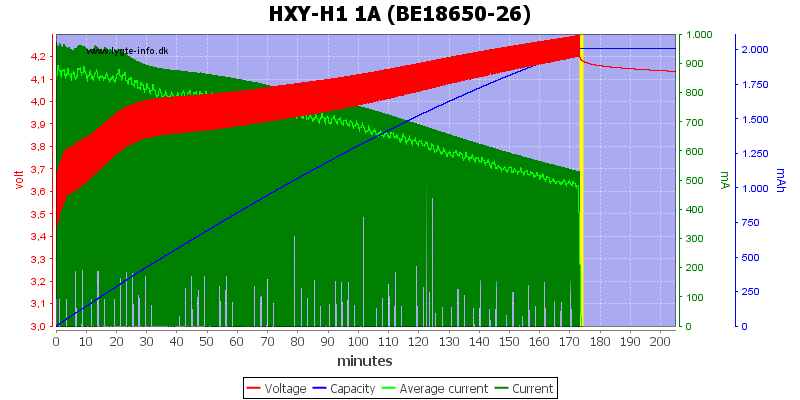
This is an older cell and the simulated CC/CV means voltage goes above 4.2V and when it terminates there is a fairly large voltage drop.
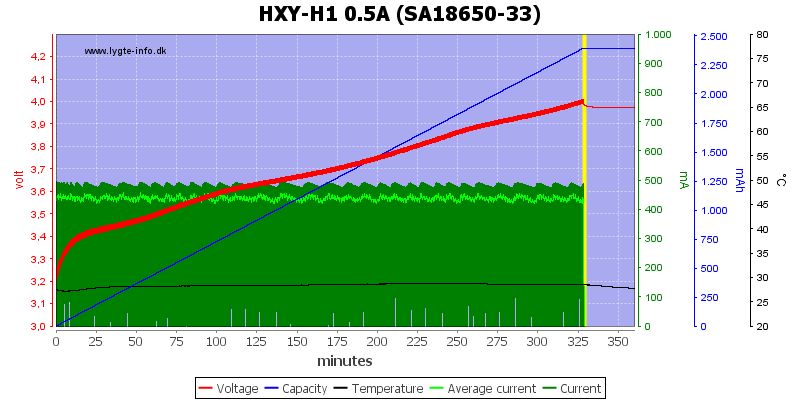
The charger terminates early on this cell, maybe duee to a timer.
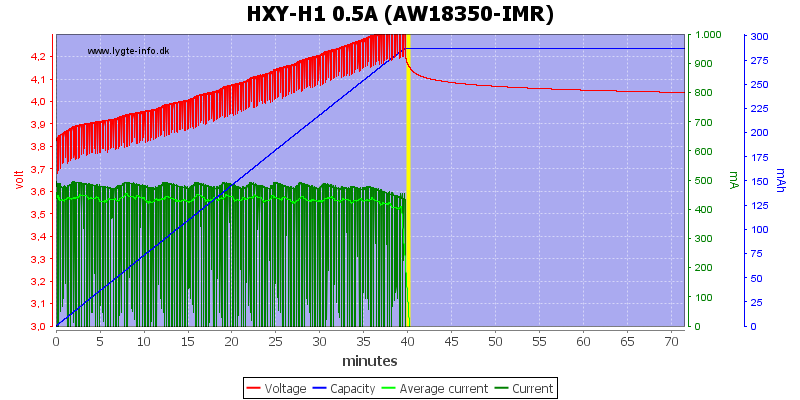
This old and worn out cell do not like this charge algorithm.
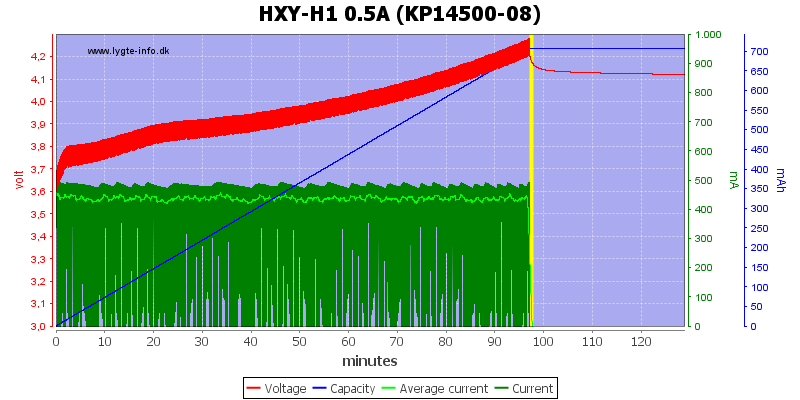
It works better with this cell, but the high termination current is a problem.
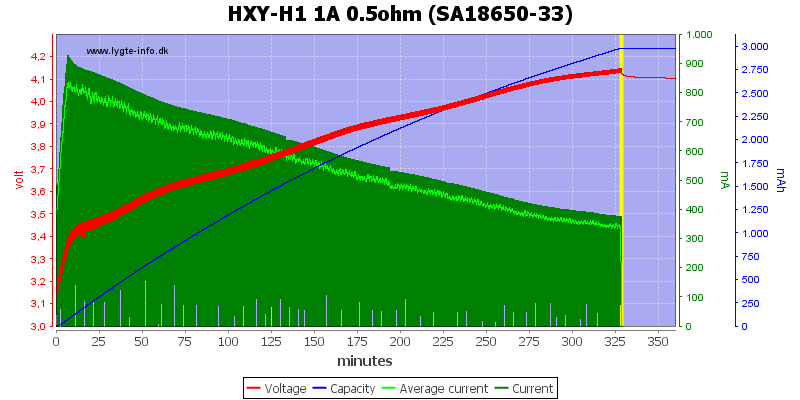
Adding a 0.5ohm resistor to simulate a long cable or weak charger did not work perfectly, the charger stops too early (Probably a timeout).
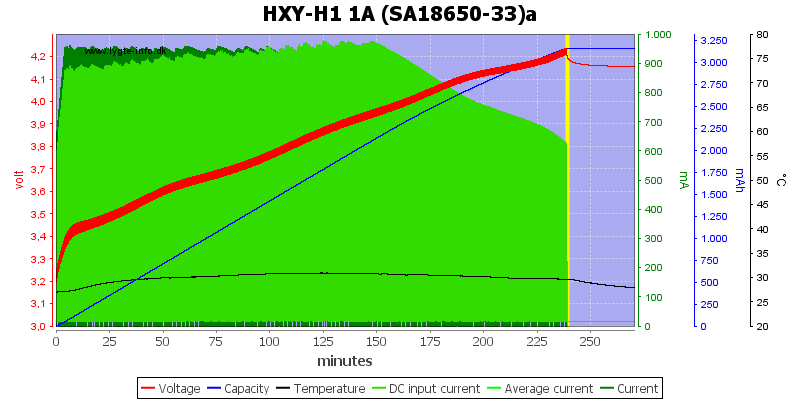
It uses up to about 1A from usb when charging.
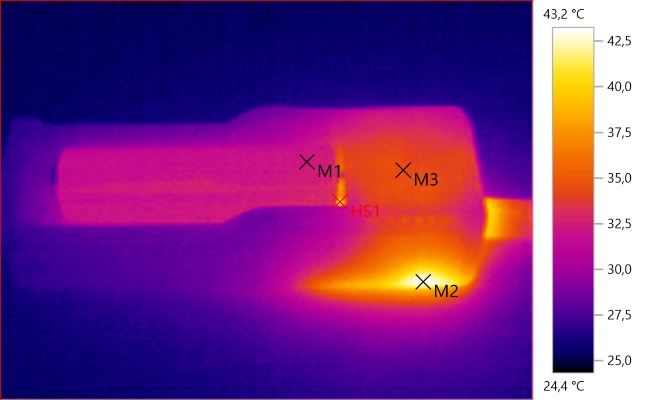
M1: 32,2°C, M2: 43,1°C, M3: 34,4°C, HS1: 43,2°C
The battery do not heat much in this charger.
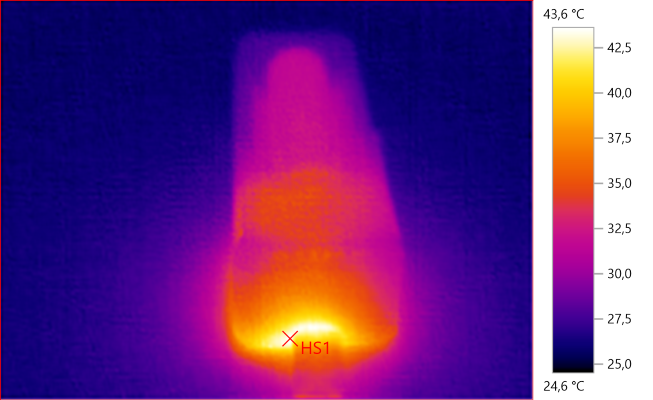
HS1: 43,6°C
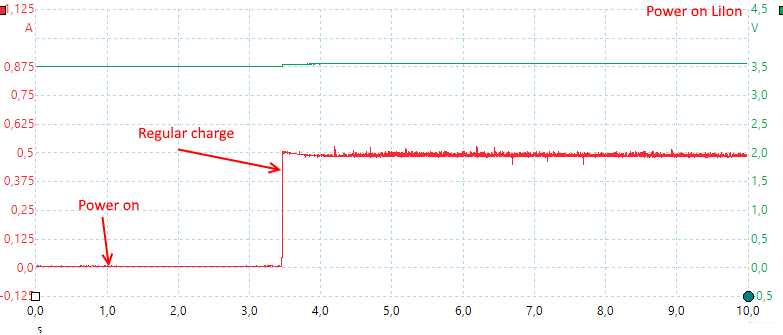
The charger needs about 2.5second to start.
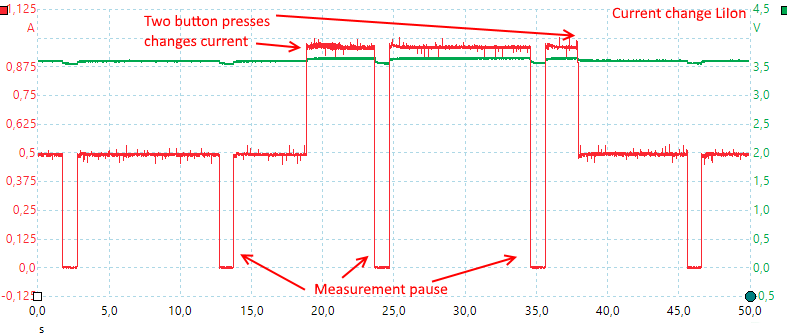
It pauses every 10 seconds to measure the voltage, it is acceptable for displaying voltage, but is not really a good way to control charging. The current can be changed at any time.
Charging LiFePO4
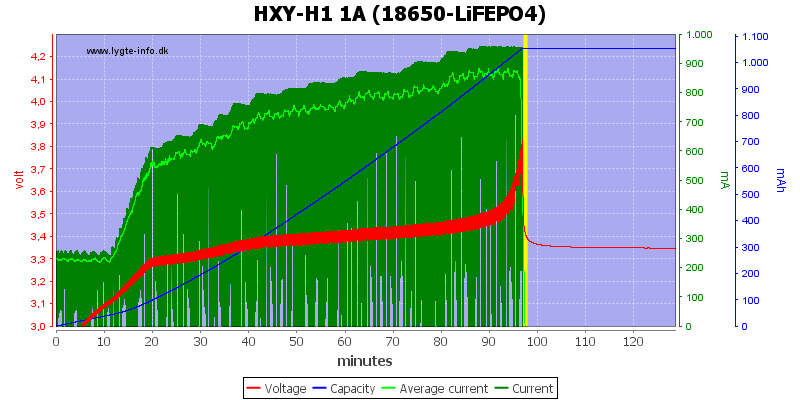
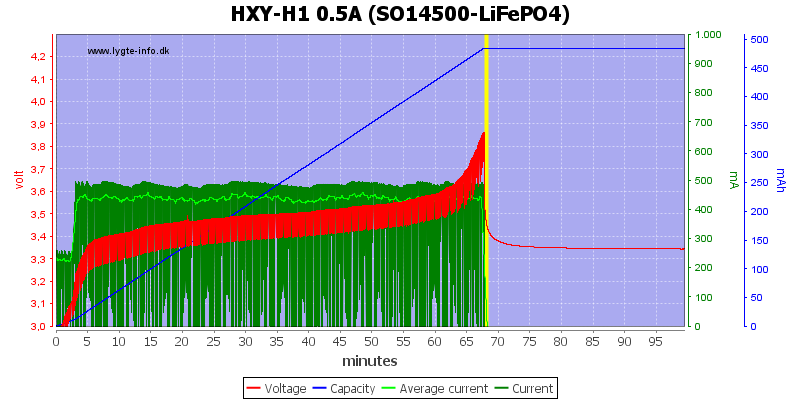
With LiFePO4 it stops without tapering the current.
Charging NiMH
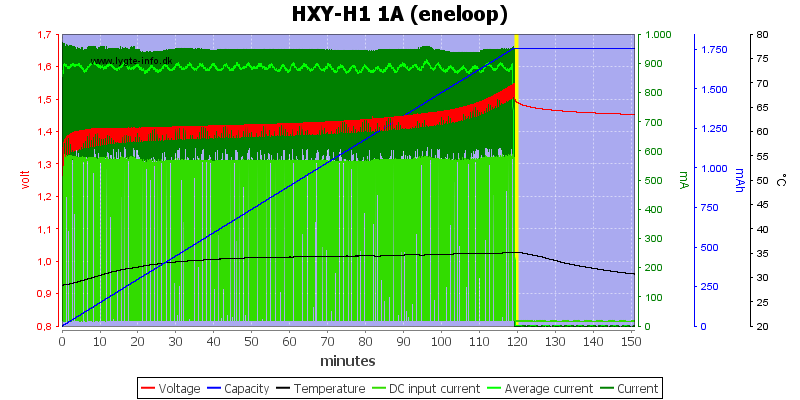
The charger stops on voltage and there is no trickle charger, this means the batteries will be slightly below full charge.
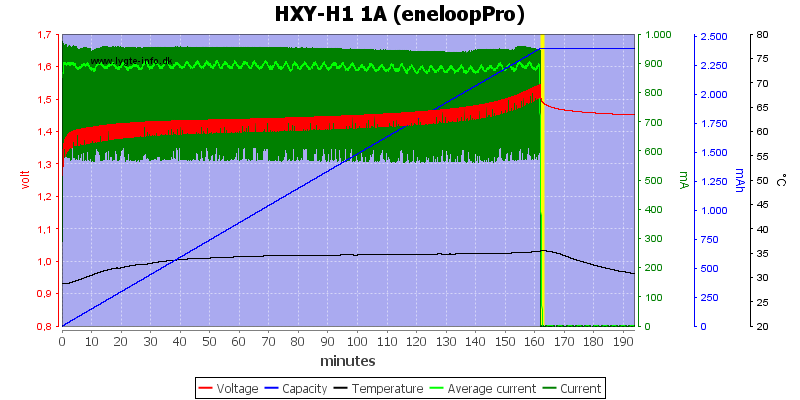
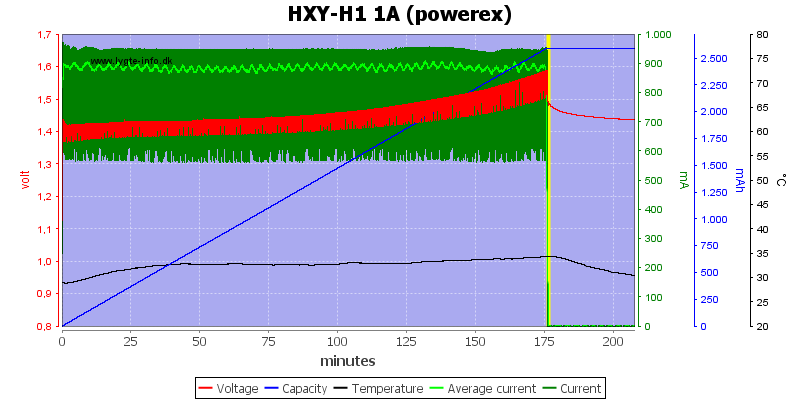
The two high capacity cells looks fine
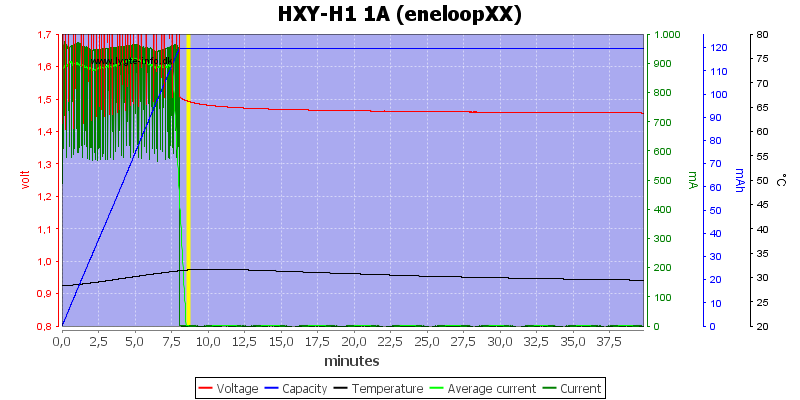
The eneloopXX has way to high internal resistance to be charged on this charger (The cell is basically worn down).
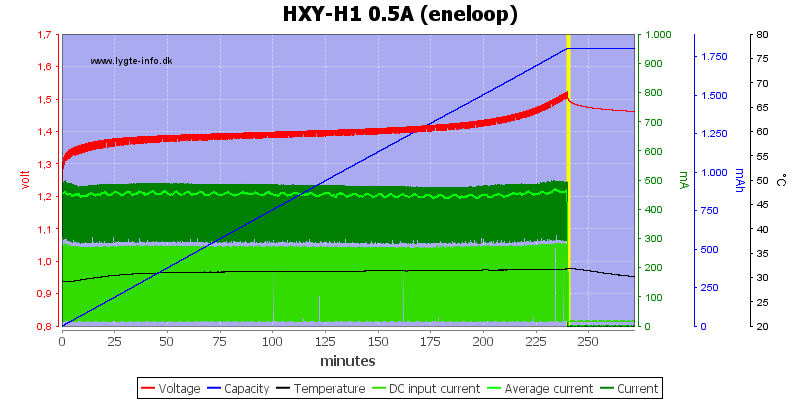
No problem terminating at 0.5A
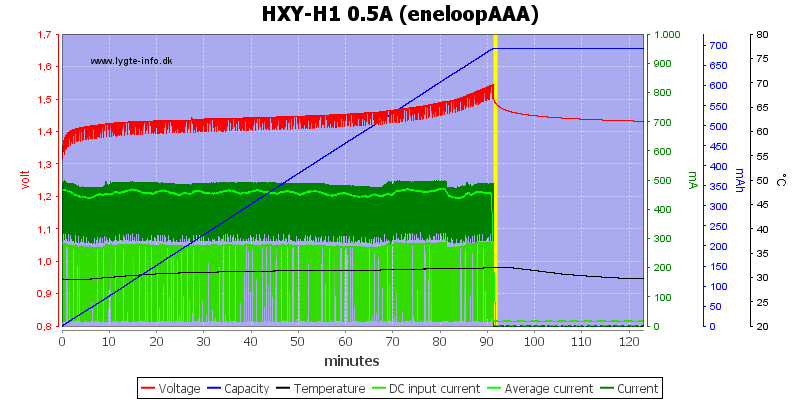
The AAA is also handled fine.
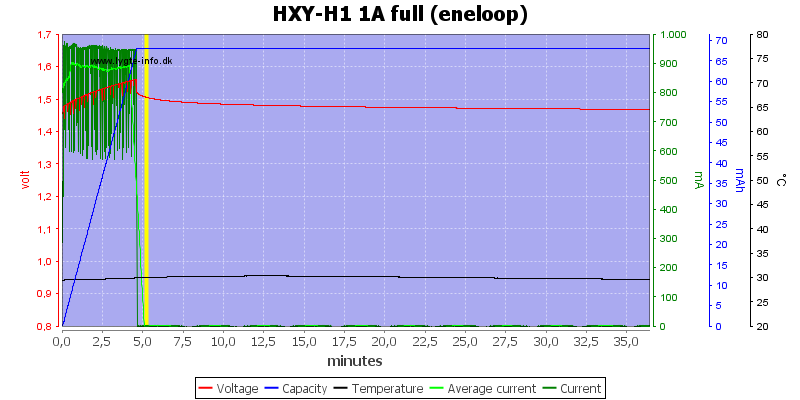
With voltage termination it is fairly fast to stop on a full cell, here it takes 5 minutes.
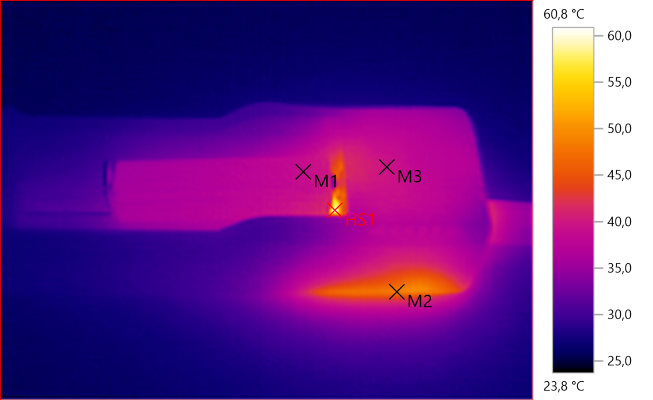
M1: 38,8°C, M2: 48,2°C, M3: 39,6°C, HS1: 60,8°C
With NiMH everything gets a bit warmer.

HS1: 46,9°C
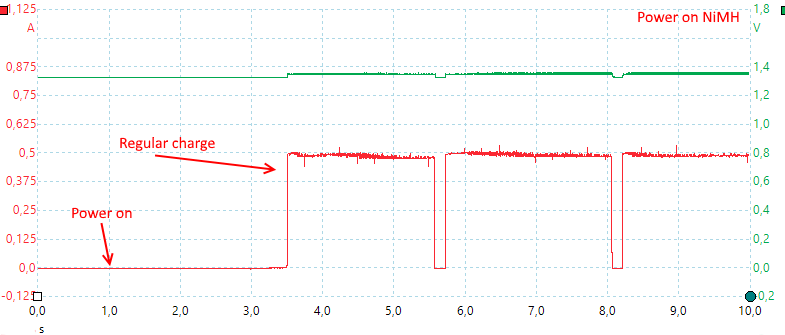
Again the charger needs 2.5 second to start, here the measuring pulses occur more often.
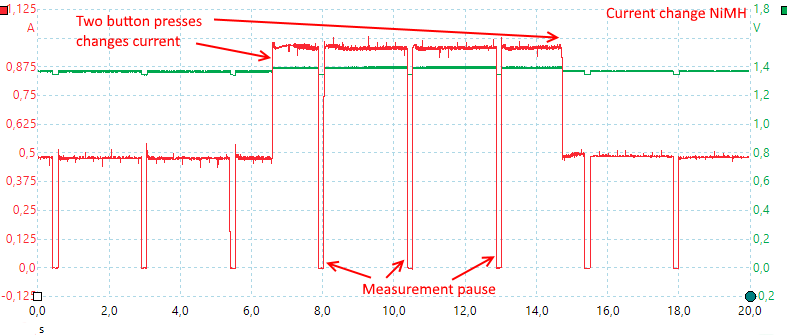
Voltage measurements are done more frequently when charging NiMH.
Conclusion
The LiIon charging is not with the recommended voltage and the batteries will get some over voltage, for older batteries the final charge will also be slightly low.
NiMH is charging to just about full but I am missing the top-off charge, this would have stuffed slightly more energy into the batteries.
I will rate the charger as acceptable.
Notes
The charger was supplied by Banggood for review.
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger



















































