Charger JetBeam i4 Pro



JetBeam and NiteCore worked together at one time, but split. They both wanted to continue the i4 charger line and this is the current JetBeam version of the i4.



The cardboard box lists lot of specifications, battery types and features.

The box contains the charger and a mains cable.

The charger has two power connectors, one for mains input (100-240VAC 50/60Hz) and one for 12 VDC input.

The charger has a blue led in the corner, that is on when power is on. For each battery there are 3 yellow leds to show the charge state or flash due to an error.


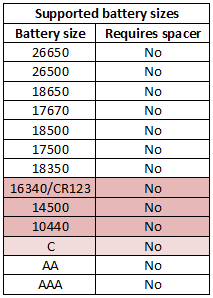
The slots uses the usual construction and works well. They can handle batteries from 30mm to 69.3 mm long.
That excludes some of the longest batteries, especially some protected 26650.









The charger can handle 69.3 mm long batteries, inclusive flat top cells.
With C and 26xxx batteries there are some restrictions due to battery size.
With smaller batteries the charge current can be too high, this will reduce the lifetime of the batteries.
Measurements
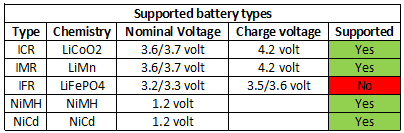
- At 0.8 volt the charger will assume NiMH and start charging.
- The charger will assume NiMH below 2 volt and LiIon above 2 volt.
- Charges with 0.2mA when LiIon battery is full.
- Will not restart if battery voltage drops.
- Power consumption when idle is 0.6 watt
- Discharges NiMH with 0.04mA when not connected to power
- Discharges LiIon with 0.25mA when not connected to power
- Slot #1 & #2 are paired and time shares a charging circuit
- Slot #3 & #4 are paired and time shares a charging circuit
- Time sharing is only active when charging, a full cell with not be part of it.
- Charge will restart charging after power loss or battery insertion.
LiIon charging
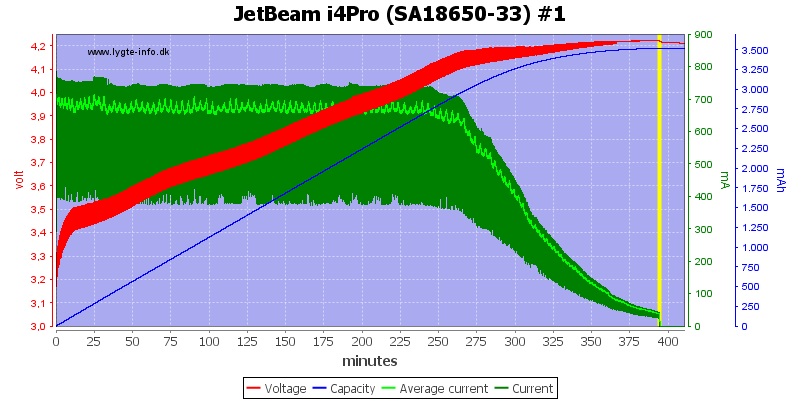
With a single cell the charge current is 700mA and the charger uses a CC/CV charge profile with a termination around 50mA.
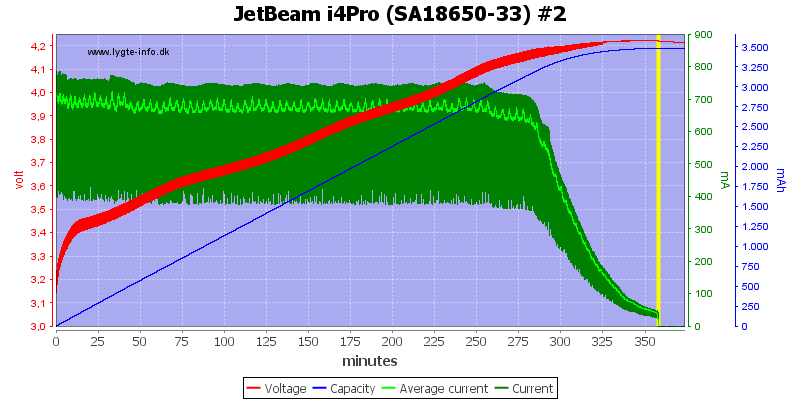
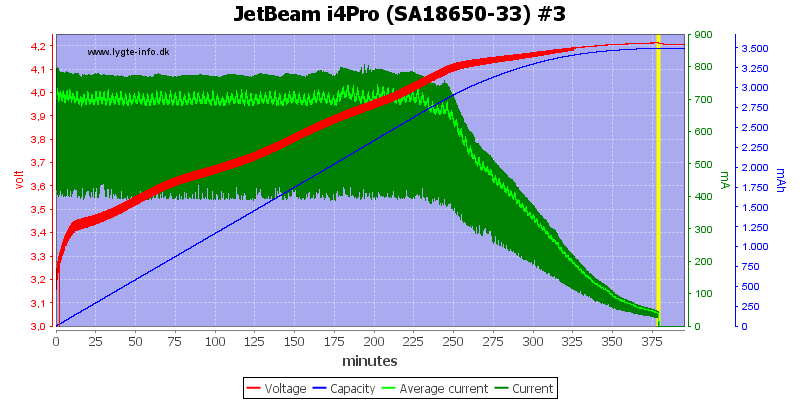
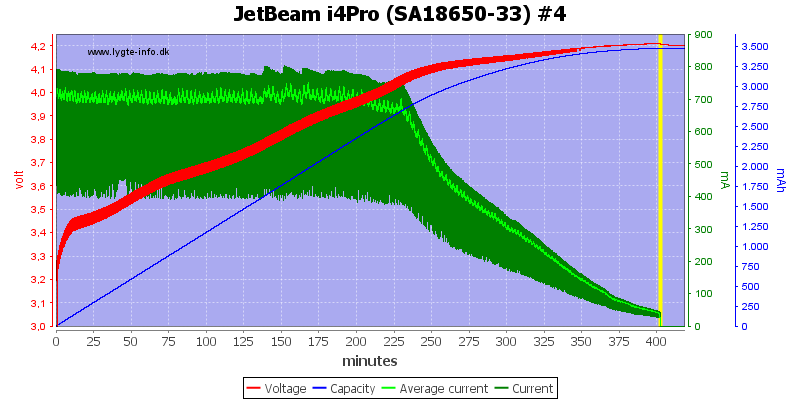
The other 3 slots looks the same.
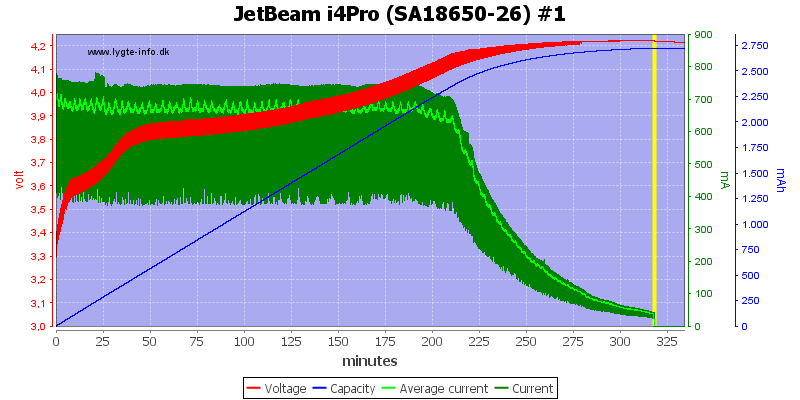
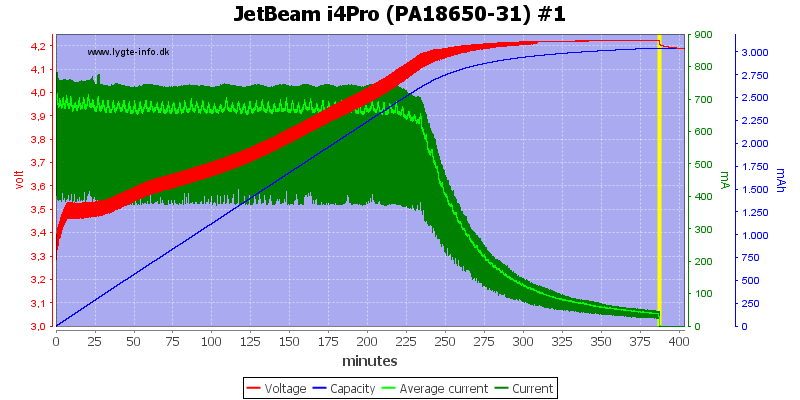
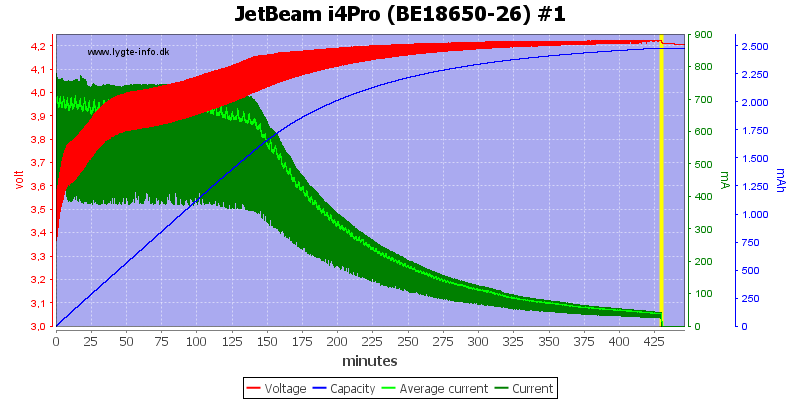
There is no surprices with different capacity or an old cell.
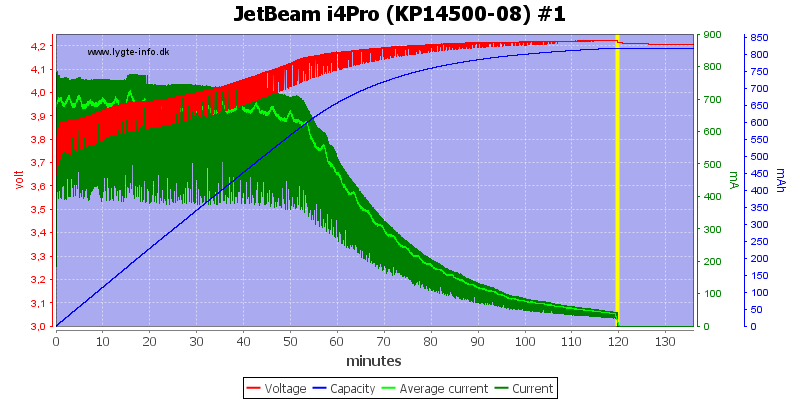
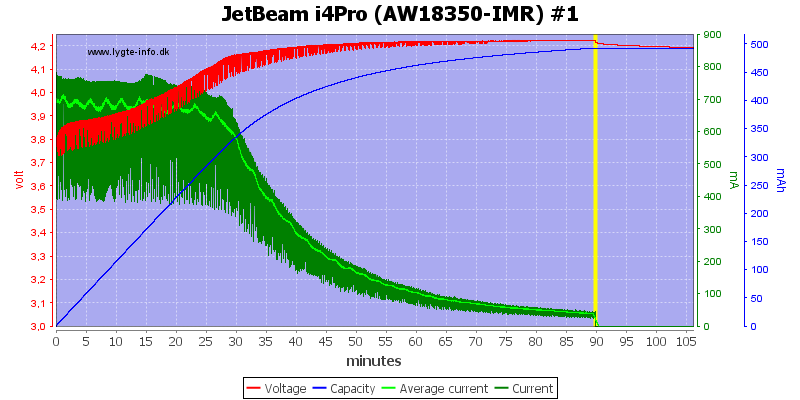
The small cells are handled the same way, but here the current is a bit high.
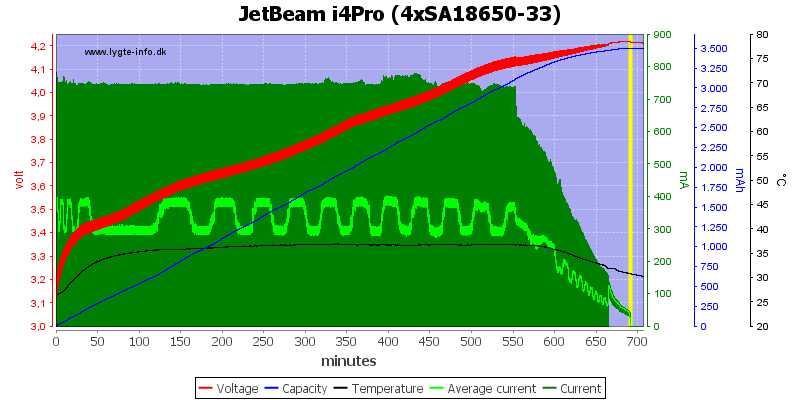
With four cells the charge current drops to 350mA, the charging works fine again.
Note: The jumping up and down on the average current is probably interference between my sample rate and the time sharing between slots. I do not believe it is changes in current.
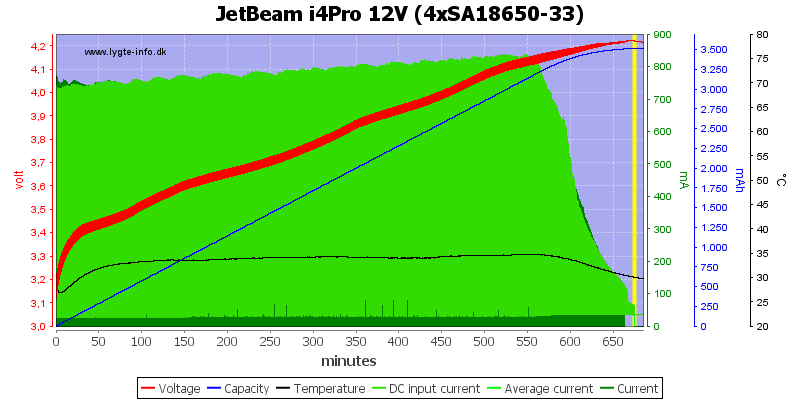
The 12V input must supply just below 0.9A.
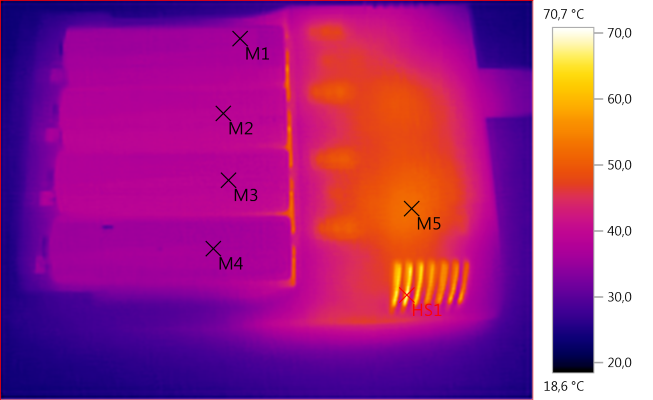
M1: 36,5°C, M2: 38,7°C, M3: 38,2°C, M4: 36,3°C, M5: 52,3°C, HS1: 70,7°C
Temperature is fine.
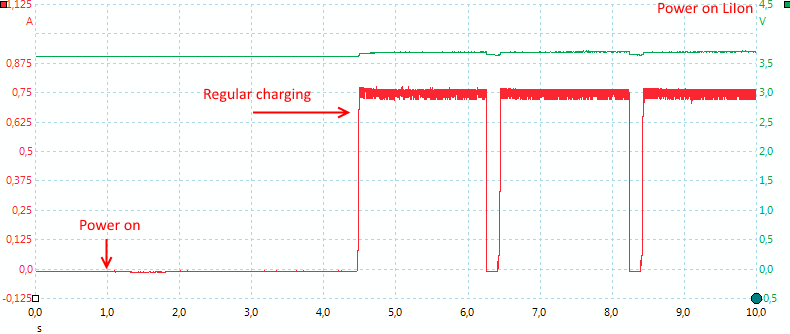
The charger needs about 3.5 second to initialize, before charging.
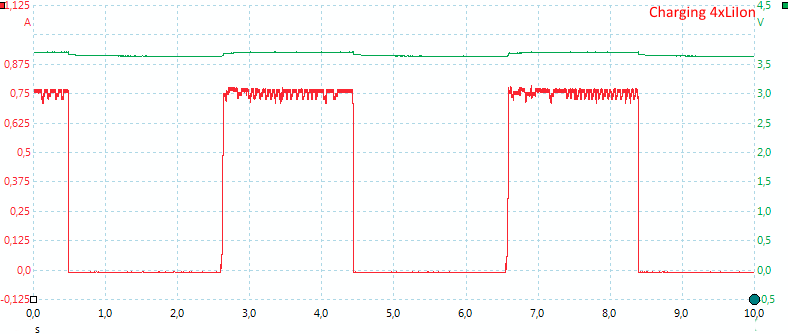
When two slots are time sharing they only get about 50% of the time each, this means the average current will be about 50% or 0.375A.
NiMH charging
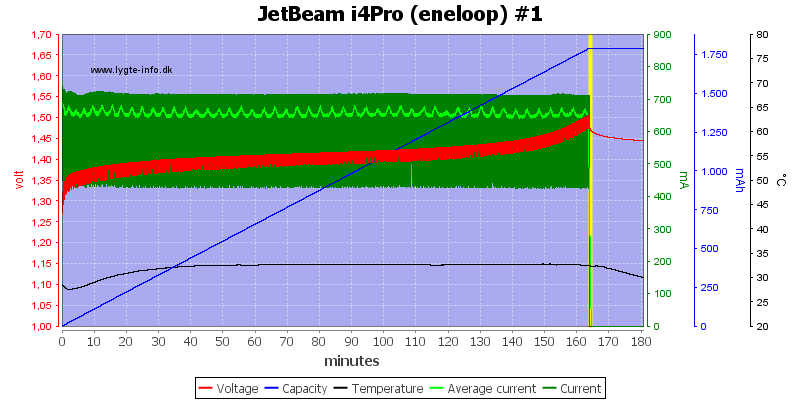
NiMH charging uses voltage termination, this means it stops a bit before the battery is full and without any top-off or trickle charge the battery will not be completely filled.
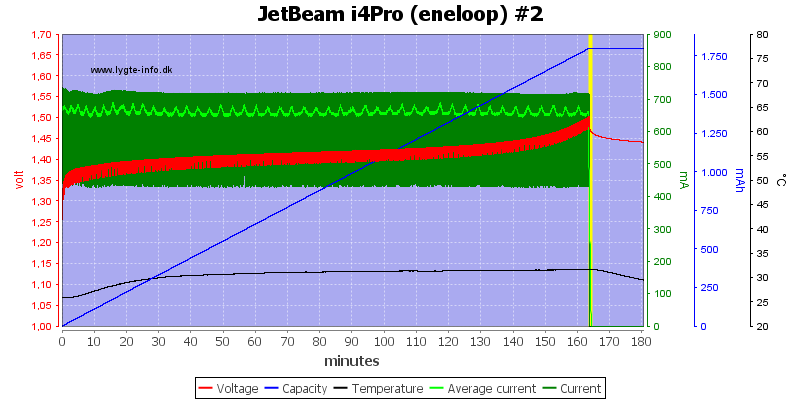
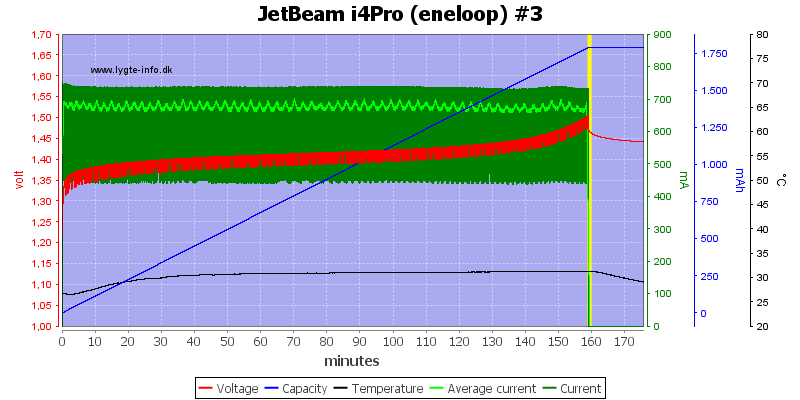
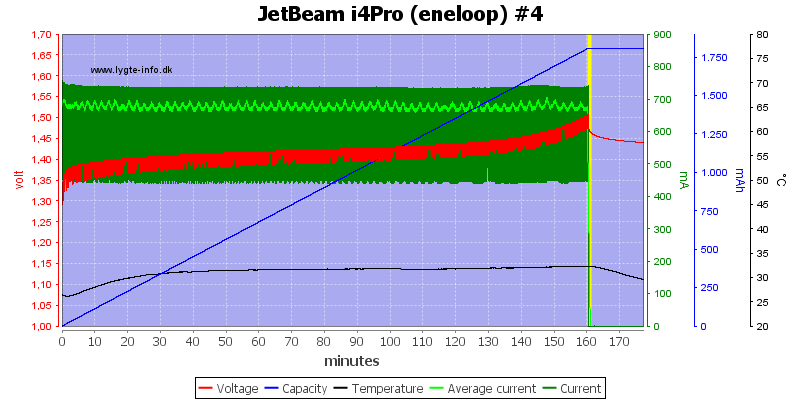
The 3 other slots works the same way.
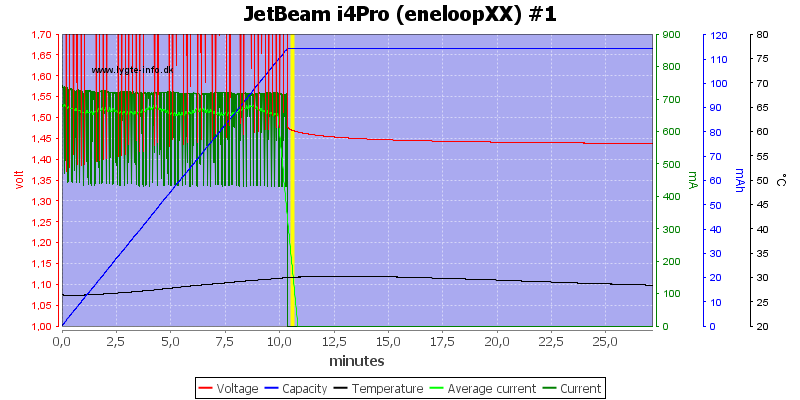
The charge gave up on this old cell, not really surprising.
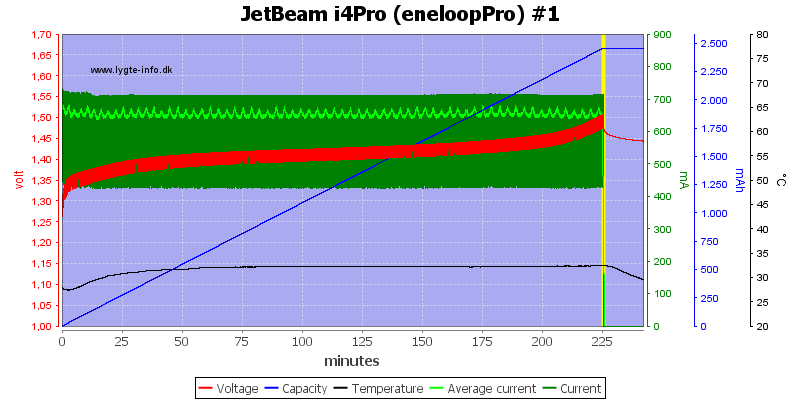
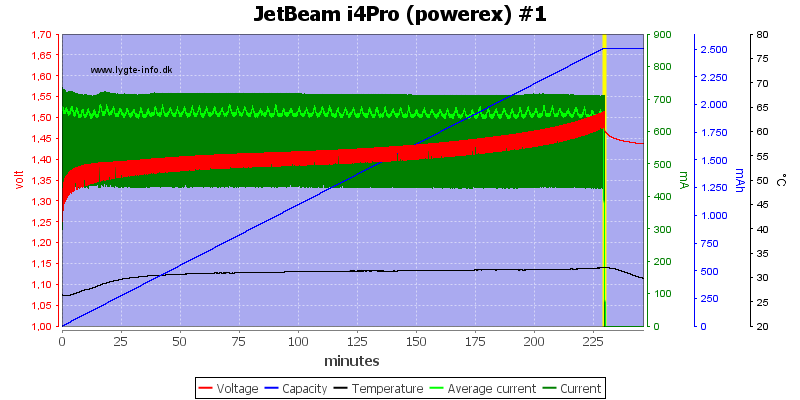
The two other high capacity cell is handled fine
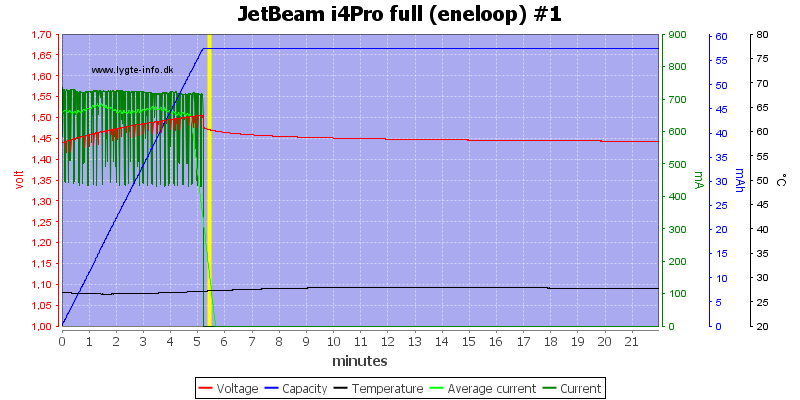
A full cell is detected fairly fast due to the voltage termination.
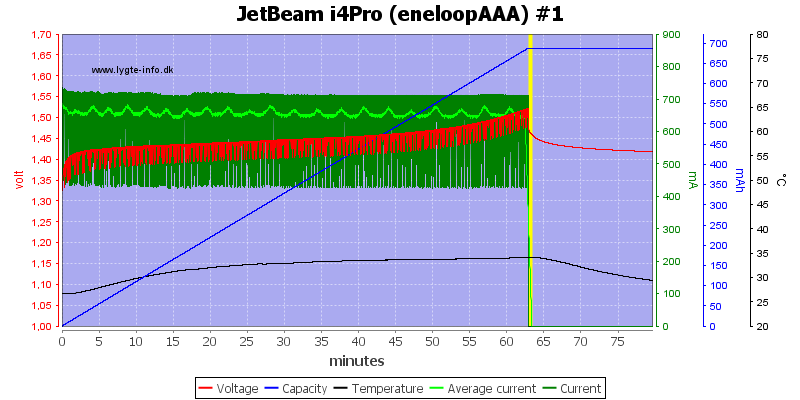
AAA is handled just as fine.
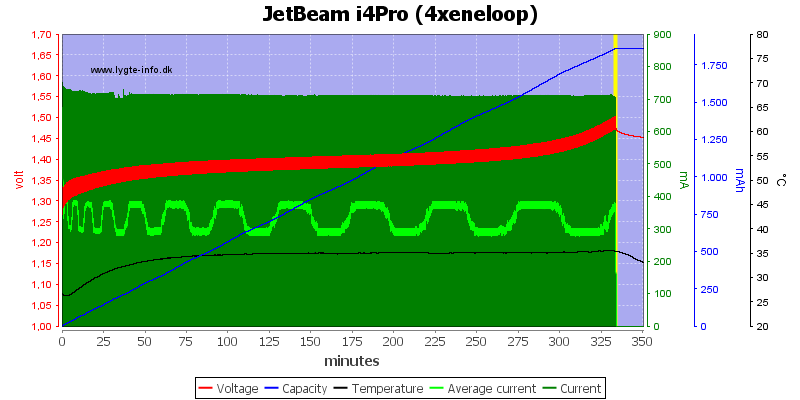
With four cells the charge current drops to 350mA, the charging works fine and voltage termination works fine at this low current.
Note: The jumping up and down on the average current is probably interference between my sample rate and the time sharing between slots. I do not believe it is changes in current.
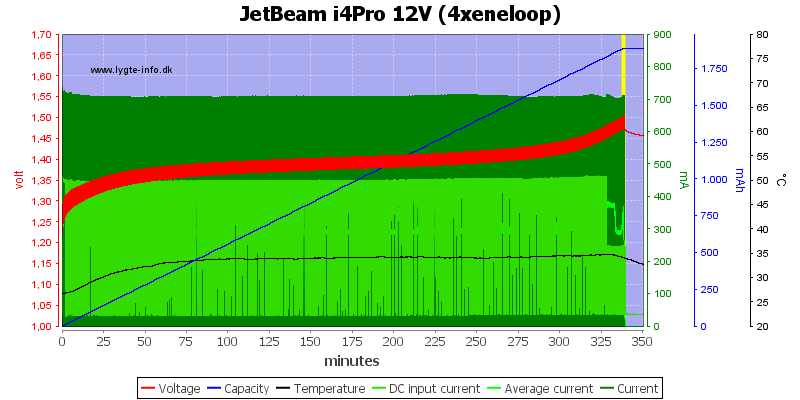
The charger needs a bit below 500mA on 12V
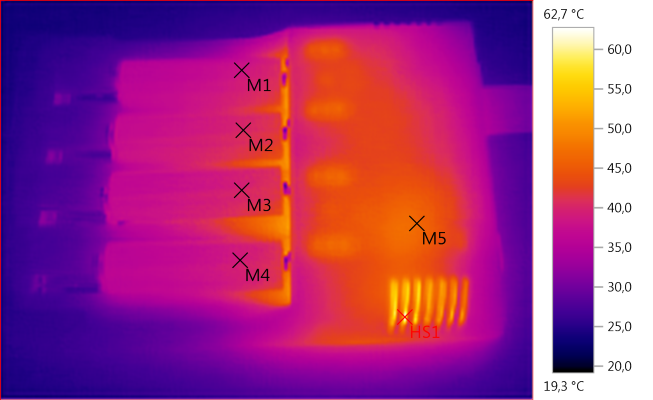
M1: 38,5°C, M2: 40,0°C, M3: 40,3°C, M4: 39,1°C, M5: 46,6°C, HS1: 62,7°C
Temperature is acceptable.
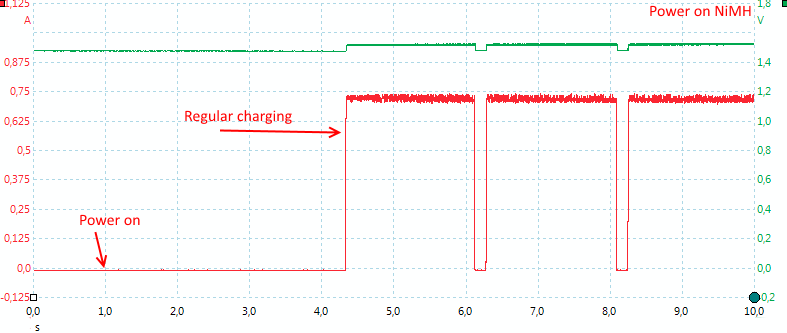
NiMH also needs about 3.5 second to start.
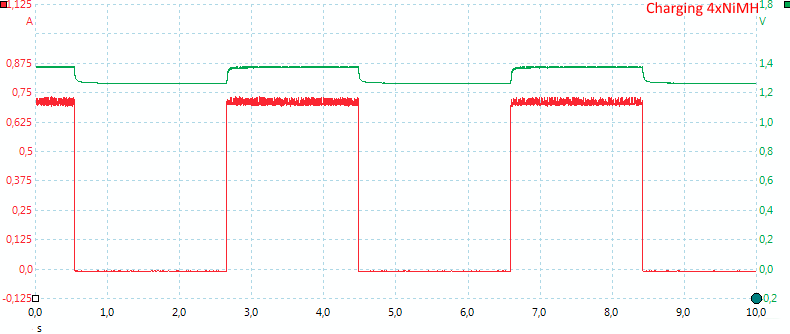
Time sharing works the same way.
Testing with 2830 volt and 4242 volt between mains and low volt side, did not show any safety problems.
Conclusion
Charging single single 14500 and 16340 will cost a bit lifetime on the cells due to the high charge current. Charging two empty cells at a time will improve this (Remember to use slot #1 & #2).
Generally the charger is a easy to use and good universal charger for most battery sizes.
Notes
The charger was supplied by a Gearbest for review.
Review of old i4 (V2)
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger


















































