Charger Soshine H4



Soshine makes a couple of chargers of varying quality, this charger is a four channel charger for NiMH and 2 different LiIon voltages. It is possible to select charge current and battery chemistry for each slot.




The charger arrives in a cardboard box with specifications and manual on it.

The box contains the charger a mains power supply and a car power adapter.

Power input is 12V from a barrel connector.

The user interface is a LCD display showing status for each channel and 3 buttons to select battery chemistry and current.
The right arrow is used to select slot, the down arrow to select value and the square button to change between settings and save selected value.
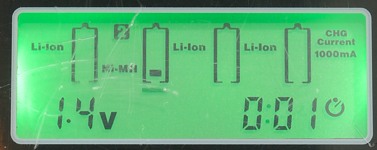
Charger is charging, the battery symbols for slot #1 and #2 are animated. Slot #1 has a LiIon battery and slot #2 has a NiMH battery. Slot #2 is selected, the battery has 1.4V and has charged for 1 minute. The selected channel is charging with 1A (1000mA).
For LiIon batteries the charger will also show xx% on the display.
The background light will turn off one minute after the last keypress.

Pressing the square button on a idle channel will show the setting for chemistry. Pressing the down arrow will select between FEP (3.6V charging, LiFePO4) and Ion (4.2V charging, LiIon) for that channel.

Pressing once more on the square button will move to the current setting. Pressing the down button will select between 500mA, 250mA and 1000mA for that channel.
The selected chemistry and current will be remembered, even when not powered.


The slots uses the classical slider construction and works smooth.
The slots can handle batteries from 30mm to 72mm.
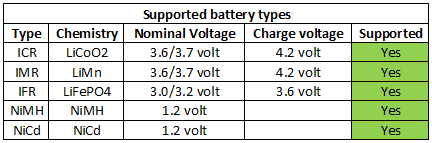
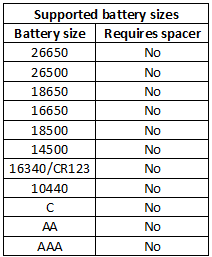










Measurements
- The charger will charge with about 100mA from 0 volt.
- At 0.6 volt regular charge current will be applied and a battery will be detected.
- When a LiIon battery is detected the minimum voltage reading is 3.2V (With LiFePO4 it is 2.9V).
- Maximum voltage reading for a LiIon is 4.2V (With LiFePO4 it is 3.6V).
- When charging is done the meter is frozen.
- If the voltage stays between 2.0 and 2.5 volt the charger will say "bat fail".
- Below 2V the charger assumed NiMH and above 2.5V the charger assumes LiIon.
- Charger will not officially restart if voltage drops, but charge current will increase.
- Charge will restart charging after power loss, or battery insertion.
- When not connected to power it will drain about 6mA from a LiIon battery and 1.6mA from a NiMH battery.
- The chemistry and current settings are remembered, even if the power is removed.
LiIon batteries 4.2V
%20%231.png)
The charger uses a simulated CC/CV charge algorithm, but does never turn the charge current off. The change from CC to CV is rather soft (It starts at about 3.9 volt), this does not reduce the quality of the charging, but makes it a bit slower.
According to the display I charged 2692mAh into the battery.
%20%232.png)
%20%233.png)
%20%234.png)
The 3 other channels looks similar.
According to the display I charged 2649mAh, 2733mAh and 2749mAh into the batteries.
%20%231.png)
With the average charge current at 0.5A the CC to CV transition gets a bit faster.
According to the display I charged 2713mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
And at 0.25A the transition starts at about 4.13 volt.
According to the display I charged 2801mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
According to the display I charged 2089mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
According to the display I charged 3028mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
The charge has no problem with my old 16340 cell.
According to the display I charged 162mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
The 1A curve looks very similar to the 0.25A curve, because the internal resistance is rather high in the cell.
According to the display I charged 158mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
The 18350 is charged fine.
According to the display I charged 679mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
Same with the 14500.
According to the display I charged 721mAh into the battery.
.png)
Charging 4 cells at full 1A does generate some heat, but not more than accceptable.
.png)
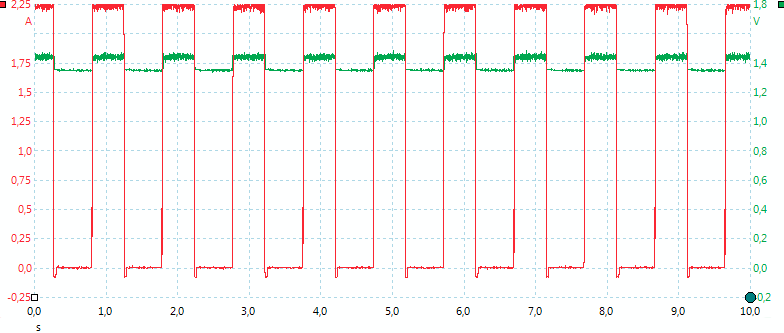
The charger needs 2A input current.
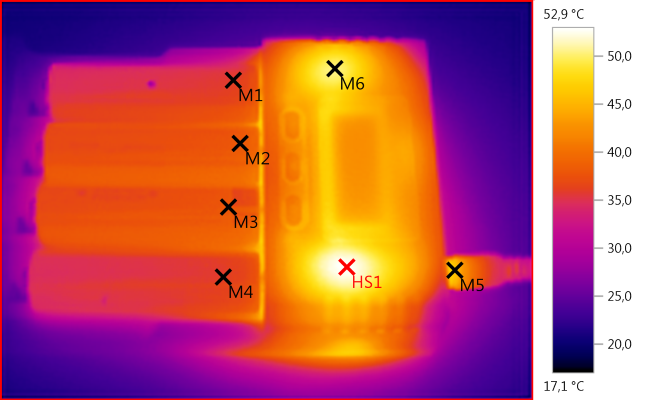
M1: 36,0°C, M2: 38,1°C, M3: 38,0°C, M4: 35,9°C, M5: 46,1°C, M6: 50,4°C, HS1: 52,9°C
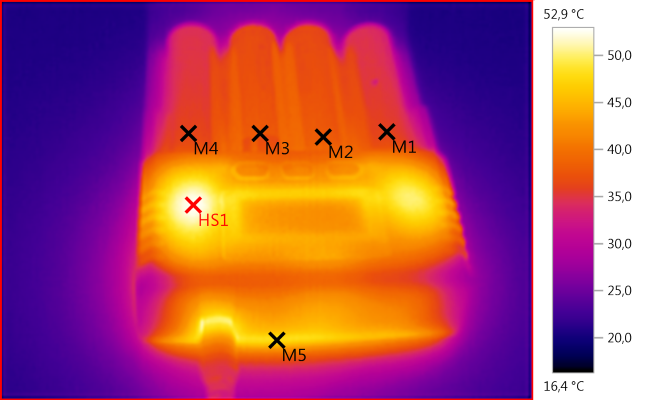
M1: 36,0°C, M2: 38,2°C, M3: 37,7°C, M4: 36,2°C, M5: 48,0°C, HS1: 52,9°C
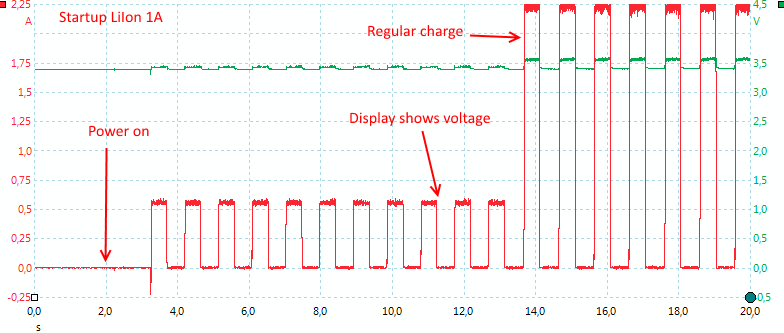
The charger starts with a low charge current and after some time it switches to full current..
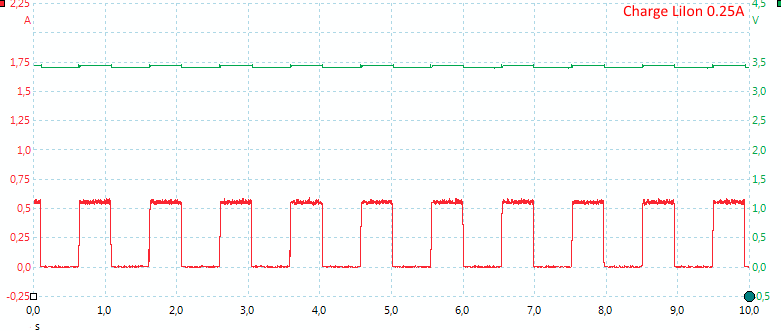
The charge current is only on half the time, probably because the charge circuit is shared between two channels. The two channels does not affect each other, but works completely independently.
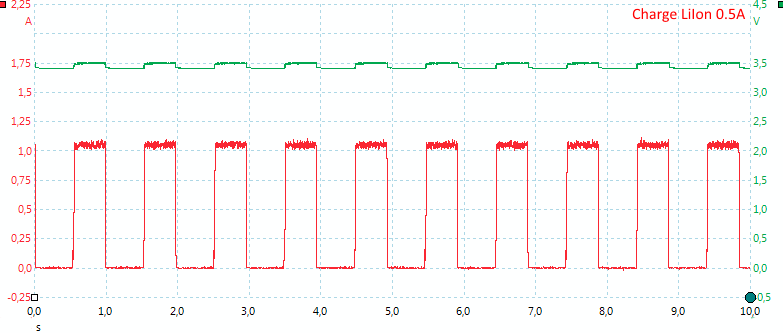
With higher charge current the current is increased, but the duty cycle remains the same.
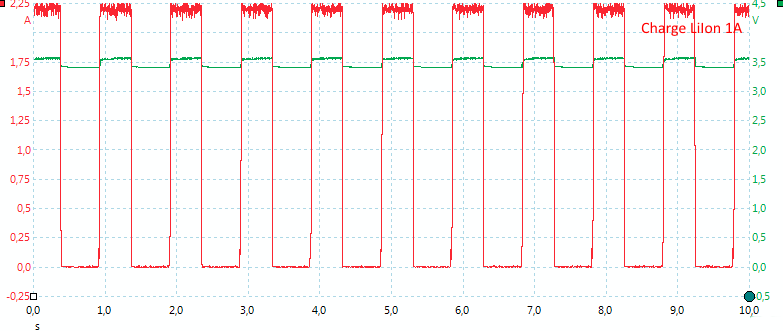
At the full 1A charge current, the actual current is 2A, but only 50% of the time.
LiIon batteries 3.6V (LiFePO4)
%20%231.png)
The charger uses 3.6 volt for LiFePO4 cells, but it does not turn the charge current off.
NiMH batteries
%20%231.png)
It looks like the charger uses voltage termination and then trickle current. There is no temperature raise showing the battery is fully charged. The charged capacity does also suggest the charger stops early.
According to the display I charged 1629mAh into the battery.
%20%232.png)
%20%233.png)
%20%234.png)
The other channels looks the same.
According to the display I charged 1633mAh, 1690mAH and 1658mAh into the batteries.
%20%231.png)
Reducing the charge current will also reduce the pulses used during trickle charge.
According to the display I charged 1689mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
The termination is more sensitive with the lower charge current, i.e. the charger has no problem termination with 0.25A charge current.
According to the display I charged 1703mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
According to the display I charged 2190mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
According to the display I charged 1764mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
According to the display I charged 2088mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
According to the display I charged 581mAh into the battery.
%20%231.png)
The charger uses 20 minutes when starting with a full battery, the first 10 minutes with low charge current.
The curve here looks like a -dv/dt termination
.
.png)
No problem with 4 batteries.
.png)
With the lower voltage on the batteries, the charger only needs about 1.2A input current.
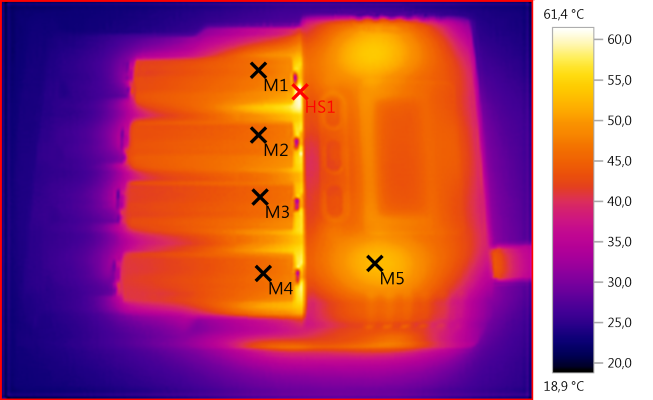
M1: 46,5°C, M2: 45,9°C, M3: 45,1°C, M4: 45,9°C, M5: 52,6°C, HS1: 61,4°C
NiMH gets warmer than LiIon batteries.
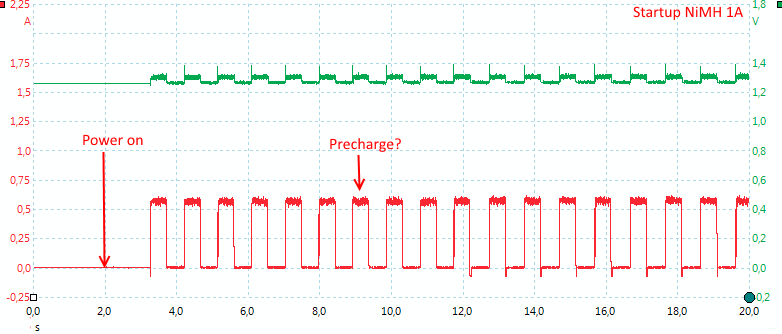
With NiMH the charger uses about 10 minutes, before changing to full charge current. It uses the same pulsing scheme as LiIon.
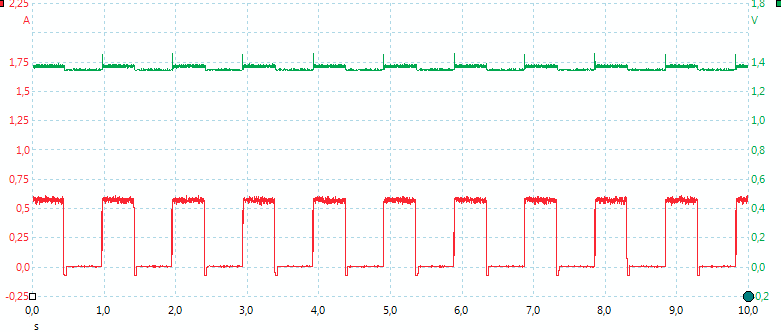
The charge current is about double of selected current, but only 50% of the time.
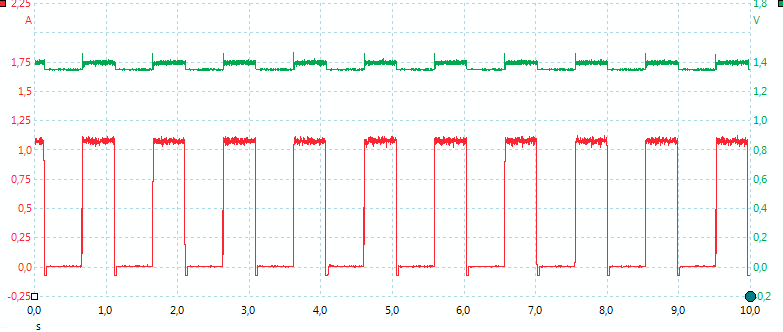
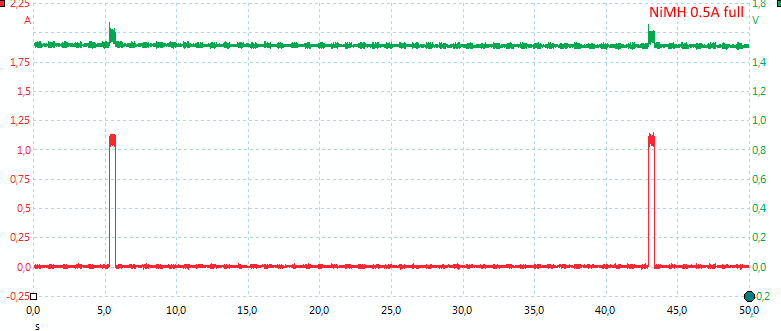
When NiMH batteries are full the charge changes to trickle charge. In this mode the charger will pulse the current once every 38 seconds. The pulse is about 0.45 second long.
Mixing NiMH and LiIon batteries
.png)
.png)
There is no problem charging a mix of NiMH and LiIon batteries.
The charger passed a isolation test with 2500 volt, but failed a 5000 volt test, this makes the charger acceptable for 110VAC usage, but doubtful for 230VAC usage. Usage with 12 volt (in a car) is, of course, always possible and safe.
Conclusion
It is an interesting feature that it is possible to select current and chemistry for each slot, but it do requires more presses on the buttons than a common selection. That the charger remembers the selected currents and chemistry can be useful in some cases.
The LiIon charging is acceptable, but remember to remove the batteries within a few hours after charge termination.
With NiMH it is the other way around, they has to stay for some time after termination, before they are fully charged.
I will not rate it as more than acceptable.
Notes
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger



























%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
%20%233.png)
%20%234.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
.png)
.png)






%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%232.png)
%20%233.png)
%20%234.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
%20%231.png)
.png)
.png)






.png)
.png)