2S 3A LiIon charger TS-2012H

Official specifications:
- Input: 110-240Vac 60/60Hz
- Output: 8.4V 3000mA DC
This charger is for battery packs with 2S2P (2 in series 2 in parallel) or 2S3P or more parallel LiIon cells. The battery pack is supposed to contains its own protection and balancing.

I got the charger in a simple cardboard box.

Contents was the charger and a couple of different mains plugs.





It is fairly easy to replace the mains plug.


The led is a two color led, it will show red when charging and green at all other times.
Measurements
- Connector is 5.5mm/2.1mm
- Idle power consumption: 0.31 watt
- Unloaded voltage 8.47 volt
- Charger has no short circuit protection, the current will be above 10A when shorted.
- Above about 0.9 volt the output current is limited and the red led will flash.
- Will start charging at 3.9 volt.
- Led shows green when only connected to a battery, but not mains
- Green led is on when connected to mains, but not a battery.
Testing with 4 cells means a 2S2P pack.
.png)
The charge curve is a CC/CV, but the charger never stops, it just reports battery full (Green led) and continues to charge.
%20Efficiency.png)
Same curve as above, I have just replaced capacity with efficiency, it is at about 80% during charge.
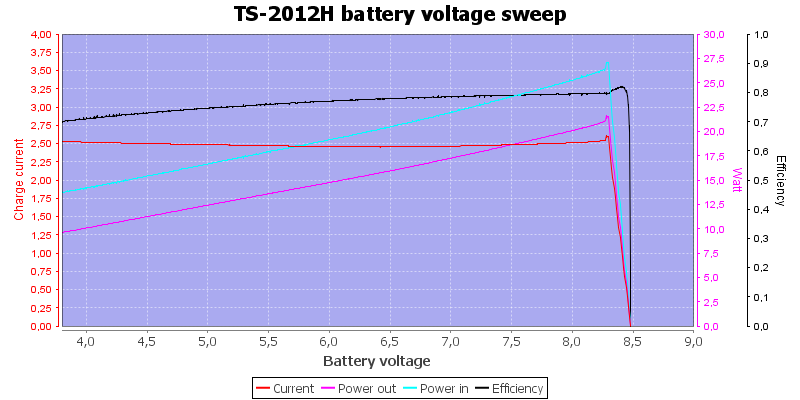
In the above curve I simulated a battery voltage from over discharge to fully charged. The charger is good at maintaining a constant current. The charger do not have a short circuit protection, but will limit the current from 0.9V to 3.9V!
During a charge I took IR photos at regular intervals of the hottest part of the charger:
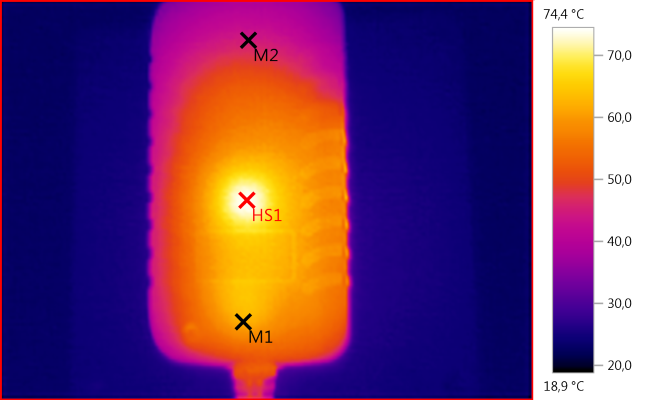
M1: 62,1°C, M2: 44,7°C, HS1: 74,4°C
HS1 is the transformer.
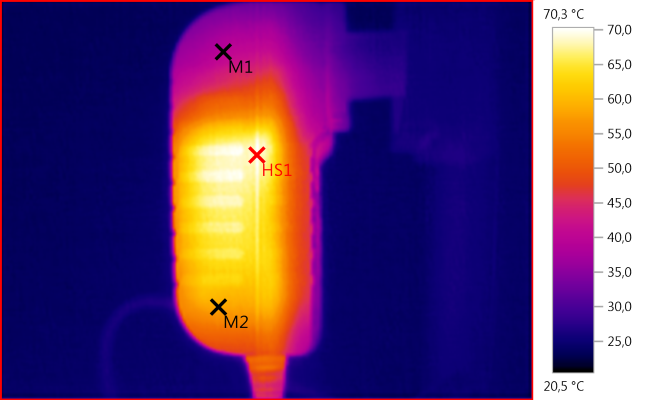
M1: 39,7°C, M2: 58,3°C, HS1: 70,3°C
The fairly warm side is the heatsink on the rectifier diode, the actual hotspot is where the diode is mounted.
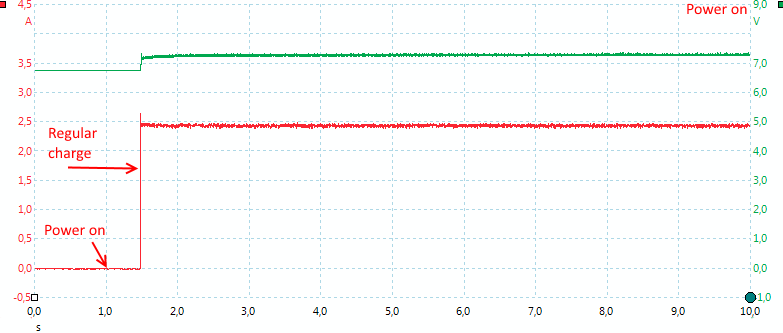
The charger starts fast a charges with a steady current.
Tear down

As usual the charger could be opened by putting some pressure on it.

Being a battery charger and not only a usb charger it needs a bit more parts on the low voltage side.
At the mains input it has a fuse, bridge rectifier (4 diodes below capacitor), capacitor and a common mode coil. There is also the switch mode controller with a heatsink and optical feed back.

From this angle the rectifier diode on a large heatsink is easier too see.


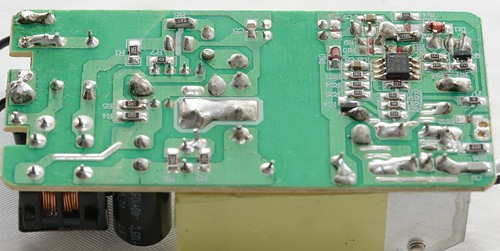
The loop covered in black tube (RS1) is the resistor used for measuring and adjusting the charge current.

This side is mostly used for the rectifier diode heatsink and the common mode coil. The yellow tape around the heatsink is for voltage isolation, because the heatsink is connected to the low voltage side, but is very close to some mains connected parts.
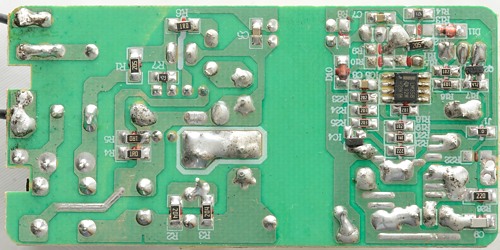
On the bottom the charge controller (A dual opAmp) can be seen, it is measuring the voltage accross the RS1 resistor and using the IC2 opto coupler to control the mains switcher.
There is a good isolation distance.
Testing with 2500 volt and 5000 volt between mains and low volt side, did not show any safety problems.
Conclusion
This type of charger is not nearly as advanced as single cell chargers. With only two wires to the battery pack it is impossible to do any balancing. The charger has a couple of issues: It is missing short circuit protection, it will slowly discharge the battery without mains connected (Will drain the battery in a few weeks) and it never turns the charge current off.
Calling it a 3A (3000mA) charger is also a bit optimistic, 2.5A is more correct.
The replaceable mains plug can be useful for traveling (If you can keep track of the plugs).
I will give this charger an acceptable rating.
Notes
The charger is from ShenZhen TengShun Power Supply Co.,Ltd, I got it with the help of BLF/MTBR user Ledoman.
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger










.png)
%20Efficiency.png)












