Charger Varta LCD Plug charger 57677



Varta makes both batteries and chargers, here I am looking on a simple four channel charger with a LCD display.




I got the charger in a blister pack. As can be seen on the pack the charger needs four hours to charge batteries, but a small note says it is for 1600mAh cells, i.e. the more normal 2000 to 2500mAh cells will take longer.

The pack contained the charger, four batteries (2100mAh) and a multi language instruction sheet.

In addition to charge batteries the charger also has a usb power output.
This output can be used while charging batteries.

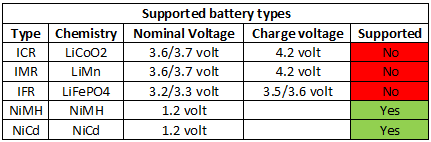
The charger has a simple LCD display with indicators for AA/AAA charging progress, indicator for 9V charging (No progress) and indicator for usb power drawn or overloaded.
It also shows the Varta name that is rather useless, a scale for 9V charging would have been much more useful.
Note: The photo shows the sticker that in on the charger when delivered, the display looks the same.



The charger has the typically two level slots used for AA and AAA batteries.

It is also possible to charge a 9 volt battery, it will block the AA slots, i.e. the charger can either charge AA or 9V, not both at the same time.


Measurements charger
- The charger is only 230VAC (220-240VAC 50Hz), not multi voltage.
- Power consumption when idle is 0.5 watt
- When not powered it will discharge with about 0.8mA on AA cells.
- Charge will restart charging after power loss, or battery insertion.
- Can only charge in pairs.
%2012.png)
The charge curve looks acceptable with a -dv/dt termination and a one hour top-off charge.
The problem is that the charger has two cells in series, i.e. if they are not charged to the same level, the termination will only be correct for one of the cell. The top-off charge tries to balance that.
%2034.png)
It is the same on the other channel.
%2012.png)
%2012.png)
%2012.png)
There is no problem with any of the high capacity cells.
%2012.png)
With AAA cells the current is reduced.
%2012.png)
The charger is not very fast at detecting full cells and they do also get the top-off charge.
.png)
The charge speed is the same with four cells.
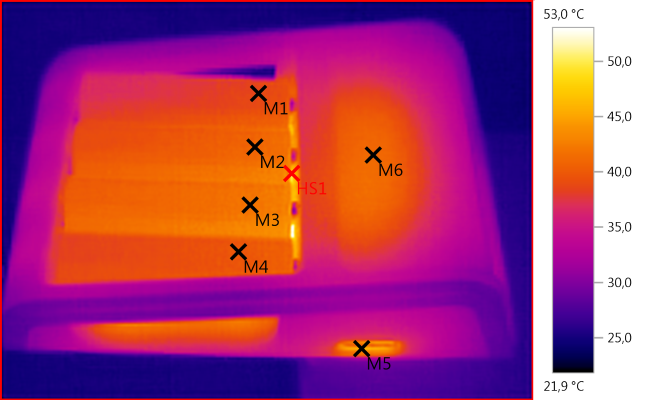
M1: 38,8°C, M2: 40,9°C, M3: 42,2°C, M4: 39,9°C, M5: 46,0°C, M6: 41,1°C, HS1: 53,0°C
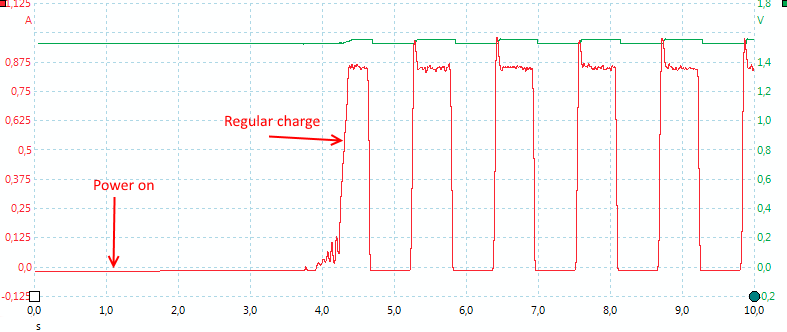
The charger need about 3 seconds to start.
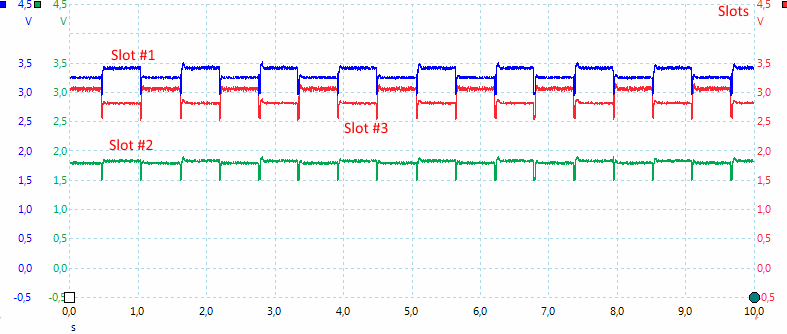
Measuring on 3 slots (using usb gnd as reference) shows how the charger works.
Slot #1 and #2 are in series. Slot #1, #2 and #3, #4 alternates, this means the charger only has one 3V charge circuit for AA/AAA batteries and will time share it between the two groups of batteries.
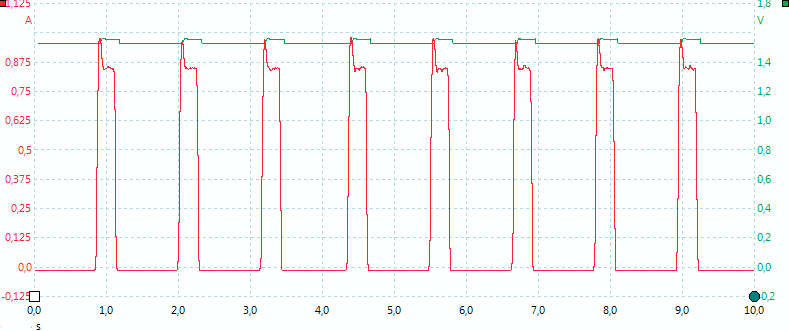
Top-off charge is done by reducing the duty cycle to 1/4, instead of 1/2.
Charging 9V
.png)
The 9V charging looks to be on time, i.e. it terminates after a fixed time, not when the battery is full and matches the time specified on the pack (8 hours).
USB output
- USB output is rated at 0.5A, but can deliver 1A.
- USB output is coded as Apple 0.5A
- USB will flash when usb output is loaded, it starts at about 80mA and turns off at 50mA
- If usb is overloaded the border around USB will flash.
- USB output can be used while charging batteries
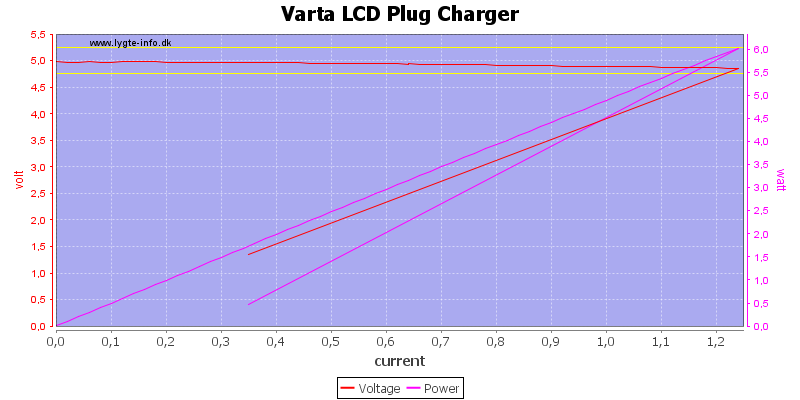
The usb output can easily deliver 1A and has a overload protection at about 1.2A, this is good.
%20load%20sweep.png)
When charging at the same time as usb output is used there is a problem at about maximum current.
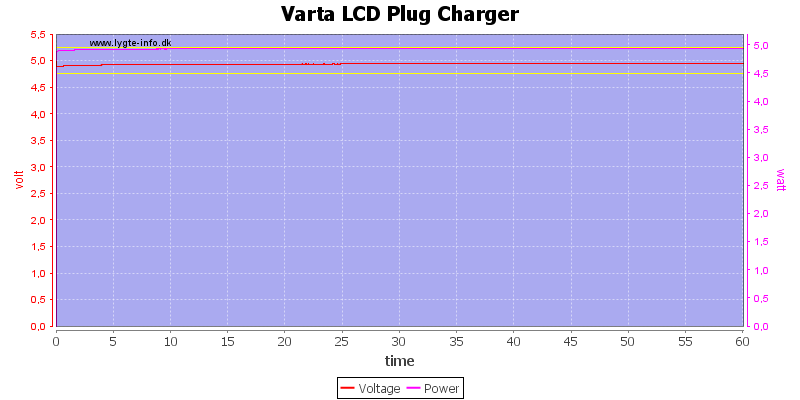
This test is done with usb only, no charging was active. I tested with 1A current.
The temperature photos below are taken between 30 minutes and 60 minutes into the one hour test.
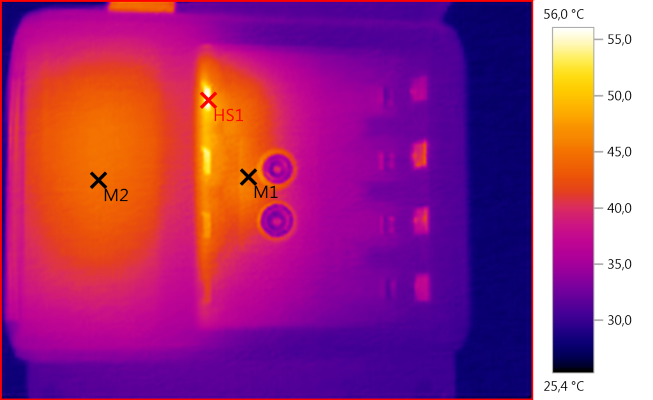

M1: 45,3°C, M2: 44,5°C, HS1: 56,0°C
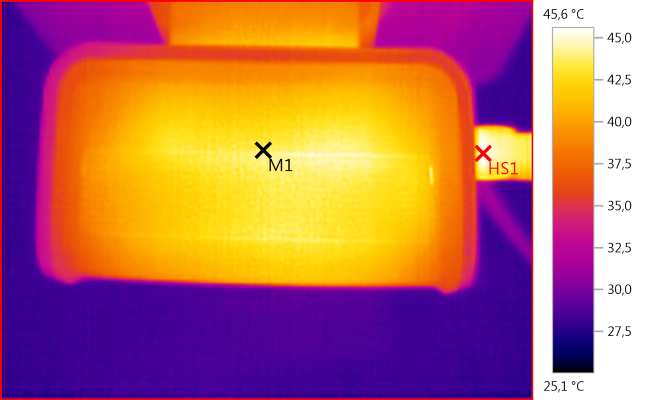
M1: 43,6°C, HS1: 45,6°C
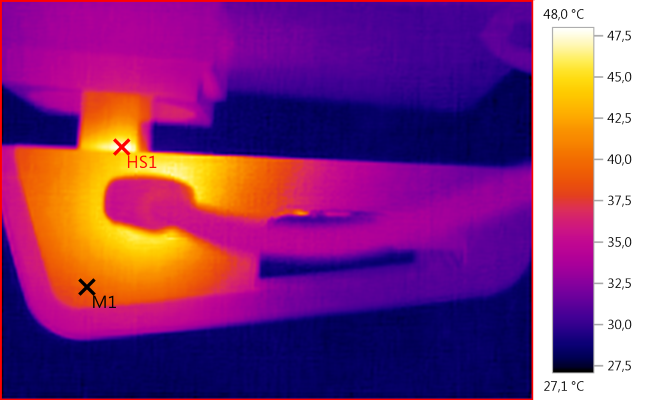
M1: 39,0°C, HS1: 48,0°C
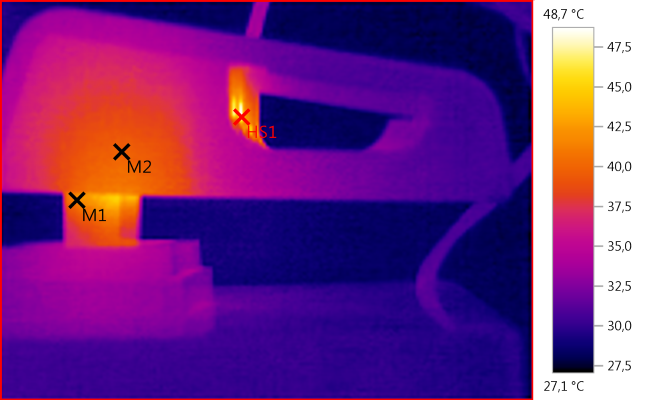
M1: 41,6°C, M2: 39,8°C, HS1: 48,7°C
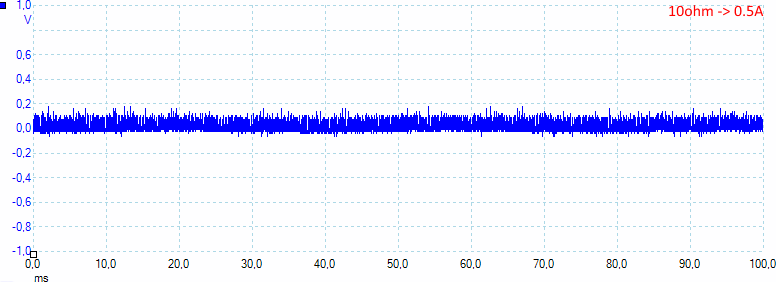
At 0.5A there 38mV rms and 300mVPP noise.
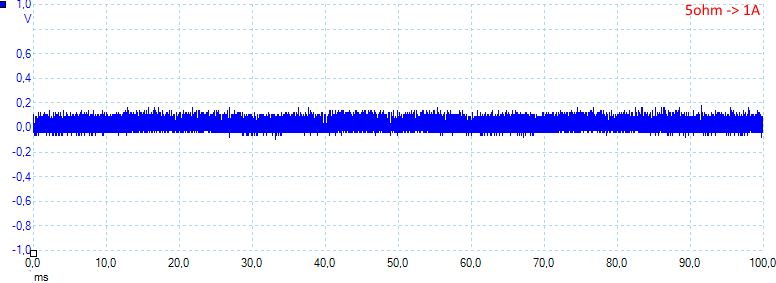
At 1A there is 53mV rms and 270mVPP noise.
Testing the mains transformer with 2500 volt and 5000 volt between mains and low volt side, did not show any safety problems.
Conclusion
As usual I am not happy about charging NiMH in series, this only works correctly if they are used in series, in this case 2 or 4. The top-off charge will compensate for small differences in usage. The 9V is a simple timer based charge.
USB output works good and can deliver double the rated power.
I will call it a acceptable battery charger.
Notes
Here is an explanation on how I did the above charge curves: How do I test a charger


















%2012.png)
%2034.png)
%2012.png)
%2012.png)
%2012.png)
%2012.png)
%2012.png)
.png)




.png)

%20load%20sweep.png)






